|
Tara Tree
''Tara spinosa'', commonly known as ''tara'' ( Quechua), also known as Peruvian carob or spiny holdback, is a small leguminous tree or thorny shrub native to Peru. ''T. spinosa'' is cultivated as a source of tannins based on a galloylated quinic acid structure. This chemical structure has been confirmed also by LC–MS.M. N. Clifford, S. Stoupi and N. Kuhnert''Profiling and Characterization by LC-MSn of the Galloylquinic Acids of Green Tea, Tara Tannin, and Tannic Acid'' J. Agric. Food Chem., 2007, 55 (8), pp. 2797-2807. DOI: 10.1021/jf063533l. Publication Date (Web): March 24, 2007. It is also grown as an ornamental plant because of its large colorful flowers and pods. Names and taxonomy Its common names include spiny holdback, ''tara'', ''taya'', and ''algarroba tanino'' (Peru). ''Tara spinosa'' is placed in the family Fabaceae, subfamily Caesalpinioideae, and tribe Caesalpinieae. Description ''Tara spinosa'' typically grows tall; its bark is dark gray with scattered prickl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Ignacio Molina
Fr. Juan Ignacio Molina (; (June 24, 1740 – September 12, 1829) was a Chilean-Spanish Jesuit priest, natural history, naturalist, historian, translator, geographer, botanist, ornithologist, and linguist. He is usually referred to as Abate Molina (Abbot Molina), and is also sometimes known by the Italian form of his name, Giovanni Ignazio Molina. He was one of the precursors of the theory of the gradual evolution of species, 44 years before Charles Darwin, Darwin, who repeatedly quoted him in "The Origin of Species". Biography Early years Molina was born at Guaraculén, a big farm located near Villa Alegre, Chile, Villa Alegre (General Captaincy of Chile), where he lived until he was 5 years old. In the current province of Linares Province, Linares, in the Maule Region of Chile. His parents were Agustín Molina and Francisca González Bruna. From an early age he was attracted to the nature of his environment, and in addition to his school work, he enjoyed observing nature on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leaflet (botany)
A leaflet (occasionally called foliole) in botany is a leaf-like part of a compound leaf. Though it resembles an entire leaf, a leaflet is not borne on a main plant stem or branch, as a leaf is, but rather on a leaf, petiole or a branch of the leaf. Compound leaves are common in many plant families and they differ widely in morphology (biology), morphology. The two main classes of compound leaf morphology are Leaf shape, palmate and pinnate. For example, a ''Cannabis, hemp'' plant has palmate compound leaves, whereas some species of ''Acacia sensu lato, Acacia'' have pinnate leaves. The ultimate free division (or leaflet) of a compound leaf, or a pinnate subdivision of a multipinnate leaf is called a pinnule or pinnula. Image:Ветвь акации.jpg, Pinnate leaf of a Fabaceae, legume with 10 leaflets Image:Mimosa Pudica.gif, ''Mimosa pudica'' folding leaflets inward. See also * Compound leaf References Leaf morphology {{plant-morphology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mordant
A mordant or dye fixative is a substance used to set (i.e., bind) dyes on fabrics. It does this by forming a coordination complex with the dye, which then attaches to the fabric (or tissue). It may be used for dyeing fabrics or for intensifying stains in cell or tissue preparations. Although mordants are still used, especially by small batch dyers, they have been largely displaced in industry by substantive dyes.} The term mordant comes from the Latin ''mordere'', "to bite". In the past, it was thought that a mordant helped the dye "bite" onto the fiber so that it would hold fast during washing. A mordant is often a polyvalent metal ion, and one example is chromium (III). The resulting coordination complex of dye and ion is colloidal and can be either acidic or alkaline. Common dye mordants Mordants include tannic acid, oxalic acid, alum, chrome alum, sodium chloride, and certain salts of aluminium, chromium, copper, iron, iodine, potassium, sodium, tungsten, and tin. Io ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
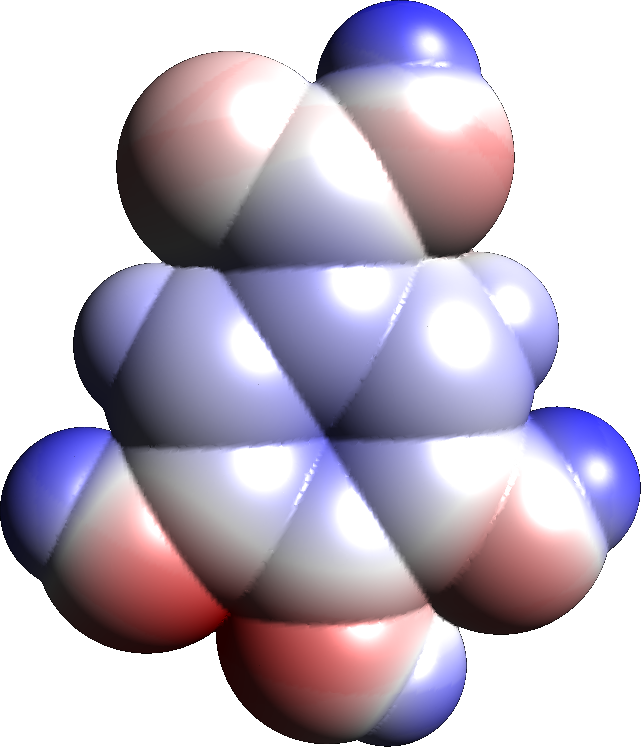
Quinic Acid
Quinic acid is an organic compound with the formula . The compound is classified as a cyclitol, a cyclic polyol, and a cyclohexanecarboxylic acid. It is a colorless solid that can be extracted from plant sources. Quinic acid is implicated in the perceived acidity of coffee, where it occurs around 13% by weight. Occurrence and preparation The compound is obtained from cinchona bark, coffee beans, and the bark of ''Eucalyptus globulus''. It is a constituent of the tara tannins. ''Urtica dioica'', the European stinging nettle, is another common source. It is made synthetically by hydrolysis of chlorogenic acid. Quinic acid is also implicated in the perceived acidity of coffee. History and biosynthesis This substance was isolated for the first time in 1790 by German pharmacist Friedrich Christian Hofmann in Leer from Cinchona. Its transformation into hippuric acid by animal metabolism was studied by German chemist Eduard Lautemann in 1863.Lautemann, E. (1863"Ueber die Reduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of Biomolecule, biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallic Acid
Gallic acid (also known as 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid) is a trihydroxybenzoic acid with the formula C6 H2( OH)3CO2H. It is classified as a phenolic acid. It is found in gallnuts, sumac, witch hazel, tea leaves, oak bark, and other plants. It is a white solid, although samples are typically brown owing to partial oxidation. Salts and esters of gallic acid are termed "gallates". Its name is derived from oak galls, which were historically used to prepare tannic acid. Despite the name, gallic acid does not contain gallium. Isolation and derivatives Gallic acid is easily freed from gallotannins by acidic or alkaline hydrolysis. When heated with concentrated sulfuric acid, gallic acid converts to rufigallol. Hydrolyzable tannins break down on hydrolysis to give gallic acid and glucose or ellagic acid and glucose, known as gallotannins and ellagitannins, respectively. Biosynthesis Gallic acid is formed from 3-dehydroshikimate by the action of the enzyme shikimat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolysable Tannin
A hydrolysable tannin or pyrogallol-type tannin is a type of tannin that, on heating with hydrochloric or sulfuric acids, yields gallic or ellagic acids. At the center of a hydrolysable tannin molecule, there is a carbohydrate (usually D-glucose but also cyclitols like quinic or shikimic acids). The hydroxyl groups of the carbohydrate are partially or totally esterified with phenolic groups such as gallic acid in gallotannins or ellagic acid in ellagitannins. Hydrolysable tannins are mixtures of polygalloyl glucoses and/or poly-galloyl quinic acid derivatives containing in between 3 up to 12 gallic acid residues per molecule. Hydrolysable tannins are hydrolysed by weak acids or weak bases to produce carbohydrate and phenolic acids. Examples of gallotannins are the gallic acid esters of glucose in tannic acid (C76H52O46), found in the leaves and bark of many plant species. Hydrolysable tannins can be extracted from different vegetable plants, such as chestnut wood (''Cast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-fouling Paint
Anti-fouling paint is a specialized category of coatings applied as the outer (outboard) layer to the hull of a ship or boat, to slow the growth of and facilitate detachment of subaquatic organisms that attach to the hull and can affect a vessel's performance and durability. It falls into a category of commercially available underwater hull paints, also known as ''bottom paints''. Anti-fouling paints are often applied as one component of multi-layer coating systems which may have other functions in addition to their antifouling properties, such as acting as a barrier against corrosion on metal hulls that will degrade and weaken the metal, or improving the flow of water past the hull of a fishing vessel or high-performance racing yachts. Although commonly discussed as being applied to ships, antifouling paints are also of benefit in many other sectors such as off-shore structures and fish farms. History In the Age of Sail, sailing vessels suffered severely from the growth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lomas
''Lomas'' (Spanish for "hills"), also called fog oases and mist oases, are areas of fog-watered vegetation in the coastal desert of Peru and northern Chile. About 100 lomas near the Pacific Ocean are identified between 5°S and 30°S latitude, a north–south distance of about . Lomas range in size from a small vegetated area to more than and their flora includes many endemic species. Apart from river valleys and the lomas the coastal desert is almost without vegetation. Scholars have described individual lomas as "an island of vegetation in a virtual ocean of desert." In a nearly rainless desert, the lomas owe their existence to the moist dense fog and mist which rolls in from the Pacific. The fog is called garúa in Peru and Camanchaca in Chile. Environment According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, the coastal desert of Peru and the Atacama Desert of Chile feature a rare desert climate, that is abbreviated "BWn" on climate maps with the n denoting frequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indehiscent
Dehiscence is the splitting of a mature plant structure along a built-in line of weakness to release its contents. This is common among fruits, anthers and sporangia. Sometimes this involves the complete detachment of a part. Structures that open in this way are said to be dehiscent. Structures that do not open in this way are called indehiscent, and rely on other mechanisms such as decay, digestion by herbivores, or predation to release the contents. A similar process to dehiscence occurs in some flower buds (e.g., '' Platycodon'', '' Fuchsia''), but this is rarely referred to as dehiscence unless circumscissile dehiscence is involved; anthesis is the usual term for the opening of flowers. Dehiscence may or may not involve the loss of a structure through the process of abscission. The lost structures are said to be caducous. Association with crop breeding Manipulation of dehiscence can improve crop yield since a trait that causes seed dispersal is a disadvantage for f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stamen
The stamen (: stamina or stamens) is a part consisting of the male reproductive organs of a flower. Collectively, the stamens form the androecium., p. 10 Morphology and terminology A stamen typically consists of a stalk called the filament and an anther which contains sporangium, microsporangia. Most commonly, anthers are two-lobed (each lobe is termed a locule) and are attached to the filament either at the base or in the middle area of the anther. The sterile (i.e. nonreproductive) tissue between the lobes is called the Connective (botany), connective, an extension of the filament containing conducting strands. It can be seen as an extension on the dorsal side of the anther. A pollen grain develops from a microspore in the microsporangium and contains the male gametophyte. The size of anthers differs greatly, from a tiny fraction of a millimeter in ''Wolfia'' spp up to five inches (13 centimeters) in ''Canna iridiflora'' and ''Strelitzia nicolai''. The stamens in a flower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sepal
A sepal () is a part of the flower of angiosperms (flowering plants). Usually green, sepals typically function as protection for the flower in bud, and often as support for the petals when in bloom., p. 106 Etymology The term ''sepalum'' was coined by Noël Martin Joseph de Necker in 1790, and derived . Collectively, the sepals are called the ''calyx'' (plural: calyces), the outermost Whorl (botany), whorl of parts that form a flower. The word ''calyx'' was adopted from the Latin ,Jackson, Benjamin, Daydon; A Glossary of Botanic Terms with their Derivation and Accent; Published by Gerald Duckworth & Co. London, 4th ed 1928 not to be confused with 'cup, goblet'. The Latin ''calyx'' is derived from Greek 'bud, calyx, husk, wrapping' ( Sanskrit 'bud'), while is derived from Greek 'cup, goblet'; both words have been used interchangeably in botanical Latin. Description The term ''tepal'' is usually applied when the parts of the perianth are difficult to distinguish, e. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |