|
Sustainable Consumption
Sustainable consumption (sometimes abbreviated to "SC") is the use of products and services in ways that minimizes human impact on the environment, impacts on the environment. Sustainable consumption can be undertaken in such a way that needs are met for present-day humans and also for future generations. Sustainable consumption is often paralleled with sustainable production; consumption refers to use and disposal (or recycling) not just by individuals and households, but also by governments, businesses, and other organizations. Sustainable consumption is closely related to sustainable products, sustainable production and sustainable living, sustainable lifestyles. "A sustainable lifestyle minimizes Ecology, ecological impacts while enabling a flourishing life for individuals, households, communities, and beyond. It is the product of individual and collective decisions about aspirations and about satisfying needs and adopting practices, which are in turn conditioned, facilitated, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumer Council (Hong Kong)
The Consumer Council is an independent statutory authority in Hong Kong, established in 1974 and formalised in April 1977 under the Consumer Council Ordinance (Cap. 216). Its role is to enhance consumer welfare and empower consumers to Consumer protection, protect themselves.Consumer Council - Mission (government info) Over the course of the past four decades the expansion in the council's duties and services on consumer protection, such as the publishing of the CHOICE Magazine in 1976, the recent launch of online price-watching tools, and conducting studies on different aspects of the consumer market, have coincided with the socio-economic development of Hong Kong. Apart from being a consumer advisor, it has assumed the role as a key stakeholder in making of consumer-related policies. The chai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waste
Waste are unwanted or unusable materials. Waste is any substance discarded after primary use, or is worthless, defective and of no use. A by-product, by contrast is a joint product of relatively minor Value (economics), economic value. A waste product may become a by-product, joint product or resource through an invention that raises a waste product's value above zero. Examples include municipal solid waste (household trash/refuse), hazardous waste, wastewater (such as sewage, which contains bodily wastes (feces and urine) and surface runoff), radioactive waste, and others. Definitions What constitutes waste depends on the eye of the beholder; one person's waste can be a resource for another person. Though waste is a physical object, its generation is a physical and psychological process. The definitions used by various agencies are as below. United Nations Environment Program According to the Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethical Consumerism
Ethical consumerism (alternatively called ethical consumption, ethical purchasing, moral purchasing, ethical sourcing, or ethical shopping and also associated with sustainable and green consumerism) is a type of consumer activism based on the concept of dollar voting. People practice it by buying ethically made products that support small-scale manufacturers or local artisans and protect animals and the environment, while boycotting products that exploit children as workers, are tested on animals, or damage the environment. The term "ethical consumer", now used generically, was first popularised by the UK magazine '' Ethical Consumer'', first published in 1989. ''Ethical Consumer'' magazine's key innovation was to produce "ratings tables", inspired by the criteria-based approach of the then-emerging ethical investment movement. ''Ethical Consumer''s ratings tables awarded companies negative marks (and overall scores, starting in 2005) across a range of ethical and environmental c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sustainable Lifestyle
Sustainable living describes a lifestyle that attempts to reduce the use of Earth's natural resources by an individual or society. Its practitioners often attempt to reduce their ecological footprint (including their carbon footprint) by altering their home designs and methods of transportation, energy consumption and diet. Its proponents aim to conduct their lives in ways that are consistent with sustainability, naturally balanced, and respectful of humanity's symbiotic relationship with the Earth's natural ecology. The practice and general philosophy of ecological living closely follows the overall principles of sustainable development. One approach to sustainable living, exemplified by small-scale urban transition towns and rural ecovillages, seeks to create self-reliant communities based on principles of simple living, which maximize self-sufficiency, particularly in food production. These principles, on a broader scale, underpin the concept of a bioregional economy. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitigation Of Climate Change
Mitigation is the reduction of something harmful that has occurred or the reduction of its harmful effects. It may refer to measures taken to reduce the harmful effects of hazards that remain ''in potentia'', or to manage harmful incidents that have already occurred. It is a stage or component of emergency management and of risk management. The theory of mitigation is a frequently used element in criminal law and is often used by a judge to try cases such as murder, where a perpetrator is subject to varying degrees of responsibility as a result of one's actions. Disaster mitigation An all-hazards approach to disaster management considers all known hazards and their natural and anthropogenic potential risks and impacts, with the intention of ensuring that measures taken to mitigate one type of risk do not increase vulnerability to other types of risks. Proactive disaster mitigation (also hazard mitigation) measures are generally more effective than reactive measures in eliminating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Fix
A structural fix refers to solving a problem or resolving a conflict by bringing about structural changes that change the underlying structures that provoked or sustain these problems. According to Thomas Heberlein such changes modify human behavior by regulating the social settings or the 'structures' in which the behavior occurs − their context. Such fixes are typically long-term opposed to temporary and require open and in-depth inquiry for the root structural causes of a problem and understanding of a system. Effectively changing norms would be an example of a structural fix. Often structural fixes involve a change of incentive In general, incentives are anything that persuade a person or organization to alter their behavior to produce the desired outcome. The laws of economists and of behavior state that higher incentives amount to greater levels of effort and therefo ...s. See also References {{reflist Change Problem solving methods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sustainable Development Goals
The ''2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development'', adopted by all United Nations (UN) members in 2015, created 17 world Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The aim of these global goals is "peace and prosperity for people and the planet" – while tackling climate change and working to preserve oceans and forests. The SDGs highlight the connections between the environmental, social and economic aspects of sustainable development. Sustainability is at the center of the SDGs, as the term ''sustainable development'' implies. These goals are ambitious, and the reports and outcomes to date indicate a challenging path. Most, if not all, of the goals are unlikely to be met by 2030. Rising inequalities, climate change, and biodiversity loss are topics of concerns threatening progress. The COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 to 2023 made these challenges worse, and some regions, such as Asia, have experienced significant setbacks during that time. There are cross-cutting issues and synergy, syner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
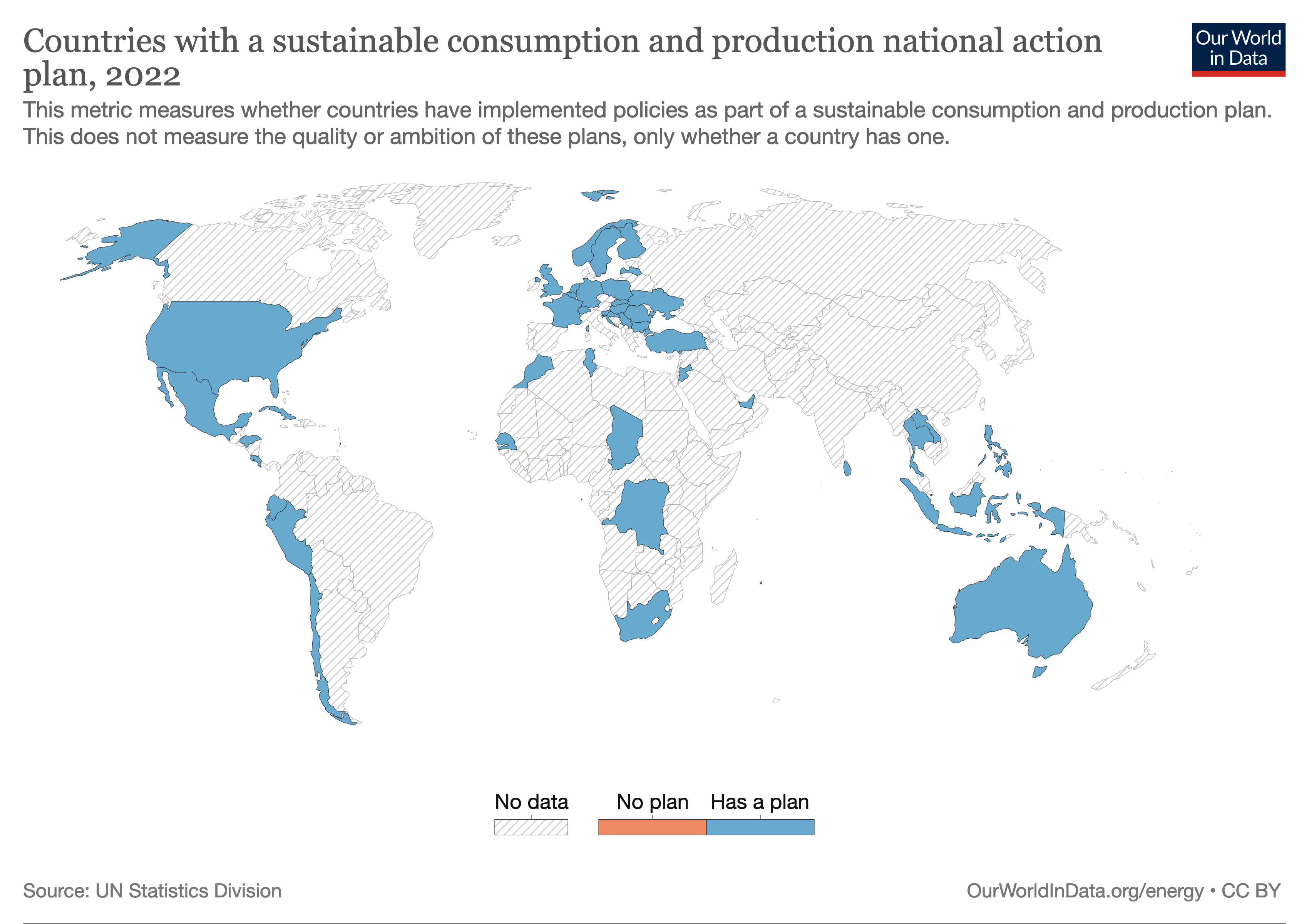
Goal 12
Sustainable Development Goal 12 (SDG 12 or Global Goal 12), titled "responsible consumption and production", is one of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations in 2015. The official wording of SDG 12 is "Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns".United Nations (2017) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 6 July 2017, Work of the Statistical Commission pertaining to the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable DevelopmentA/RES/71/313 SDG 12 is meant to ensure good use of resources, improve energy efficiency and sustainable infrastructure, provide access to basic services, create green and decent jobs, and ensure a better quality of life for all. SDG 12 has 11 targets to be achieved by at least 2030, and progress towards the targets is measured using 13 indicators. Sustainable Development Goal 12 has 11 targets. The first 8 are ''outcome targets'', which are: implement the 10‑Year Framework of Programs on Sustainable Consumption and Prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intergenerational Equity
Intergenerational equity in economic, psychological, and sociological contexts, is the idea of Social justice, fairness or justice between generations. The concept can be applied to fairness in dynamics between children, youth, adults, and Old age, seniors. It can also be applied to equity (law), fairness between generations currently living and future generations. Conversations about intergenerational equity may include basic human needs, economic needs, environmental needs and subjective human well-being. It is often discussed in public economics, especially with regard to transition economics, social policy, and Government budget, government budget-making. Many cite the growing U.S. national debt as an example of intergenerational inequity, as future generations will shoulder the consequences. Intergenerational equity is also explored in Environmentalism, environmental concerns, including sustainable development, and climate change. The continued depletion of natural resource ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product Life-cycle
In industry, product lifecycle management (PLM) is the process of managing the entire lifecycle of a product from its inception through the engineering Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, s ..., Product design, design, and Manufacturing, manufacture, as well as the service and disposal of manufactured products. PLM integrates people, data, processes, and business systems and provides a product information backbone for companies and their extended enterprises. History The inspiration for the burgeoning business process now known as PLM came from American Motors Corporation (AMC). The automaker was looking for a way to speed up its product development process to compete better against its larger competitors in 1985, according to François Castaing, Vice President for P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upcycling
Upcycling, also known as creative reuse, is the process of transforming by-products, waste materials, useless, or unwanted products into new materials or products perceived to be of greater quality, such as artistic value or environmental value. Description Upcycling is the opposite of downcycling, which is the other part of the recycling process. Downcycling involves converting materials and products into new materials, sometimes of lesser quality. Most recycling involves converting or extracting useful materials from a product and creating a different product or material. The terms upcycling and ''downcycling'' were first used in print in an article in SalvoNEWS by Thornton Kay quoting Reiner Pilz and published in 1994. ''Upsizing'' was the title of the German edition of a book about upcycling, first published in English in 1998 by Gunter Pauli and given the revised title of ''Upcycling'' in 1999. The German edition was adapted to the German language and culture by Joh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |