|
Tachyarrhythmia
Tachycardia, also called tachyarrhythmia, is a heart rate that exceeds the Heart rate#Resting heart rate, normal resting rate. In general, a resting heart rate over 100 pulse, beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia in adults. Heart rates above the resting rate may be normal (such as with exercise) or abnormal (such as with electrical problems within the heart). Complications Tachycardia can lead to fainting. When the rate of blood flow becomes too rapid, or fast blood flow passes on damaged endothelium, it increases the friction within vessels resulting in turbulence and other disturbances. According to the Virchow's triad, this is one of the three conditions (along with hypercoagulability and endothelial dysfunction, endothelial injury/dysfunction) that can lead to thrombosis (i.e., blood clots within vessels). Causes Some causes of tachycardia include: * Adrenergic storm * Anaemia * Anxiety * Atrial fibrillation * Atrial flutter * Atrial tachycardia * Atrioventricu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palpitations
Palpitations occur when a person becomes aware of their heartbeat. The heartbeat may feel hard, fast, or uneven in their chest. Symptoms include a very fast or irregular heartbeat. Palpitations are a sensory symptom. They are often described as a skipped beat, a rapid flutter, or a pounding in the chest or neck. Palpitations are not always the result of a physical problem with the heart and can be linked to anxiety. However, they may signal a arrhythmia, fast or irregular heartbeat. Palpitations can be brief or long-lasting. They can be intermittent or continuous. Other symptoms can include dizziness, shortness of breath, sweating, headaches, and chest pain. There are a variety of causes of palpitations not limited to the following: Palpitation may be associated with coronary artery disease, coronary heart disease, perimenopause, hyperthyroidism, adult heart muscle diseases like hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, congenital heart diseases like atrial septal defects, diseases causing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AV Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia
AV-nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) is a type of abnormal fast heart rhythm. It is a type of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), meaning that it originates from a location within the heart above the bundle of His. AV nodal reentrant tachycardia is the most common regular supraventricular tachycardia. It is more common in women than men (approximately 75% of cases occur in females). The main symptom is palpitations. Treatment may be with specific physical maneuvers, medications, or, rarely, synchronized cardioversion. Frequent attacks may require radiofrequency ablation, in which the abnormally conducting tissue in the heart is destroyed. AVNRT occurs when a reentrant circuit forms within or just next to the atrioventricular node. The circuit usually involves two anatomical pathways: the fast pathway and the slow pathway, which are both in the right atrium. The slow pathway (which is usually targeted for ablation) is located inferior and slightly posterior to the AV node, of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
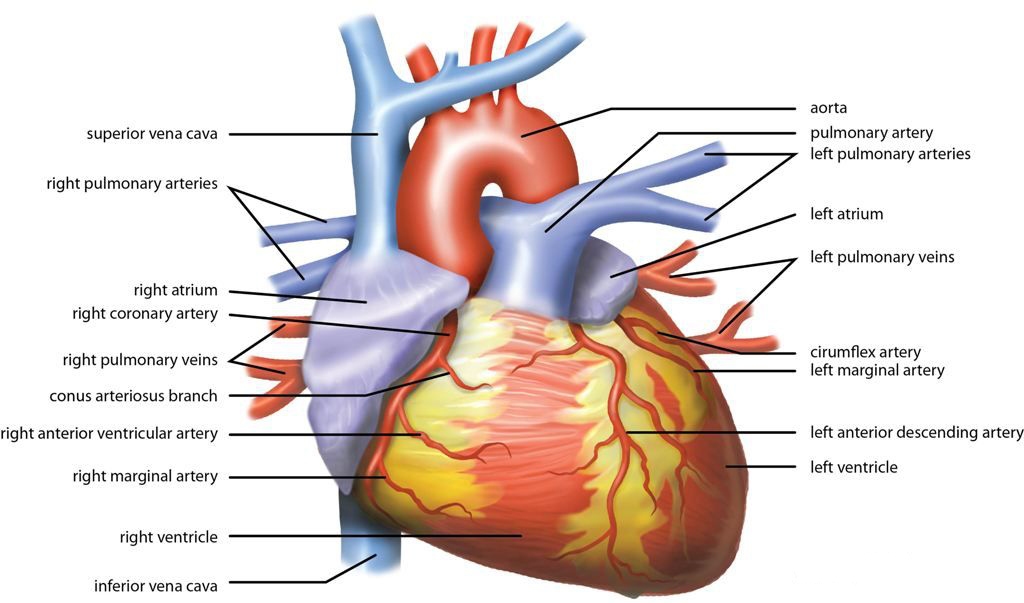
Heart Rate
Heart rate is the frequency of the cardiac cycle, heartbeat measured by the number of contractions of the heart per minute (''beats per minute'', or bpm). The heart rate varies according to the body's Human body, physical needs, including the need to absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide. It is also modulated by numerous factors, including (but not limited to) genetics, physical fitness, Psychological stress, stress or psychological status, diet, drugs, hormonal status, environment, and disease/illness, as well as the interaction between these factors. It is usually equal or close to the pulse rate measured at any peripheral point. The American Heart Association states the normal resting adult human heart rate is 60–100 bpm. An ultra-trained athlete would have a resting heart rate of 37–38 bpm. ''Tachycardia'' is a high heart rate, defined as above 100 bpm at rest. ''Bradycardia'' is a low heart rate, defined as below 60 bpm at rest. When a human sleeps, a heartbeat with ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraventricular Tachycardia
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is an umbrella term for fast heart rhythms arising from the upper part of the heart. This is in contrast to the other group of fast heart rhythms – ventricular tachycardia, which start within the lower chambers of the heart. There are four main types of SVT: atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT), and Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome. The symptoms of SVT include palpitations, feeling of faintness, sweating, shortness of breath, and/or chest pain. These abnormal rhythms start from either the atria or atrioventricular node. They are generally due to one of two mechanisms: re-entry or increased automaticity. Diagnosis is typically by electrocardiogram (ECG), Holter monitor, or event monitor. Blood tests may be done to rule out specific underlying causes such as hyperthyroidism, pheochromocytomas, or electrolyte abnormalities. A normal resting heart rate is 60 to 100 beats per minute. A r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrial Tachycardia
Atrial tachycardia is a type of heart rhythm problem in which the heart's electrical impulse comes from an ectopic pacemaker (that is, an abnormally located cardiac pacemaker) in the upper chambers ( atria) of the heart, rather than from the sinoatrial node, the normal origin of the heart's electrical activity. As with any other form of tachycardia (rapid heart beat), the underlying mechanism can be either the rapid discharge of an abnormal focus, the presence of a ring of cardiac tissue that gives rise to a circle movement ( reentry),''Curr Opin Cardiol.'' 2001 Jan;16(1):1–7. "Basic mechanisms of reentrant arrhythmias". Antzelevitch C. or a triggered rapid rhythm due to other pathological circumstances (as would be the case with some drug toxicities, such as digoxin toxicity). Classification Forms of atrial tachycardia (ATach) include multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT), focal atrial tachycardia and atrial flutter. Text was copied from this source, which is available und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Rate
Heart rate is the frequency of the cardiac cycle, heartbeat measured by the number of contractions of the heart per minute (''beats per minute'', or bpm). The heart rate varies according to the body's Human body, physical needs, including the need to absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide. It is also modulated by numerous factors, including (but not limited to) genetics, physical fitness, Psychological stress, stress or psychological status, diet, drugs, hormonal status, environment, and disease/illness, as well as the interaction between these factors. It is usually equal or close to the pulse rate measured at any peripheral point. The American Heart Association states the normal resting adult human heart rate is 60–100 bpm. An ultra-trained athlete would have a resting heart rate of 37–38 bpm. ''Tachycardia'' is a high heart rate, defined as above 100 bpm at rest. ''Bradycardia'' is a low heart rate, defined as below 60 bpm at rest. When a human sleeps, a heartbeat with ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion characterised by an unpleasant state of inner wikt:turmoil, turmoil and includes feelings of dread over Anticipation, anticipated events. Anxiety is different from fear in that fear is defined as the emotional response to a present threat, whereas anxiety is the anticipation of a future one. It is often accompanied by nervous behavior such as pacing back and forth, Somatic anxiety, somatic complaints, and Rumination (psychology), rumination. Anxiety is a feeling of uneasiness and worry, usually generalized and unfocused as an overreaction to a situation that is only subjectively seen as menacing. It is often accompanied by muscular tension, restlessness, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, inability to catch one's breath, tightness in the abdominal region, nausea, and problems in concentration. Anxiety is closely related to fear, which is a response to a real or perceived immediate threat (fight-or-flight response); anxiety involves the expectation of a future t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AF, AFib or A-fib) is an Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) characterized by fibrillation, rapid and irregular beating of the Atrium (heart), atrial chambers of the heart. It often begins as short periods of abnormal cardiac cycle, beating, which become longer or continuous over time. It may also start as other forms of arrhythmia such as atrial flutter that then transform into AF. Episodes can be asymptomatic. Symptomatic episodes may involve heart palpitations, syncope (medicine), fainting, Presyncope, lightheadedness, Unconsciousness, loss of consciousness, or shortness of breath. Atrial fibrillation is associated with an increased risk of heart failure, dementia, and stroke. It is a type of supraventricular tachycardia. Atrial fibrillation frequently results from bursts of tachycardia that originate in muscle bundles extending from the Atrium (heart), atrium to the pulmonary veins. Pulmonary vein isolation by catheter ablation, trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrial Flutter
Atrial flutter (AFL) is a common abnormal heart rhythm that starts in the atrial chambers of the heart. When it first occurs, it is usually associated with a fast heart rate and is classified as a type of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). Atrial flutter is characterized by a sudden-onset (usually) regular abnormal heart rhythm on an electrocardiogram (ECG) in which the heart rate is fast. Symptoms may include a feeling of the heart beating too fast, too hard, or skipping beats, chest discomfort, difficulty breathing, a feeling as if one's stomach has dropped, a feeling of being light-headed, or loss of consciousness. Although this abnormal heart rhythm typically occurs in individuals with cardiovascular disease (e.g., high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, and cardiomyopathy) and diabetes mellitus, it may occur spontaneously in people with otherwise normal hearts. It is typically not a stable rhythm and often degenerates into atrial fibrillation (AF). But rar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrioventricular Reentrant Tachycardia
Atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia (AVRT), or atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia, is a type of heart arrhythmia with an abnormally fast rhythm (tachycardia); it is classified as a type of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). AVRT is most commonly associated with Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome, but is also seen in permanent junctional reciprocating tachycardia (PJRT). In AVRT, an accessory pathway allows electrical signals from the heart's Ventricle (heart), ventricles to enter the Atrium (heart), atria and cause earlier than normal contraction, which leads to repeated stimulation of the atrioventricular node.Josephson ME. Preexcitation syndromes. In: Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology, 4th, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia 2008. p.339 Signs and symptoms An episode of SVT may present with palpitations, dizziness, Dyspnea, shortness of breath, or Syncope (medicine), losing consciousness (fainting). The electrocardiogram, electrocardiogram (ECG) would app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinus Tachycardia
Sinus tachycardia is a sinus rhythm of the heart, with an increased rate of electrical discharge from the sinoatrial node, resulting in a tachycardia, a heart rate that is higher than the upper limit of normal (90–100 beats per minute for adult humans). The normal resting heart rate is 60–90 bpm in an average adult. Normal heart rates vary with age and level of fitness, from infants having faster heart rates (110-150 bpm) and the elderly having slower heart rates. Sinus tachycardia is a normal response to physical exercise or other stress, when the heart rate increases to meet the body's higher demand for energy and oxygen, but sinus tachycardia can also be caused by a health problem. Signs and symptoms Tachycardia is often asymptomatic. It is often a resulting symptom of a primary disease state and can be an indication of the severity of a disease. If the heart rate is too high, cardiac output may fall due to the markedly reduced ventricular filling time. Rapid rates, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |