|
Technical Architecture
Information technology (IT) architecture is the process of development of methodical information technology specifications, models and guidelines, using a variety of information technology notations, for example Unified Modeling Language (UML), within a coherent information technology architecture framework, following formal and informal information technology solution, enterprise, and infrastructure architecture processes. These processes have been developed in the past few decades in response to the requirement for a coherent, consistent approach to delivery of information technology capabilities. They have been developed by information technology product vendors and independent consultancies, such as for example the Open Group, based on real experiences in the information technology marketplace and collaboration amongst industry stakeholders. Best practice information technology architecture encourages the use of open technology standards and global technology interoperability. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Technology
Information technology (IT) is a set of related fields within information and communications technology (ICT), that encompass computer systems, software, programming languages, data processing, data and information processing, and storage. Information technology is an application of computer science and computer engineering. The term is commonly used as a synonym for computers and computer networks, but it also encompasses other information distribution technologies such as television and telephones. Several products or services within an economy are associated with information technology, including computer hardware, software, electronics, semiconductors, internet, Telecommunications equipment, telecom equipment, and e-commerce.. An information technology system (IT system) is generally an information system, a communications system, or, more specifically speaking, a Computer, computer system — including all Computer hardware, hardware, software, and peripheral equipment � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
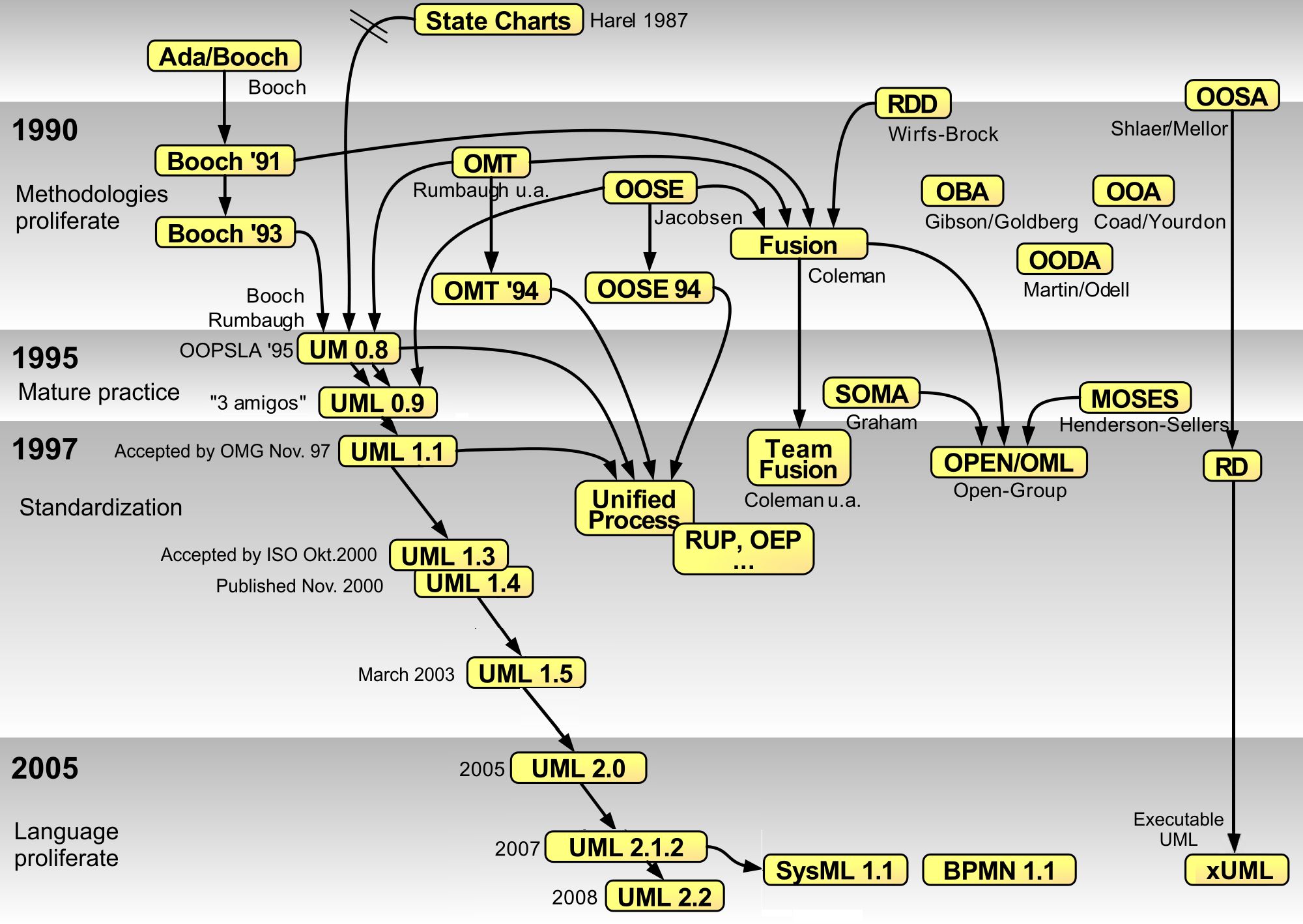
Unified Modeling Language
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a general-purpose visual modeling language that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system. UML provides a standard notation for many types of diagrams which can be roughly divided into three main groups: behavior diagrams, interaction diagrams, and structure diagrams. The creation of UML was originally motivated by the desire to standardize the disparate notational systems and approaches to software design. It was developed at Rational Software in 1994–1995, with further development led by them through 1996. In 1997, UML was adopted as a standard by the Object Management Group (OMG) and has been managed by this organization ever since. In 2005, UML was also published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as the ISO/IEC 19501 standard. Since then the standard has been periodically revised to cover the latest revision of UML. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Architecture Framework
The ISO/ IEC/IEEE 42010 Conceptual Model of Architecture Description defines the term architecture framework within systems engineering and software development Software development is the process of designing and Implementation, implementing a software solution to Computer user satisfaction, satisfy a User (computing), user. The process is more encompassing than Computer programming, programming, wri ... as: "An architecture framework establishes a common practice for creating, interpreting, analyzing and using architecture descriptions within a particular domain of application or stakeholder community. Examples of Architecture Frameworks: MODAF, TOGAF, Kruchten's 4+1 view model, RM-ODP." Especially the domain within a company or other organization is covered by enterprise architecture frameworks. The Survey of Architecture Frameworks [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrastructure Architecture
Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and private physical structures such as roads, railways, bridges, airports, public transit systems, tunnels, water supply, sewers, electrical grids, and telecommunications (including Internet connectivity and broadband access). In general, infrastructure has been defined as "the physical components of interrelated systems providing commodities and services essential to enable, sustain, or enhance societal living conditions" and maintain the surrounding environment. Especially in light of the massive societal transformations needed to mitigate and adapt to climate change, contemporary infrastructure conversations frequently focus on sustainable development and green infrastructure. Acknowledging this importance, the international community has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Open Group
The Open Group is a global consortium that seeks to "enable the achievement of business objectives" by developing " open, vendor-neutral technology standards and certifications." It has 900+ member organizations and provides a number of services, including strategy, management, innovation and research, standards, certification, and test development. It was established in 1996 when X/Open merged with the Open Software Foundation. The Open Group is the certifying body for the UNIX trademark, and publishes the Single UNIX Specification technical standard, which extends the POSIX standards. The Open Group also develops and manages the TOGAF standard, which is an industry standard enterprise architecture framework. Members The 900+ members include a range of technology vendors and buyers as well as government agencies, including, for example, Capgemini, Fujitsu, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, Orbus Software, IBM, Huawei, the United States Department of Defense and NASA. There is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interoperability
Interoperability is a characteristic of a product or system to work with other products or systems. While the term was initially defined for information technology or systems engineering services to allow for information exchange, a broader definition takes into account social, political, and organizational factors that impact system-to-system performance. Types of interoperability include syntactic interoperability, where two systems can communicate with each other, and cross-domain interoperability, where multiple organizations work together and exchange information. Types If two or more systems use common data formats and communication protocols then they are capable of communicating with each other and they exhibit ''syntactic interoperability''. XML and SQL are examples of common data formats and protocols. Low-level data formats also contribute to syntactic interoperability, ensuring that alphabetical characters are stored in the same ASCII or a Unicode format in all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grady Booch
Grady Booch (born February 27, 1955) is an American software engineer, best known for developing the Unified Modeling Language (UML) with Ivar Jacobson and James Rumbaugh. He is recognized internationally for his innovative work in software architecture, software engineering, and collaborative development environments. Education Booch earned his bachelor's degree in 1977 from the United States Air Force Academy and a master's degree in electrical engineering in 1979 from the University of California, Santa Barbara. Career and research Booch worked at Vandenberg Air Force Base after he graduated. He started as a project engineer and later managed ground-support missions for the space shuttle and other projects. After he gained his master's degree he became an instructor at the Air Force Academy. Booch served as Chief Scientist of Rational Software Corporation from its founding in 1981 through its acquisition by IBM in 2003, where he continued to work until March 2008. After thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivar Jacobson
Ivar Hjalmar Jacobson (; born September 2, 1939) is a Swedish computer scientist and software engineer, known as a major contributor to UML, Objectory, Rational Unified Process (RUP), aspect-oriented software development, and Essence. Biography Ivar Jacobson was born in Ystad, on September 2, 1939. He received his Master of Electrical Engineering degree at Chalmers Institute of Technology in Gothenburg in 1962. After his work at Ericsson, he formalized the language and method he had been working on in his PhD at the Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm in 1985 on the thesis "Language Constructs for Large Real Time Systems". After his master's degree, Jacobson joined Ericsson and worked in R&D on computerized switching systems AKE and AXE including PLEX. In April 1987, he started Objective Systems. A majority stake of the company was acquired by Ericsson in 1991, and the company was renamed Objectory AB. Jacobson developed the software method Object-Oriented Sof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Rumbaugh
James E. Rumbaugh (born August 22, 1947) is an American computer scientist and object-oriented methodologistBiography on InformIT Accessed 22 Jan 2010. who is best known for his work in creating the Object Modeling Technique (OMT) and the Unified Modeling Language (UML). Biography Born in , Rumbaugh received a B.S. in |
Modeling Language
A modeling language is any artificial language that can be used to express data, information or knowledge or systems in a structure that is defined by a consistent set of rules. The rules are used for interpretation of the meaning of components in the structure of a programming language. Overview A modeling language can be graphical or textual. * ''Graphical'' modeling languages use a diagramming technique, diagram technique with named symbols that represent concepts and lines that connect the symbols and represent relationships and various other graphical notation to represent constraints. * ''Textual'' modeling languages may use standardized keywords accompanied by parameters or natural language terms and phrases to make computer-interpretable expressions. An example of a graphical modeling language and a corresponding textual modeling language is EXPRESS (data modeling language), EXPRESS. Not all modeling languages are executable, and for those that are, the use of them does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Footnotes
In publishing, a note is a brief text in which the author comments on the subject and themes of the book and names supporting citations. In the editorial production of books and documents, typographically, a note is usually several lines of text at the bottom of the page, at the end of a chapter, at the end of a volume, or a house-style typographic usage throughout the text. Notes are usually identified with superscript numbers or a symbol.''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (1992) p. 709. Footnotes are informational notes located at the foot of the thematically relevant page, whilst endnotes are informational notes published at the end of a chapter, the end of a volume, or the conclusion of a multi-volume book. Unlike footnotes, which require manipulating the page design (text-block and page layouts) to accommodate the additional text, endnotes are advantageous to editorial production because the textual inclusion does not alter the design of the publication. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterprise Architecture
Enterprise architecture (EA) is a business function concerned with the structures and behaviours of a business, especially business roles and processes that create and use business data. The international definition according to the Federation of Enterprise Architecture Professional Organizations is "a well-defined practice for conducting enterprise (economics), enterprise analysis, design, planning, and implementation, using a comprehensive approach at all times, for the successful development and execution of strategy. Enterprise architecture applies architecture principles and practices to guide organizations through the business, information, process, and technology changes necessary to execute their strategies. These practices utilize the various aspects of an enterprise to identify, motivate, and achieve these changes." The United States Government, United States Federal Government is an example of an organization that practices EA, in this case with its Capital Planning an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |