|
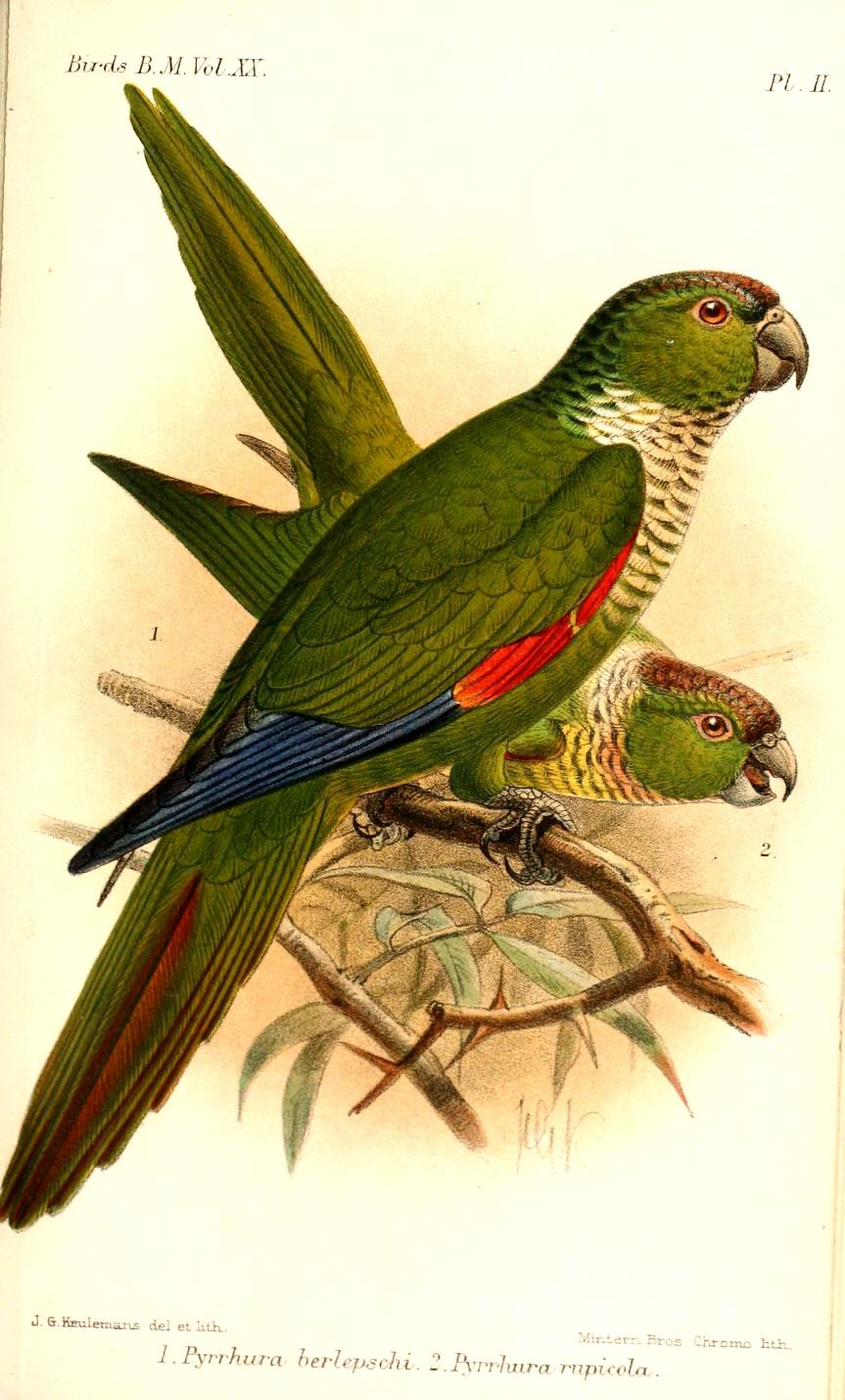
Sulphur-winged Parakeet
The sulphur-winged parakeet (''Pyrrhura hoffmanni''), also known as Hoffmann's conure in aviculture, is a species of bird in subfamily Arinae of the family Psittacidae, the African and New World parrots. It is found in Costa Rica and Panama. Taxonomy and systematics The sulphur-winged parakeet has two subspecies, the nominate ''P. h. hoffmanni'' ( Cabanis, 1861) and ''P. h. gaudens'' (Bangs, 1906). It is named for the German naturalist Karl Hoffmann. Description The sulphur-winged parakeet is about long and weighs an average of . The sexes are the same. Adults of the nominate subspecies are mostly green. Their head, nape, and throat have some yellow inclusions; bare white skin surrounds their eye and their ear coverts are bright terracotta. Their breast has a dull orange wash. Their wing is mostly green with yellow primary coverts, inner primaries, and outer secondaries; the outer primaries are blue. Their tail's upperside is rufous olive with green fringes on the feat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Cabanis
Jean Louis Cabanis (8 March 1816 – 20 February 1906) was a German ornithologist. He worked at the bird collections of the Natural History Museum in Berlin becoming its first curator of birds in 1850. He founded the ''Journal für Ornithologie'' in 1853''.'' Biography Cabanis was born in Berlin to an old Huguenot family who had moved from France. His father Benoit-Jean (1774–1838) and mother Maria Luise (1783–1849) both came from families that were in the textile industry. Little is known of his early life. He studied at the University of Berlin from 1835 to 1839, and then travelled to North America, working as a museum assistant in Carolina. He returned in 1841 with a large natural history collection. He was assistant at the Natural History Museum, Berlin, Natural History Museum of Berlin (which was at the time the Berlin University Museum) and in 1850 he became the curator of birds, taking over from Martin Lichtenstein. Charles Lucien Bonaparte had offered him a positio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondaries (birds)
Flight feathers (''Pennae volatus'') are the long, stiff, asymmetrically shaped, but symmetrically paired pennaceous feathers on the Bird wing, wings or tail of a bird; those on the wings are called remiges (), singular remex (), while those on the tail are called rectrices ( or ), singular rectrix (). The primary function of the flight feathers is to aid in the generation of both thrust and lift (force), lift, thereby enabling bird flight, flight. The flight feathers of some birds perform additional functions, generally associated with territorial displays, courtship rituals or feeding methods. In some species, these feathers have developed into long showy plumes used in visual courtship displays, while in others they create a sound during display flights. Tiny serrations on the leading edge of their remiges help owls to fly silently (and therefore hunt more successfully), while the extra-stiff rectrices of woodpeckers help them to brace against tree trunks as they hammer on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Birds Of The Talamancan Montane Forests
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or, in scientific literature, as an ''endemite''. Similarly, many species found in the Western ghats of India are examples of endemism. Endemism is an important concept in conservation biology for measuring biodiversity in a particular place and evaluating the risk of extinction for species. Endemism is also of interest in evolutionary biology, because it provides clues about how changes in the environment cause species to undergo range shifts (potentially expanding their range into a larger area or becomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrrhura
''Pyrrhura'' (Greek Red/Fire Tail) is a genus of parrots in the Arini tribe. They occur in tropical and subtropical South America and southern Central America (Panama and Costa Rica). Most are restricted to humid forest and adjacent habitats, but one species, the blaze-winged parakeet, prefers deciduous or gallery woodland, and another, the Pfrimer's parakeet, is restricted to dry regions. Some species are highly endangered. Depending on the species, the total length range from . All have long, pointed tails, a mainly green plumage, and a relatively narrow, dark greyish to white eye-ring. Many have scaly or barred chest-patterns and a whitish, pale grey, buff or reddish ear-patch. They typically move around in small, noisy flocks, flying swiftly at or below canopy level. Once settled in a tree they tend to be silent (especially if aware of danger) and difficult to spot. They nest in a tree-crevice. Some species are popular in aviculture, where they are commonly referred t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IUCN
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the status of the natural world and the measures needed to safeguard it. It is involved in data gathering and Data analysis, analysis, research, field projects, advocacy, and education. IUCN's mission is to "influence, encourage and assist societies throughout the world to conserve nature and to ensure that any use of natural resources is equitable and ecologically sustainable". Over the past decades, IUCN has widened its focus beyond conservation ecology and now incorporates issues related to sustainable development in its projects. IUCN does not itself aim to mobilize the public in support of nature conservation. It tries to influence the actions of governments, business and other stakeholders by providing information and advice and through buildin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Forest
A secondary forest (or second-growth forest) is a forest or woodland area which has regenerated through largely natural processes after human-caused Disturbance (ecology), disturbances, such as Logging, timber harvest or agriculture clearing, or equivalently disruptive natural phenomena. It is distinguished from an old-growth forest (primary or primeval forest), which has not recently undergone such disruption, and complex early Seral community, seral forest, as well as third-growth forests that result from harvest in second growth forests. Secondary forest regrowing after timber harvest differs from forest Ecological succession, regrowing after natural Disturbance (ecology), disturbances such as Wildfire, fire, insect infestation, or windthrow because the dead trees remain to provide nutrients, structure, and water retention after natural disturbances. Secondary forests are notably different from primary forests in their composition and biodiversity; however, they may still be hel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
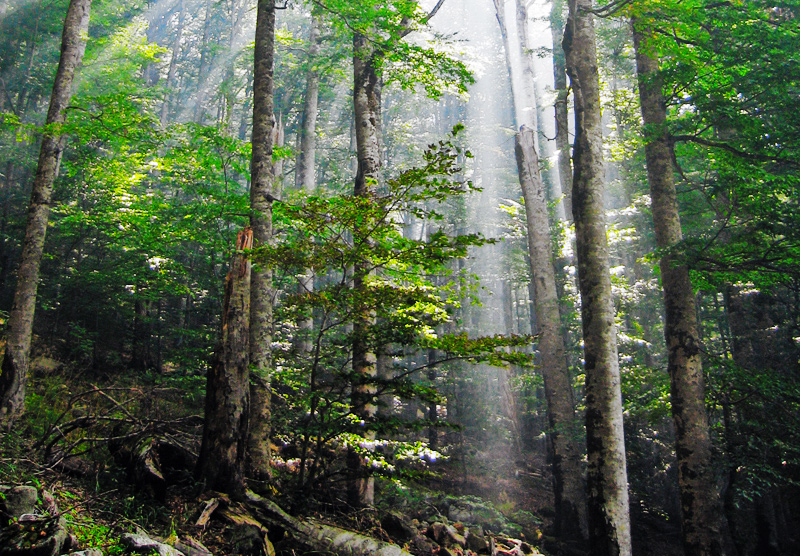
Montane Forest
Montane ecosystems are found on the slopes of mountains. The alpine climate in these regions strongly affects the ecosystem because temperatures lapse rate, fall as elevation increases, causing the ecosystem to stratify. This stratification is a crucial factor in shaping plant community, biodiversity, metabolic processes and ecosystem dynamics for montane ecosystems. Dense montane forests are common at moderate elevations, due to moderate temperatures and high rainfall. At higher elevations, the climate is harsher, with lower temperatures and higher winds, preventing the growth of trees and causing the plant community to transition to montane grasslands and shrublands or alpine tundra. Due to the unique climate conditions of montane ecosystems, they contain increased numbers of endemic species. Montane ecosystems also exhibit variation in ecosystem services, which include carbon storage and water supply. Life zones As elevation increases, the alpine climate, climate becomes co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Forest
An old-growth forest or primary forest is a forest that has developed over a long period of time without Disturbance (ecology), disturbance. Due to this, old-growth forests exhibit unique ecological features. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations defines primary forests as naturally regenerated forests of native tree species where there are no clearly visible indications of human activity and the ecological processes are not significantly disturbed. One-third (34 percent) of the world's forests are primary forests. Old-growth features include diverse tree-related structures that provide diverse wildlife habitats that increases the biodiversity of the forested ecosystem. Virgin or first-growth forests are old-growth forests that have never been logged. The concept of diverse tree structure includes multi-layered canopies and Canopy (biology), canopy gaps, greatly varying tree heights and diameters, and diverse tree species and classes and sizes of woody debr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veraguas Province
Veraguas () is a province of Panama, located in the centre-west of the country. The capital is the city of Santiago de Veraguas. It is the only Panamanian province to border both the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. It covers an area of 10,587.6 km² and in 2023 it had a population of 259,791. History Veraguas was originally inhabited by the Veraguas culture. Veraguas was explored by Christopher Columbus on his fourth voyage. He tried to establish the first colony in the new Spanish mainland but failed due to resistance from Indigenous peoples. Diego de Nicuesa also tried to establish a colony and failed, which made him create a colony to fight against the Indigenous population, which he named Nombre de Dios. Its capital, Santiago de Veraguas, was founded about 1636. A province called Veraguas containing Santiago de Veraguas, but with changing boundaries over time, existed in Gran Colombia, the Republic of New Granada, and at times during the Panama State era. It is sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dota (canton)
Dota is a canton in the San José province of Costa Rica. The head city of the canton is Santa María. It is part of Los Santos Zone, together with Tarrazú and León Cortés Castro. History Dota was created on 23 July 1925 by decree 80. Government Mayor According to Costa Rica's Municipal Code, mayors are elected every four years by the population of the canton. As of the latest municipal elections in 2024, the Social Christian Unity Party (PUSC) candidate, Adrián Cordero Cordero, was elected mayor of the canton with 79.33% of the votes, with Susy Calderón Arguedas and Jorge Orlando Serrano Salazar as first and second vice mayors, respectively. Municipal Council Like the mayor and vice mayors, members of the Municipal Council (called ) are elected every four years. Dota's Municipal Council has 5 seats for regidores and their substitutes, who can participate in meetings but not vote unless the owning regidor () is absent. The Municipal Council's composition fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cordillera De Talamanca
The Cordillera de Talamanca is a mountain range that lies in the southeast half of Costa Rica and the far west of Panama. Much of the range and the area around it is included in La Amistad International Park, which also is shared between the two countries. This range in the south of Costa Rica stretches from southwest of San José to beyond the border with Panama and contains the highest peaks of both Costa Rica and Panama, among them Cerro Chirripó at , and the more accessible high peak of Cerro de la Muerte. Much of the Caribbean areas of the range are still unexplored. Exploration and classification The range is covered by the Talamancan montane forests to elevations of approximately . Much of it is covered by rainforests. Above elevations of these are dominated by huge oak trees ('' Quercus costaricensis''). Above , the forests transition to enclaves of sub-páramo, a sort of shrub and dwarf bamboo '' Chusquea'' dominated scrub, above this becomes Costa Rican páramo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primaries (birds)
Flight feathers (''Pennae volatus'') are the long, stiff, asymmetrically shaped, but symmetrically paired pennaceous feathers on the wings or tail of a bird; those on the wings are called remiges (), singular remex (), while those on the tail are called rectrices ( or ), singular rectrix (). The primary function of the flight feathers is to aid in the generation of both thrust and lift, thereby enabling flight. The flight feathers of some birds perform additional functions, generally associated with territorial displays, courtship rituals or feeding methods. In some species, these feathers have developed into long showy plumes used in visual courtship displays, while in others they create a sound during display flights. Tiny serrations on the leading edge of their remiges help owls to fly silently (and therefore hunt more successfully), while the extra-stiff rectrices of woodpeckers help them to brace against tree trunks as they hammer on them. Even flightless birds still reta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |