|
Supernova Explosions
A supernova (: supernovae or supernovas) is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. A supernova occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star, or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion. The original object, called the ''progenitor'', either collapses to a neutron star or black hole, or is completely destroyed to form a diffuse nebula. The peak optical luminosity of a supernova can be comparable to that of an entire galaxy before fading over several weeks or months. The last supernova directly observed in the Milky Way was Kepler's Supernova in 1604, appearing not long after Tycho's Supernova in 1572, both of which were visible to the naked eye. The remnants of more recent supernovae have been found, and observations of supernovae in other galaxies suggest they occur in the Milky Way on average about three times every century. A supernova in the Milky Way would almost certainly be observable through modern astronomical telescopes. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SN 1987A
SN 1987A was a Type II supernova in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. It occurred approximately from Earth and was the closest observed supernova since Kepler's Supernova in 1604. Light and neutrinos from the explosion reached Earth on February 23, 1987, and it was designated "SN 1987A" as the first supernova discovered that year. Its brightness peaked in May of that year, with an apparent magnitude of about 3, brighter than the constellation's brightest star, Alpha Doradus. It was the first supernova that modern astronomers were able to study in great detail, and its observations have provided much insight into core-collapse supernovae. SN 1987A provided the first opportunity to confirm by direct observation the radioactive source of the energy for visible light emissions, by detecting predicted gamma-ray line radiation from two of its abundant radioactive nuclei. This proved the radioactive nature of the long-duration po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speed Of Light
The speed of light in vacuum, commonly denoted , is a universal physical constant exactly equal to ). It is exact because, by international agreement, a metre is defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of second. The speed of light is invariant (physics), the same for all observers, no matter their relative velocity. It is the upper limit for the speed at which Information#Physics_and_determinacy, information, matter, or energy can travel through Space#Relativity, space. All forms of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, travel at the speed of light. For many practical purposes, light and other electromagnetic waves will appear to propagate instantaneously, but for long distances and sensitive measurements, their finite speed has noticeable effects. Much starlight viewed on Earth is from the distant past, allowing humans to study the history of the universe by viewing distant objects. When Data communication, comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Mass
The solar mass () is a frequently used unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is approximately equal to the mass of the Sun. It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxies and black holes. More precisely, the mass of the Sun is The solar mass is about times the mass of Earth (), or times the mass of Jupiter (). History of measurement The value of the gravitational constant was first derived from measurements that were made by Henry Cavendish in 1798 with a torsion balance. The value he obtained differs by only 1% from the modern value, but was not as precise. The diurnal parallax of the Sun was accurately measured during the transits of Venus in 1761 and 1769, yielding a value of (9 arcseconds, compared to the present value of ). From the value of the diurnal parallax, one can determine the distance to the Sun from the geometry of Earth. The first known estimate of the solar mass was by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metallicity
In astronomy, metallicity is the Abundance of the chemical elements, abundance of Chemical element, elements present in an object that are heavier than hydrogen and helium. Most of the normal currently detectable (i.e. non-Dark matter, dark) matter in the universe is either hydrogen or helium, and astronomers use the word ''metals'' as convenient shorthand for ''all elements except hydrogen and helium''. This word-use is distinct from the conventional chemical or physical definition of a metal as an electrically conducting element. Stars and nebulae with relatively high abundances of heavier elements are called ''metal-rich'' when discussing metallicity, even though many of those elements are called ''Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetals'' in chemistry. Metals in early spectroscopy In 1802, William Hyde WollastonMelvyn C. UsselmanWilliam Hyde WollastonEncyclopædia Britannica, retrieved 31 March 2013 noted the appearance of a number of dark features in the solar spectrum. In 1814, Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
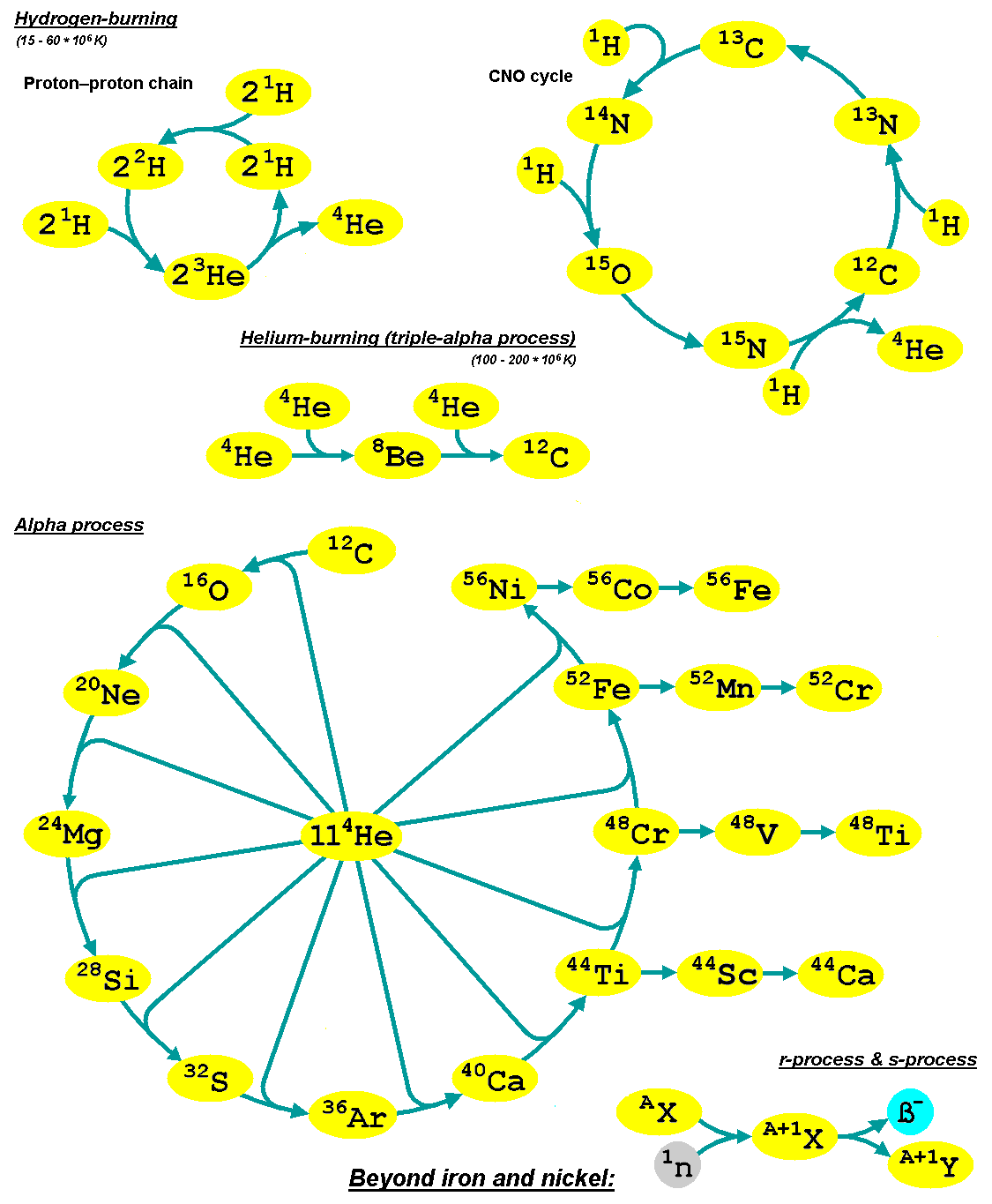
Alpha Process
The alpha process, also known as alpha capture or the alpha ladder, is one of two classes of nuclear fusion reactions by which stars convert helium into heavier elements. The other class is a cycle of reactions called the triple-alpha process, which consumes only helium, and produces carbon. The alpha process most commonly occurs in massive stars and during supernovae. Both processes are preceded by hydrogen fusion, which produces the helium that fuels both the triple-alpha process and the alpha ladder processes. After the triple-alpha process has produced enough carbon, the alpha-ladder begins and fusion reactions of increasingly heavy elements take place, in the order listed below. Each step only consumes the product of the previous reaction and helium. The later-stage reactions which are able to begin in any particular star, do so while the prior stage reactions are still under way in outer layers of the star. :\begin \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Merger
A stellar collision is the coming together of two stars caused by stellar dynamics within a star cluster, or by the orbital decay of a binary star due to stellar mass loss or gravitational radiation, or by other mechanisms not yet well understood. Any stars in the universe can collide, whether they are "alive", meaning fusion is still active in the star, or "dead", with fusion no longer taking place. White dwarf stars, neutron stars, black holes, main sequence stars, giant stars, and supergiants are very different in type, mass, temperature, and radius, and accordingly produce different types of collisions and remnants. Types of stellar collisions and mergers Binary star mergers About half of all the stars in the sky are part of binary systems, with two stars orbiting each other. Some binary stars orbit each other so closely that they share the same atmosphere, giving the system a peanut shape. While most such contact binary systems are stable, some do become unstable a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accretion (astrophysics)
In astrophysics, accretion is the accumulation of particles into a massive object by gravity, gravitationally attracting more matter, typically gaseous matter, into an accretion disk. Most astronomical objects, such as galaxy, galaxies, stars, and planets, are formed by accretion processes. Overview The accretion model that Earth and the other terrestrial planets formed from meteoric material was proposed in 1944 by Otto Schmidt, followed by the ''protoplanet theory'' of William McCrea (astronomer), William McCrea (1960) and finally the ''capture theory'' of Michael Woolfson. For details of Kant's position, see In 1978, Andrew Prentice resurrected the initial Laplacian ideas about planet formation and developed the ''modern Laplacian theory''. None of these models proved completely successful, and many of the proposed theories were descriptive. The 1944 accretion model by Otto Schmidt was further developed in a quantitative way in 1969 by Viktor Safronov. He calculated, in deta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Star
A binary star or binary star system is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved as separate stars using a telescope, in which case they are called ''visual binaries''. Many visual binaries have long orbital periods of several centuries or millennia and therefore have orbits which are uncertain or poorly known. They may also be detected by indirect techniques, such as spectroscopy (''spectroscopic binaries'') or astrometry (''astrometric binaries''). If a binary star happens to orbit in a plane along our line of sight, its components will eclipse and transit each other; these pairs are called ''eclipsing binaries'', or, together with other binaries that change brightness as they orbit, ''photometric binaries''. If components in binary star systems are close enough, they can gravitationally distort each other's outer stellar atmospheres. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Runaway
Thermal runaway describes a process that is accelerated by increased temperature, in turn releasing Thermal energy, energy that further increases temperature. Thermal runaway occurs in situations where an increase in temperature changes the conditions in a way that causes a further increase in temperature, often leading to a destructive result. It is a kind of uncontrolled positive feedback. In chemistry (and chemical engineering), thermal runaway is associated with strongly exothermic reactions that are accelerated by temperature rise. In electrical engineering, thermal runaway is typically associated with increased Electric current, current flow and power dissipation. Thermal runaway can occur in civil engineering, notably when the heat released by large amounts of Concrete#Curing, curing concrete is not controlled. In astrophysics, runaway nuclear fusion reactions in stars can lead to nova and several types of supernova explosions, and also occur as a less dramatic event in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Core
A stellar core is the extremely hot, dense region at the center of a star. For an ordinary main sequence star, the core region is the volume where the temperature and pressure conditions allow for energy production through thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium. This energy in turn counterbalances the mass of the star pressing inward; a process that self-maintains the conditions in Thermal equilibrium, thermal and hydrostatic equilibrium. The minimum temperature required for stellar hydrogen fusion exceeds 107 Kelvin, K (), while the density at the core of the Sun is over . The core is surrounded by the stellar envelope, which transports energy from the core to the stellar atmosphere where it is radiated away into space. Main sequence Main sequence stars are distinguished by the primary energy-generating mechanism in their central region, which joins four hydrogen nuclei to form a single helium atom through thermonuclear fusion. The Sun is an example of this class of star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Collapse
Gravitational collapse is the contraction of an astronomical object due to the influence of its own gravity, which tends to draw matter inward toward the center of gravity. Gravitational collapse is a fundamental mechanism for structure formation in the universe. Over time an initial, relatively smooth distribution of matter, after sufficient accretion, may collapse to form pockets of higher density, such as stars or black holes. Star formation involves a gradual gravitational collapse of interstellar medium into clumps of molecular clouds and potential protostars. The compression caused by the collapse raises the temperature until thermonuclear fusion occurs at the center of the star, at which point the collapse gradually comes to a halt as the outward thermal pressure balances the gravitational forces. The star then exists in a state of dynamic equilibrium. During the star's evolution a star might collapse again and reach several new states of equilibrium. Star formation A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |