|
Superfire
Superfiring armament is a naval design technique in which two or more turrets are located one behind the other, with the rear turret located above ("super") the one in front so that it can fire over the first. This configuration meant that both forward and aft turrets could fire at any target within their sector, even when the target was directly ahead of the turrets. History Historically, large surface warships were known by the generic label of battleships, with a further distinction between pre-dreadnoughts and dreadnoughts. The era of technical evolution occurred roughly from 1900 to 1945. Part of the technical evolution was driven by the need to compress as much large-gun firepower into the smallest space possible. In early designs, the large-caliber turrets were all located on the same plane firing to one side or the other. In firing ahead or to the rear, usually only the forward-most or rearmost turret could fire, especially at low angles. An early concern was tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperatritsa Mariya-class Battleship
The ''Imperatritsa Mariya''-class () battleships were the first dreadnoughts built for the Black Sea Fleet of the Imperial Russian Navy. All three ships were built in Mykolaiv, Nikolayev during World War I; two of the ships were built by the Shipyard named after 61 Communards, Rossud Dockyard and the third was built by the Black Sea Shipyard, Associated Factories and Shipyards of Nikolayev (). Two ships were delivered in 1915 and saw some combat against German Empire, ex-German warships that had been 'gifted' to the Ottoman Empire, but the third was not completed until 1917 and saw no combat due to the disorder in the navy after the February Revolution earlier that year. was sunk by a magazine (artillery), magazine explosion in Sevastopol harbor in 1916. , having been renamed ''Svobodnaya Rossiya'' in 1917, was scuttled in Novorossiysk harbor in 1918 to prevent her from being turned over to the Germans as required by the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk. The crew of ''Volia'', as had bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Battleship Henri IV
''Henri IV'' was a pre-dreadnought battleship of the French Navy built to test some of the ideas of the prominent naval architect Louis-Émile Bertin. She began World War I as guardship at Bizerte. She was sent to reinforce the Allied naval force in the Dardanelles campaign of 1915, although some of her secondary armament had been removed for transfer to Serbia in 1914. Afterwards, she was relegated to second-line roles before being sent to Taranto as a depot ship in 1918. She was struck from the navy list in 1920 and scrapped the following year. Design ''Henri IV'' was designed by the famous French naval architect Louis-Émile Bertin to evaluate some of his ideas. She was designed to make her a small target and lacked most of the normal rear superstructure common to ships of her period, other than that needed to keep her rear turret from being washed out. Her rear hull had only of freeboard, although she was built up to the normal upper deck height amidships and at the bow for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minas Geraes From Bow
Minas or MINAS may refer to: People with the given name Minas * Menas of Ethiopia (died 1563) * Saint Menas (Minas, 285–309) * Minias of Florence (Minas, Miniato, died 250) * Minas Alozidis (born 1984), Greek hurdler * Minas Avetisyan (1928–1975) * Minas Hantzidis (born 1966), Greek footballer * Minas Hadjimichael (born 1956), Permanent Representative to the United Nations for Cyprus * Minas Hatzisavvas (1948–2015), Greek actor * Minas of Aksum, 6th-century bishop People with the surname Minas * Iskouhi Minas (1884–1951), French poet and writer of Armenian descent. Places * Minas Gerais, Brazil * Minas, Uruguay * Minas Department, Córdoba, Argentina * Minas Department, Neuquén, Argentina * Minas, Cuba, a municipality in Cuba * Minas, Iran, a village in West Azerbaijan Province, Iran * Minas Basin in Nova Scotia * Les Mines, a former Acadian community on the shores of the Minas Basin (called Minas or Mines in English) Other uses * Minas (band), an American bossa nov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
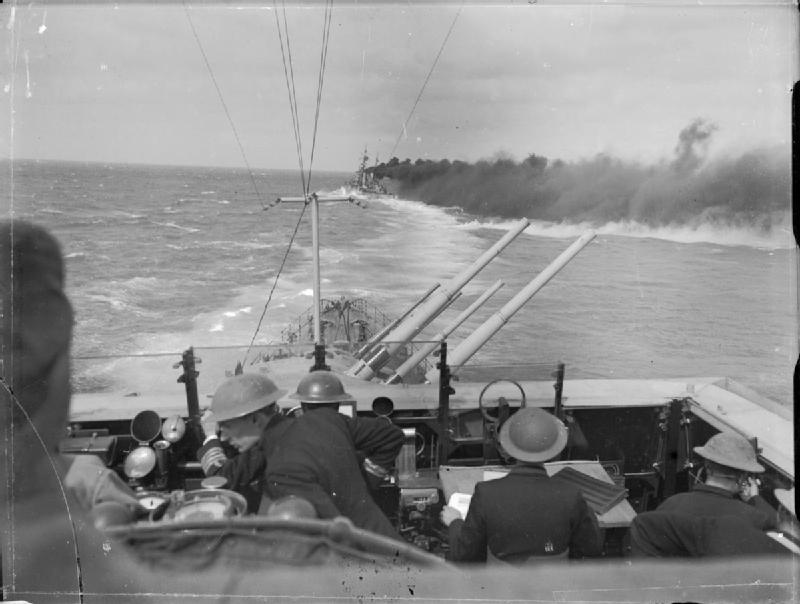
Dido-class Cruiser
The ''Dido'' class consisted of sixteen light cruisers built for the Royal Navy during World War II. The first group of three ships were commissioned in 1940; the second group of six ships and third group of two were commissioned between 1941 and 1942. A fourth group, also described as the Improved Dido or ''Bellona'' class (five ships) were commissioned between 1943 and 1944. Most members of the class were given names drawn from classical history and legend. The groups differed in armament, and for the ''Bellona''s, in function. The ''Dido'' class were designed to replace the C-class and D-class cruisers as small fleet cruisers and flotilla leaders for the destroyer screen. As designed, they mounted five twin 5.25-inch high-angle gun turrets on the centreline providing dual-purpose anti-air and anti-surface capacity; the complex new turrets were unreliable when introduced, and somewhat unsatisfactory at a time when the UK faced a fight for survival. During the war, the orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zumwalt-class Destroyer
The ''Zumwalt''-class destroyer is a class of three United States Navy guided-missile destroyers designed as multi-mission stealth ships with a focus on land attack. The class was designed with a primary role of naval gunfire support and secondary roles of surface warfare and anti-aircraft warfare. The class design emerged from the DD-21 "land attack destroyer" program as "DD(X)" and was intended to take the role of battleships in meeting a congressional mandate for naval fire support. The ship is designed around its two Advanced Gun Systems (AGS), turrets with 920 round magazines, and unique Long Range Land Attack Projectile (LRLAP) ammunition. LRLAP procurement was canceled, rendering the guns unusable, so the Navy re-purposed the ships for surface warfare. Starting in 2023, the Navy will remove the AGS from the ships and replace them with hypersonic missiles. The ships are classed as destroyers, but they are much larger than any other active destroyers or cruisers in the U.S. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Russian Navy
The Imperial Russian Navy () operated as the navy of the Russian Tsardom and later the Russian Empire from 1696 to 1917. Formally established in 1696, it lasted until being dissolved in the wake of the February Revolution and the declaration of the Russian Republic in 1917. It developed from a smaller force that had existed prior to Tsar Peter the Great's founding of the modern Russian navy during the Azov campaigns (1695–1696), Second Azov campaign in 1696, and expanded in the second half of the 18th century before reaching its peak strength by the early part of the 19th century, behind only the British and French fleets in terms of size. The Imperial Navy drew its officers from the aristocracy of the Empire, who belonged to the state Russian Orthodox Church. Young aristocrats began to be trained for leadership at a national naval boarding school, the Naval Cadet Corps (Russia), Naval Cadet Corps. From 1818 on, only officers of the Imperial Russian Navy were appointed to the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Battleship Imperator Nikolai I (1916)
''Imperator Nikolai I'' (: ''Emperor Nicholas I'') was a Russian dreadnought built during World War I for service in the Black Sea. She was designed to counter multiple prospective Ottoman dreadnoughts which had been placed under order by the Ottoman government, since this raised the possibility that the Russian dreadnoughts being built for the Black Sea Fleet could be outclassed. The ship used the same main armament as the preceding , but was larger and more heavily armored. ''Imperator Nikolai I'' was launched in 1916, but construction was suspended on 24 October 1917. The Soviets considered completing her in 1923, but later rejected the idea. She was towed to Sevastopol in 1927 and scrapped. Design and development ''Imperator Nikolai I'' was designed in response to efforts by the Ottoman Empire to acquire modern dreadnoughts from abroad. By late 1913 it appeared that the Turks would be able to muster three dreadnoughts, two of which were armed with guns, versus the three Rus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
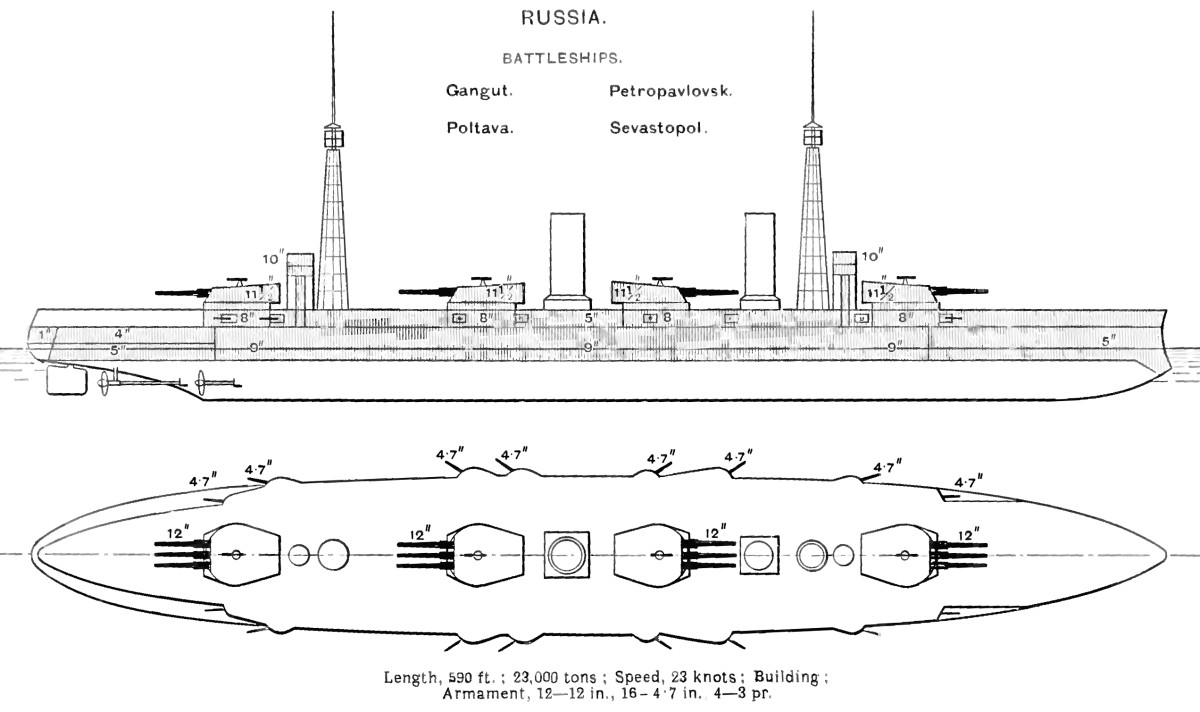
Gangut-class Battleship
The ''Gangut'' class, also known as the ''Sevastopol'' class, were the first dreadnoughts built for the Imperial Russian Navy before World War I. They had a convoluted design history involving several British companies, evolving requirements, an international design competition, and foreign protests. Four ships were ordered in 1909, , , , and . Construction was delayed by financing problems until the Duma formally authorized the ships in 1911. They were delivered from December 1914 through January 1915, although they still needed work on the gun turrets and fire-control systems until mid-1915. Their role was to defend the mouth of the Gulf of Finland against the Germans, who never tried to enter, so the ships spent their time training and providing cover for minelaying operations. Their crews participated in the general mutiny of the Baltic Fleet after the February Revolution in 1917, and joined the Bolsheviks the following year. All of the dreadnoughts except for ''Petropavlovsk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metacentric Height
The metacentric height (GM) is a measurement of the initial static stability of a floating body. It is calculated as the distance between the centre of gravity of a ship and its '' metacentre''. A larger metacentric height implies greater initial stability against overturning. The metacentric height also influences the natural period of rolling of a hull, with very large metacentric heights being associated with shorter periods of roll which are uncomfortable for passengers. Hence, a sufficiently, but not excessively, high metacentric height is considered ideal for passenger ships. Different centres The ''centre of buoyancy'' is at the centre of mass of the volume of water that the hull displaces. This point is referred to as B in naval architecture. The '' centre of gravity'' of the ship is commonly denoted as point G or CG. When a ship is at equilibrium, the centre of buoyancy is vertically in line with the centre of gravity of the ship. The metacentre is the point where th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QF 5
QF may stand for: Businesses and organisations * Qantas, an Australian airline (IATA:QF) * Qatar Foundation, a non-profit * Quiverfull, a Christian movement Military * Quds Force, an Iranian expeditionary unit * Quick-firing gun, an artillery piece * A gun breech that uses metallic cartridges; see British ordnance terms#QF * Q-Fire, a decoy fire site used in World War II Other uses * Quality factor In physics and engineering, the quality factor or factor is a dimensionless parameter that describes how underdamped an oscillator or resonator is. It is defined as the ratio of the initial energy stored in the resonator to the energy lost in ..., in physics and engineering, a measure of the "quality" of a resonant system {{disambig fr:QF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5"/38 Caliber Gun
The Mark 12 5"/38-caliber gun was a United States dual purpose gun, dual-purpose Naval artillery, naval gun, but also installed in single-purpose mounts on a handful of ships. The 38-Caliber (artillery), caliber barrel was a mid-length compromise between the previous United States standard 5"/51 caliber gun, 5"/51 low-angle gun and 5-inch/25-caliber gun, 5"/25 anti-aircraft gun. United States naval gun terminology indicates the gun fired a projectile in diameter, and the barrel was 38 Caliber (artillery), calibers long. The increased barrel length provided greatly improved performance in both anti-aircraft and anti-surface roles compared to the 5"/25 gun. However, except for the barrel length and the use of Shell (projectile)#Separate loading cased charge, semi-fixed ammunition, the 5"/38 gun was derived from the 5"/25 gun. Both weapons had power ramming, which enabled rapid fire at high angles against aircraft. The 5"/38 entered service on , commissioned in 1934, the first n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |