|
Superior Costotransverse Ligament
A superior costotransverse ligament is a ligament of the costotransverse joint that attaches onto the crest of the neck of a rib, and onto the transverse process of the vertebra Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spina ... superior to the rib. The ligament may be subdivided into a strong ''anterior costotransverse ligament'', and a weak ''posterior costotransverse ligament''. The ligament is absent in the first rib. Structure The superior costotransverse ligament is a strong,Ibrahim AF, Darwish HH, The costotransverse ligaments in human: a detailed anatomical study, Clin Anat. 2005 Jul;18(5):340-5 broad fibrous band. It comprises two layers: * The anterior layer attaches at the crest of the neck of rib, and at the inferior aspect of the transverse process of the above v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Costotransverse Joint
The costotransverse joint is the joint formed between the facet of the tubercle of the rib and the adjacent transverse process of a thoracic vertebra. The costotransverse joint is a plane type of synovial joint which, under physiological conditions, allows only gliding movement. This costotransverse joint is present in all but the eleventh and twelfth ribs. The first ten ribs have two joints in close proximity posteriorly; the costovertebral joints and the costotransverse joints. This arrangement restrains the motion of the ribs allowing them to work in a parallel fashion during breathing. If a typical rib had only one joint posteriorly the resultant swivel action would allow a rib to be non-parallel with respect to the neighboring ribs making for a very inefficient breathing. Anatomy Ligaments The ligaments of the joint are: * Costotransverse ligament A costotransverse ligament is ligament of the costotransverse joint which attaches at (the posterior aspect of) the ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transverse Process
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal segment and the particular species. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the vertebral body (also ''centrum'') is of bone and bears the load of the vertebral column. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles (pedicle of vertebral arch), two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava (ligaments of the spine). There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conduits for the spinal nerves. The body of the vertebr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
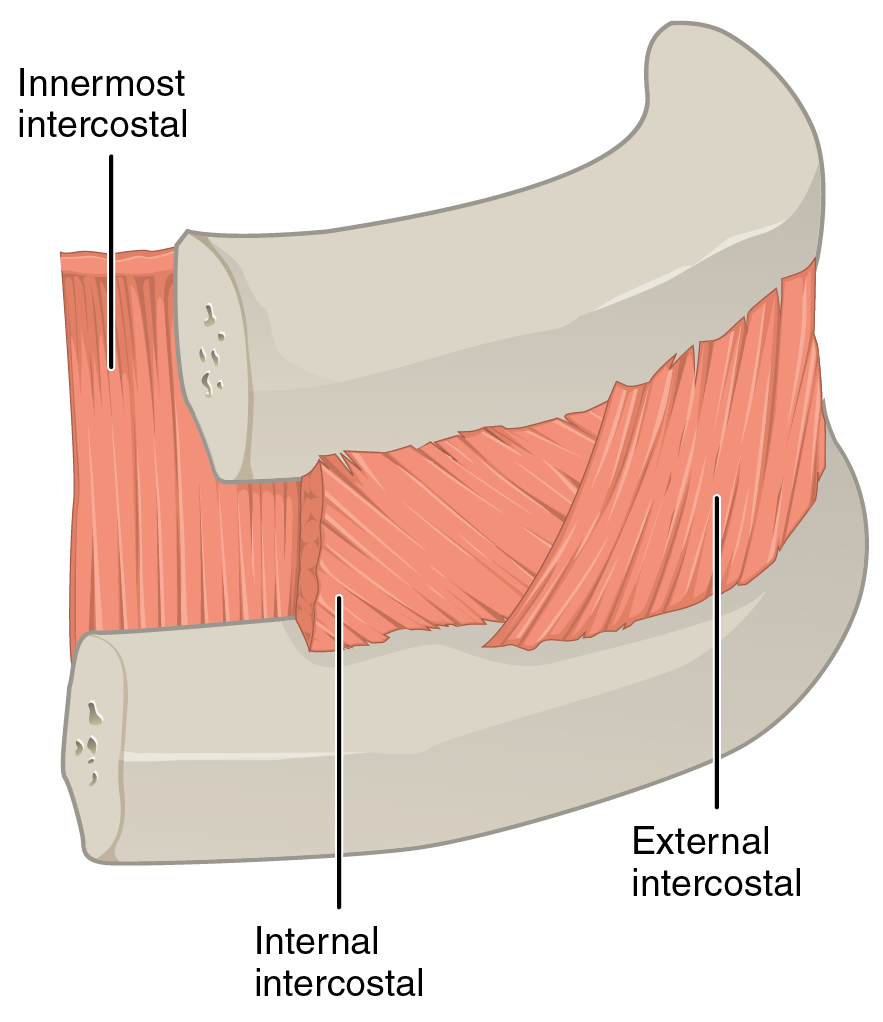
External Intercostal Muscles
The external intercostal muscles or external intercostals (intercostales externi) are eleven in number on both sides. Structure The muscles extend from the tubercles of the ribs behind, to the cartilages of the ribs in front, where they end in thin membranes, the external intercostal membranes, which are continued forward to the sternum. These muscles work in unison when inhalation occurs. The internal intercostal muscles relax while the external muscles contract causing the expansion of the chest cavity and an influx of air into the lungs. Each arises from the lower border of a rib, and is inserted into the upper border of the rib below. In the two lower spaces they extend to the ends of the cartilages, and in the upper two or three spaces they do not quite reach the ends of the ribs. They are thicker than the internal intercostals, and their fibers are directed obliquely downward and laterally on the back of the thorax, and downward, forward, and medially on the front. V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thorax (human Anatomy)
The thorax (: thoraces or thoraxes) or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the body, each in turn composed of multiple segments. The human thorax includes the thoracic cavity and the thoracic wall. It contains organs including the heart, lungs, and thymus gland, as well as muscles and various other internal structures. The chest may be affected by many diseases, of which the most common symptom is chest pain. Etymology The word thorax comes from the Greek θώραξ ''thṓrax'' "breastplate, cuirass, corslet" via . Humans Structure In humans and other hominids, the thorax is the chest region of the body between the neck and the abdomen, along with its internal organs and other contents. It is mostly protected and supported by the rib cage, spine, and shoulder girdle. Contents The contents of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |