|
Sulfolipid
Sulfolipids are a class of lipids which possess a sulfur-containing functional group. An abundant sulfolipid is sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerol, which is composed of a glycoside of sulfoquinovose and diacylglycerol. In plants, sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerides (SQDG) are important members of the sulfur cycle. Other important sulfolipids include sulfatide and seminolipid, each of which are sulfated glycolipids. Sulfolipids have been implicated in the functions of two of the core components of the photosynthetic electron transport chain and while not necessarily essential, might have a protective function when the photosynthetic apparatus is under stress. See also * Sulfatide * Galactolipid *Phospholipid Phospholipids are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Marine phospholipids typ ... * Glycolipid Referenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SQDG Chemical Structure
Sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerols, abbreviated SQDG, are a class of sulfur-containing phosphorus-free lipids (sulfolipids) found in many photosynthetic organisms. Discovery and properties In 1959 A. A. Benson and coworkers discovered a new sulfur-containing lipid in plants and identified it as sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerol (SQDG). The sulfolipid structure was defined as 1,2-di-''O''-acyl-3-O-(6-deoxy-6-sulfo-α-D-glucopyranosyl)-''sn''-glycerol (SQDG). The distinctive feature of this substance is carbon bonded directly to sulfur as C-SO3. Sulfonic acids of this type are chemically stable and strong acids. Biological occurrence and functions SQDGs have been found in all photosynthetic plants, algae, cyanobacteria, purple sulfur and non-sulfur bacteria and is localised in the thylakoid membranes, being the most saturated glycolipid. SQDGs have been found to be closely associated with certain membrane proteins. In some cases the (electrostatic) interactions may be very strong, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
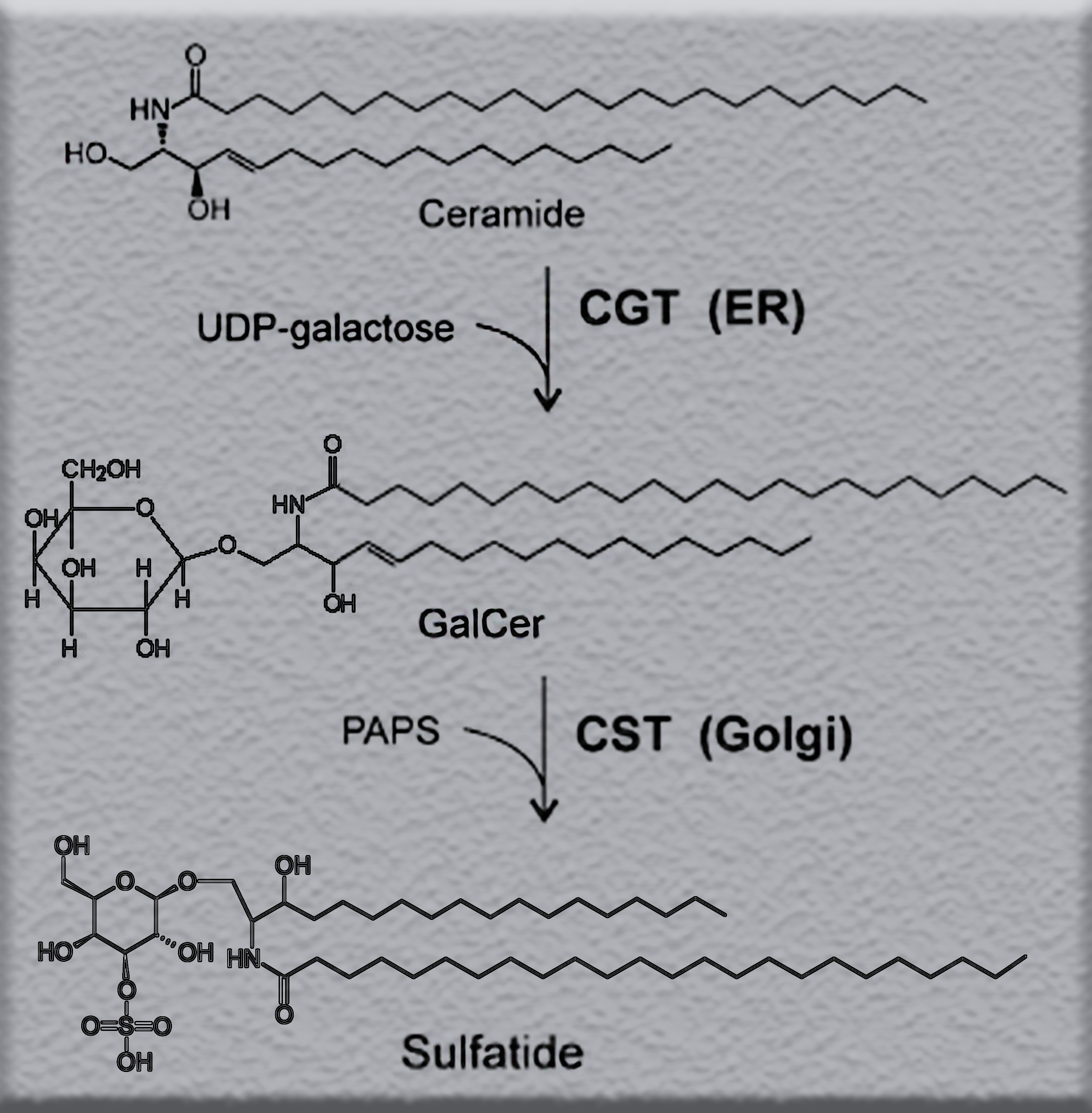
Sulfatide
Sulfatide, also known as 3-O-sulfogalactosylceramide, SM4, or sulfated galactocerebroside, is a class of sulfolipids, specifically a class of sulfoglycolipids, which are glycolipids that contain a sulfate group. Sulfatide is synthesized primarily starting in the endoplasmic reticulum and ending in the Golgi apparatus where ceramide is converted to galactocerebroside and later sulfated to make sulfatide. Of all of the galactolipids that are found in the myelin sheath, one fifth of them are sulfatide. Sulfatide is primarily found on the extracellular leaflet of the myelin plasma membrane produced by the oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system and in the Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system. However, sulfatide is also present on the extracellular leaflet of the plasma membrane of many cells in eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms. Since sulfatide is a multifunctional molecule, it can be used in multiple biological areas. Aside from being a membrane component, sulfatide func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfoquinovose
Sulfoquinovose, also known as 6-sulfoquinovose and 6-deoxy-6-sulfo-D-glucopyranose, is a monosaccharide sugar that is found as a building block in the sulfolipid sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerol (SQDG). Sulfoquinovose is a sulfonic acid derivative of glucose, the sulfonic acid group is introduced into the sugar by the enzyme An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ... UDP-sulfoquinovose synthase (SQD1). Sulfoquinovose is degraded through a metabolic process termed sulfoglycolysis. The half-life for mutarotation of sulfoquinovose at pD 7.5 and 26C is 299 minutes. See also * Sulfolipid * Sulfoglycolysis References {{Reflist Sulfonic acids Deoxy sugars Monosaccharides Sulfate esters Pyranoses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfatide
Sulfatide, also known as 3-O-sulfogalactosylceramide, SM4, or sulfated galactocerebroside, is a class of sulfolipids, specifically a class of sulfoglycolipids, which are glycolipids that contain a sulfate group. Sulfatide is synthesized primarily starting in the endoplasmic reticulum and ending in the Golgi apparatus where ceramide is converted to galactocerebroside and later sulfated to make sulfatide. Of all of the galactolipids that are found in the myelin sheath, one fifth of them are sulfatide. Sulfatide is primarily found on the extracellular leaflet of the myelin plasma membrane produced by the oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system and in the Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system. However, sulfatide is also present on the extracellular leaflet of the plasma membrane of many cells in eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms. Since sulfatide is a multifunctional molecule, it can be used in multiple biological areas. Aside from being a membrane component, sulfatide func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfate Esters
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many are prepared from that acid. Spelling "Sulfate" is the spelling recommended by IUPAC, but "sulphate" was traditionally used in British English. Structure The sulfate anion consists of a central sulfur atom surrounded by four equivalent oxygen atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement. The symmetry of the isolated anion is the same as that of methane. The sulfur atom is in the +6 oxidation state while the four oxygen atoms are each in the −2 state. The sulfate ion carries an overall charge of −2 and it is the conjugate base of the bisulfate (or hydrogensulfate) ion, , which is in turn the conjugate base of , sulfuric acid. Organic sulfate esters, such as dimethyl sulfate, are covalent compounds and esters of sulfuric acid. The tetrahedral mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipids
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins Vitamin A, A, Vitamin D, D, Vitamin E, E and Vitamin K, K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing energy, lipid signaling, signaling, and acting as structural components of cell membranes. Lipids have applications in the Cosmetic industry, cosmetic and Food industry, food industries, and in nanotechnology. Lipids are broadly defined as Hydrophobe, hydrophobic or Amphiphile, amphiphilic small molecules; the amphiphilic nature of some lipids allows them to form structures such as vesicle (biology), vesicles, multilamellar/unilamellar liposomes, or membranes in an aqueous environment. Biological lipids originate entirely or in part from two distinct types of biochemical subunits or "building-blocks": :wikt:ketoacyl, ketoacyl and isoprene groups. Using this approach, lipids may be divided into eight catego ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycolipid
Glycolipids () are lipids with a carbohydrate attached by a glycosidic (covalent) bond. Their role is to maintain the stability of the cell membrane and to facilitate cellular recognition, which is crucial to the immune response and in the connections that allow cells to connect to one another to form tissues. Glycolipids are found on the surface of all eukaryotic cell membranes, where they extend from the phospholipid bilayer into the extracellular environment. Structure The essential feature of a glycolipid is the presence of a monosaccharide or oligosaccharide bound to a lipid moiety. The most common lipids in cellular membranes are glycerolipids and sphingolipids, which have glycerol or a sphingosine backbones, respectively. Fatty acids are connected to this backbone, so that the lipid as a whole has a polar head and a non-polar tail. The lipid bilayer of the cell membrane consists of two layers of lipids, with the inner and outer surfaces of the membrane made up o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phospholipid
Phospholipids are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Marine phospholipids typically have omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA integrated as part of the phospholipid molecule. The phosphate group can be modified with simple organic molecules such as choline, ethanolamine or serine. Phospholipids are a key component of all cell membranes. They can form lipid bilayers because of their amphiphilic characteristic. In eukaryotes, cell membranes also contain another class of lipid, sterol, interspersed among the phospholipids. The combination provides fluidity in two dimensions combined with mechanical strength against rupture. Purified phospholipids are produced commercially and have found applications in nanotechnology and materials science. The first phospholipid identified in 1847 as such in biological tissues w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactolipid
Galactolipids are a type of glycolipid whose sugar group is galactose. They differ from glycosphingolipids in that they do not have nitrogen in their composition. They are the main part of plant membrane lipids where they substitute phospholipids to conserve phosphate for other essential processes. These chloroplast membranes contain a high quantity of monogalactosyldiacylglycerol (MGDG) and digalactosyldiacylglycerol (DGDG). They probably also assume a direct role in photosynthesis, as they have been found in the X-ray crystallography, X-ray structures of photosynthetic complexes. Galactolipids are more bioavailable than free fatty acids, and have been shown to exhibit COX mediated anti-inflammatory activity. Bio-guided fractionation of spinach leaves (''Spinacia oleracea'') revealed alpha-linolenic acid galactolipids (18:3, n-3) were responsible for inhibitory effects on tumor promoter-induced Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) activation. Recently, it has been demonstrated that this same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosynthetic Electron Transport Chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules which transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H+ ions) across a membrane. Many of the enzymes in the electron transport chain are embedded within the membrane. The flow of electrons through the electron transport chain is an exergonic process. The energy from the redox reactions creates an electrochemical proton gradient that drives the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In aerobic respiration, the flow of electrons terminates with molecular oxygen as the final electron acceptor. In anaerobic respiration, other electron acceptors are used, such as sulfate. In an electron transport chain, the redox reactions are driven by the difference in the Gibbs free energy of reactants and products. The free energy released when a higher-en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |