|
Superior Colliculus
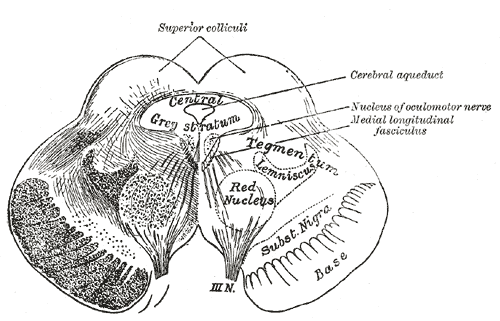
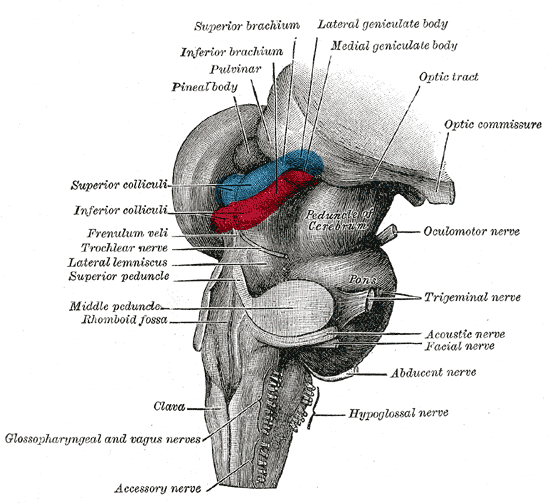
In neuroanatomy, the superior colliculus () is a structure lying on the tectum, roof of the mammalian midbrain. In non-mammalian vertebrates, the Homology (biology), homologous structure is known as the optic tectum or optic lobe. The adjective form ''tectum, tectal'' is commonly used for both structures. In mammals, the superior colliculus forms a major component of the midbrain. It is a paired structure and together with the paired inferior colliculi forms the corpora quadrigemina. The superior colliculus is a layered structure, with a pattern that is similar in all mammals. The layers can be grouped into the superficial layers (retinal nerve fiber layer, stratum opticum and above) and the deeper remaining layers. Neurons in the superficial layers receive direct input from the retina and respond almost exclusively to visual stimuli. Many neurons in the deeper layers also respond to other modalities, and some respond to stimuli in multiple modalities. The deeper layers also conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum. It is functionally associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation.Breedlove, Watson, & Rosenzweig. Biological Psychology, 6th Edition, 2010, pp. 45-46 The name ''mesencephalon'' comes from the Greek ''mesos'', "middle", and ''enkephalos'', "brain". Structure The midbrain is the shortest segment of the brainstem, measuring less than 2cm in length. It is situated mostly in the posterior cranial fossa, with its superior part extending above the tentorial notch. The principal regions of the midbrain are the tectum, the cerebral aqueduct, tegmentum, and the cerebral peduncles. Rostral and caudal, Rostrally the midbrain adjoins the diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, etc.), while Rostral and caudal, cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleus Isthmi
In neuroanatomy, the superior colliculus () is a structure lying on the roof of the mammalian midbrain. In non-mammalian vertebrates, the homologous structure is known as the optic tectum or optic lobe. The adjective form '' tectal'' is commonly used for both structures. In mammals, the superior colliculus forms a major component of the midbrain. It is a paired structure and together with the paired inferior colliculi forms the corpora quadrigemina. The superior colliculus is a layered structure, with a pattern that is similar in all mammals. The layers can be grouped into the superficial layers ( stratum opticum and above) and the deeper remaining layers. Neurons in the superficial layers receive direct input from the retina and respond almost exclusively to visual stimuli. Many neurons in the deeper layers also respond to other modalities, and some respond to stimuli in multiple modalities. The deeper layers also contain a population of motor-related neurons, capable of activa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optic Tract
In neuroanatomy, the optic tract () is a part of the visual system in the brain. It is a continuation of the optic nerve that relays information from the optic chiasm to the ipsilateral lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), pretectal nuclei, and superior colliculus. It is composed of two individual tracts, the left optic tract and the right optic tract, each of which conveys visual information exclusive to its respective contralateral half of the visual field. Each of these tracts is derived from a combination of temporal and nasal retinal fibers from each eye that corresponds to one half of the visual field. In more specific terms, the optic tract contains fibers from the ipsilateral temporal hemiretina and contralateral nasal hemiretina. Anatomy Arterial supply The optic tract receives arterial supply from the anterior choroidal artery, and posterior communicating artery. Function Visual function The optic tract carries retinal information relating to the whole visua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Geniculate Nucleus
In neuroanatomy, the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN; also called the lateral geniculate body or lateral geniculate complex) is a structure in the thalamus and a key component of the mammalian visual pathway. It is a small, ovoid, Anatomical terms of location#Dorsal_and_ventral, ventral projection of the thalamus where the thalamus connects with the optic nerve. There are two LGNs, one on the left and another on the right side of the thalamus. In humans, both LGNs have six layers of neurons (grey matter) alternating with optic fibers (white matter). The LGN receives information directly from the ascending retinal ganglion cells via the optic tract and from the reticular activating system. Neurons of the LGN send their axons through the optic radiation, a direct pathway to the primary visual cortex. In addition, the LGN receives many strong feedback connections from the primary visual cortex. In humans as well as other mammals, the two strongest pathways linking the eye to the bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalamus
The thalamus (: thalami; from Greek language, Greek Wikt:θάλαμος, θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter on the lateral wall of the third ventricle forming the wikt:dorsal, dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions, known as the thalamocortical radiations, allowing hub (network science), hub-like exchanges of information. It has several functions, such as the relaying of sensory neuron, sensory and motor neuron, motor signals to the cerebral cortex and the regulation of consciousness, sleep, and alertness. Anatomically, the thalami are paramedian symmetrical structures (left and right), within the vertebrate brain, situated between the cerebral cortex and the midbrain. It forms during embryonic development as the main product of the diencephalon, as first recognized by the Swiss embryologist and anatomist Wilhelm His Sr. in 1893. Anatomy The thalami ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Colliculus
The inferior colliculus (IC) (Latin for ''lower hill'') is the principal midbrain nucleus of the Auditory system, auditory pathway and receives input from several peripheral brainstem nuclei in the auditory pathway, as well as inputs from the auditory cortex.Shore, S. E.: ''Auditory/Somatosensory Interactions''. In: Squire (Ed.): ''Encyclopedia of Neuroscience'', Academic Press, 2009, pp. 691–695 The inferior colliculus has three subdivisions: the central nucleus, a dorsal cortex by which it is surrounded, and an external cortex which is located laterally. Its bimodal neurons are implicated in auditory-Somatosensory system, somatosensory interaction, receiving projections from Somatosensory system, somatosensory nuclei. This multisensory integration may underlie a filtering of self-effected sounds from vocalization, chewing, or respiration activities. The inferior colliculi together with the superior colliculi form the eminences of the corpora quadrigemina, and also part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Geniculate Nucleus
The medial geniculate nucleus (MGN) or medial geniculate body (MGB) is part of the auditory thalamus and represents the thalamic relay between the inferior colliculus (IC) and the auditory cortex (AC). It is made up of a number of sub-nuclei that are distinguished by their neuronal morphology and density, by their afferent and efferent connections, and by the coding properties of their neurons. It is thought that the MGN influences the direction and maintenance of attention. Divisions The MGN has three major divisions; ventral (VMGN), dorsal (DMGN) and medial (MMGN). Whilst the VMGN is specific to auditory information processing, the DMGN and MMGN also receive information from non-auditory pathways. Ventral subnucleus Cell types There are two main cell types in the ventral subnucleus of the medial geniculate body (VMGN): * Thalamocortical relay cells (or principal neurons): The dendritic input to these cells comes from two sets of dendritic trees oriented on opposite poles of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulvinar Nuclei
The pulvinar nuclei or nuclei of the pulvinar (nuclei pulvinares) are the nuclei ( cell bodies of neurons) located in the thalamus (a part of the vertebrate brain). As a group they make up the collection called the pulvinar of the thalamus (pulvinar thalami), usually just called the pulvinar. The pulvinar is usually grouped as one of the ''lateral thalamic nuclei'' in rodents and carnivores, and stands as an independent complex in primates. Pulvinar acts as an association nucleus that, along with medial dorsal nucleus, connected with parietal, occipital, and temporal lobes, but the function is largely unknown. No distinctive syndrome or obvious sensory deficit can be linked to either one. Structure By convention, the pulvinar is divided into four nuclei: Their connectomic details are as follows: * The ''lateral'' and ''inferior'' pulvinar nuclei have widespread connections with early visual cortical areas. * The dorsal part of the ''lateral'' pulvinar nucleus predominant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splenium Of Corpus Callosum
The corpus callosum (Latin for "tough body"), also callosal commissure, is a wide, thick nerve tract, consisting of a flat bundle of commissural fibers, beneath the cerebral cortex in the brain. The corpus callosum is only found in placental mammals. It spans part of the longitudinal fissure, connecting the left and right cerebral hemispheres, enabling communication between them. It is the largest white matter structure in the human brain, about in length and consisting of 200–300 million axonal projections. A number of separate nerve tracts, classed as subregions of the corpus callosum, connect different parts of the hemispheres. The main ones are known as the genu, the rostrum, the trunk or body, and the splenium. Structure The corpus callosum forms the floor of the longitudinal fissure that separates the two cerebral hemispheres. Part of the corpus callosum forms the roof of the lateral ventricles. The corpus callosum has four main parts – individual nerve tract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pineal Gland
The pineal gland (also known as the pineal body or epiphysis cerebri) is a small endocrine gland in the brain of most vertebrates. It produces melatonin, a serotonin-derived hormone, which modulates sleep, sleep patterns following the diurnal cycles. The shape of the gland resembles a pine cone, which gives it its name. The pineal gland is located in the epithalamus, near the center of the brain, between the two cerebral hemisphere, hemispheres, tucked in a groove where the two halves of the thalamus join. It is one of the neuroendocrinology, neuroendocrine Circumventricular organs, secretory circumventricular organs in which capillaries are mostly Vascular permeability, permeable to solutes in the blood. The pineal gland is present in almost all vertebrates, but is absent in Protochordata, protochordates in which there is a simple pineal homologue. The hagfish, archaic vertebrates, lack a pineal gland. In some species of amphibians and reptiles, the gland is linked to a light-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midbrain Tectum
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum. It is functionally associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation.Breedlove, Watson, & Rosenzweig. Biological Psychology, 6th Edition, 2010, pp. 45-46 The name ''mesencephalon'' comes from the Greek ''mesos'', "middle", and ''enkephalos'', "brain". Structure The midbrain is the shortest segment of the brainstem, measuring less than 2cm in length. It is situated mostly in the posterior cranial fossa, with its superior part extending above the tentorial notch. The principal regions of the midbrain are the tectum, the cerebral aqueduct, tegmentum, and the cerebral peduncles. Rostrally the midbrain adjoins the diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, etc.), while caudally it adjoins the hindbrain (pons, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |