|
Sulfine
Sulfinylmethane or sulfine is an organic compound with molecular formula H2CSO. It is the simplest sulfine. Sulfines are chemical compounds with the general structure XY=SO. IUPAC considers the term 'sulfine' obsolete, preferring instead thiocarbonyl ''S''-oxide; despite this, the use of the term sulfine still predominates in the chemical literature. Substituted sulfines The parent sulfine H2CSO is very labile, whereas substituted derivatives are more conveniently isolated. One route is a variant of ketene synthesis, in which a sulfinyl halide reacts with a hindered base. For example, syn-propanethial-S-oxide, responsible for eye-watering effects of cutting onions, is produced so from allicin. Another route is oxidation, as with thiobenzophenone from diphenylsulfine: :(C6H5)2C=S + → (C6H5)2C=S=O See also * Sulfene - related functional group with the formula H2C=SO2 *Ethenone Ethenone is the formal name for ketene, an organic compound with formula or . It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organosulfur Compounds
Organosulfur chemistry is the study of the properties and synthesis of organosulfur compounds, which are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature is abound with organosulfur compounds—sulfur is vital for life. Of the 20 common amino acids, two (cysteine and methionine) are organosulfur compounds, and the antibiotics penicillin and sulfa drugs both contain sulfur. While sulfur-containing antibiotics save many lives, sulfur mustard is a deadly chemical warfare agent. Fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are derived from ancient organisms, necessarily contain organosulfur compounds, Desulfurization, the removal of which is a Claus process, major focus of oil refineries. Sulfur shares the chalcogen group with oxygen, selenium, and tellurium, and it is expected that organosulfur compounds have similarities with carbon–oxygen, carbon� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syn-propanethial-S-oxide
''syn''-Propanethial ''S''-oxide (or (''Z'')-propanethial ''S''-oxide), a member of a class of organosulfur compounds known as thiocarbonyl S-oxide, ''S''-oxides (formerly "sulfines"), is a volatile liquid that acts as a lachrymatory agent (triggers tearing and stinging on contact with the eyes). Onion release The chemical is released from onions, ''Allium cepa'', as they are sliced. The release is due to the breaking open of the onion cells, which releases enzymes called alliinases. Alliinases then break down amino acid sulfoxides, generating sulfenic acids. A specific sulfenic acid, allicin or 1-propenesulfenic acid, is rapidly rearranged by another enzyme, the lachrymatory factor synthase (LFS) to give ''syn''-propanethial ''S''-oxide. Vapors from this volatile liquid induces tearing. Related compounds A structurally related lachrymatory compound, ''syn''-butanethial ''S''-oxide, C4H8OS, has been found in another genus ''Allium'' plant, ''Allium siculum''. Propanethial S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfene
Sulfene is an extremely reactive chemical compound with the formula H2C=SO2. It is the simplest member of the sulfenes, the group of compounds which are ''S'',''S''-dioxides of thioaldehydes and thioketones, and have the general formula R2C=SO2. Preparation The first general method for preparation of sulfene as an intermediate, reported simultaneously in 1962 by Gilbert Stork and by Günther Optiz, involved the removal of hydrogen chloride from methanesulfonyl chloride using triethylamine in the presence of an enamine as trapping agent. The formation of a thietane 1,1-dioxide derivative was taken as evidence for the intermediacy of sulfene. Because of the highly electrophilic character of sulfene, the use of amines presents difficulties, since they can intercept the sulfene to form adducts. A simple alternative which avoids the use of amines involves desilylation of trimethylsilylmethanesulfonyl chloride with cesium fluoride in the presence of trapping agents. : (CH3)3SiCH2SO2C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes (e.g. methane ) and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen (e.g. cyanide ion , hydrogen cyanide , chloroformic acid , carbon dioxide , and carbonate ion ). Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, and even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Formula
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and ''plus'' (+) and ''minus'' (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name since it does not contain any words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae. The simplest types of chemical formulae are called '' empirical formulae'', which use letters and numbers indicating the numerical ''proportions'' of atoms of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IUPAC
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC). IUPAC is registered in Zürich, Switzerland, and the administrative office, known as the "IUPAC Secretariat", is in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, United States. IUPAC's executive director heads this administrative office, currently Greta Heydenrych. IUPAC was established in 1919 as the successor of the International Congress of Applied Chemistry for the advancement of chemistry. Its members, the National Adhering Organizations, can be national List of chemistry societies, chemistry societies, national Academy of Sciences, academies of sciences, or other bodies representing chemists. There are fifty-four National Adhering Organizations and three Associate National Adhering Organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
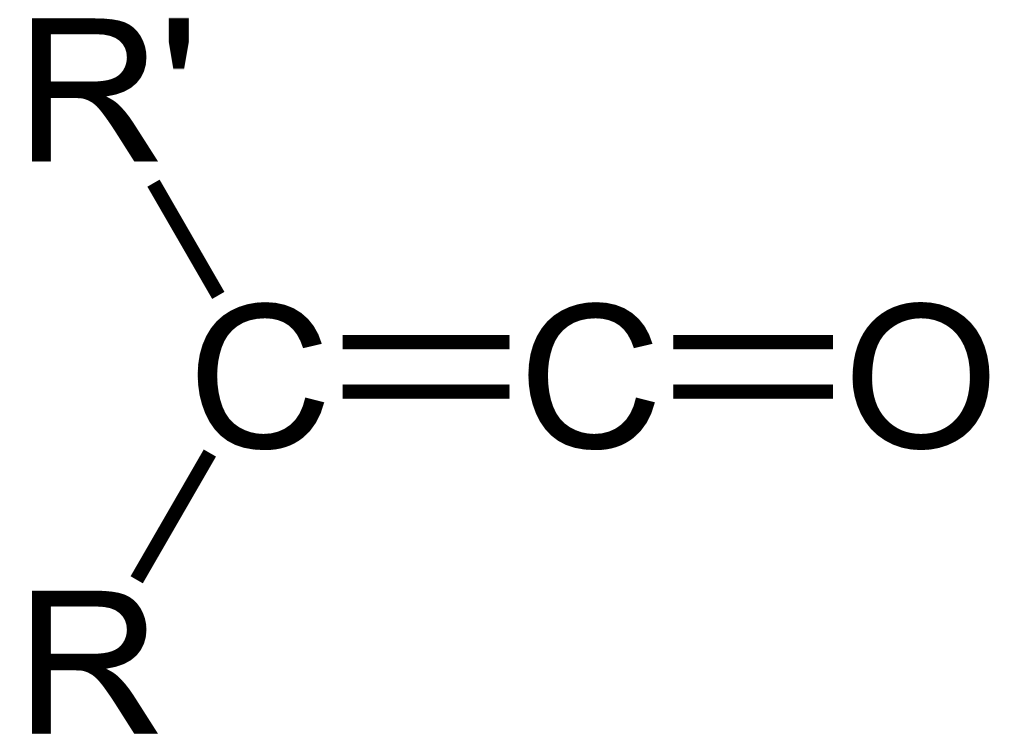
Ketene
In organic chemistry, a ketene is an organic compound of the form , where R and R' are two arbitrary valence (chemistry), monovalent functional group, chemical groups (or two separate Substituent, substitution sites in the same molecule). The name may also refer to the specific compound ethenone , the simplest ketene. Although they are highly useful, most ketenes are chemical stability, unstable. When used as reagents in a chemical procedure, they are typically generated when needed, and consumed as soon as (or while) they are produced. History Ketenes were first studied as a class by Hermann Staudinger before 1905. Ketenes were systematically investigated by Hermann Staudinger in 1905 in the form of diphenylketene (conversion of \alpha-chlorodiphenyl acetyl chloride with zinc). Staudinger was inspired by the first examples of reactive organic intermediates and stable radicals discovered by Moses Gomberg in 1900 (compounds with triphenylmethyl group). Properties Ketenes are h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfinyl Halide
Sulfinyl halide have the general formula R−S(O)−X, where X is a halogen. They are intermediate in oxidation level between sulfenyl halides, R−S−X, and sulfonyl halides, R−SO2−X. The best known examples are sulfinyl chlorides, thermolabile, moisture-sensitive compounds, which are useful intermediates for preparation of other sufinyl derivatives such as sulfinamides, sulfinates, sulfoxides, and thiosulfinates. Unlike the sulfur atom in sulfonyl halides and sulfenyl halides, the sulfur atom in sulfinyl halides is chiral, as shown for methanesulfinyl chloride. Sulfinyl chlorides Sulfinic acid chlorides, or sulfinyl chlorides, are sulfinyl halides with the general formula R−S(O)−Cl. Methanesulfinyl chloride, CH3S(O)Cl, is prepared by chlorination of dimethyl disulfide to give CH3SCl3, which is treated with acetic anhydride. It is a straw-colored liquid. Toluenesulfinyl chloride is prepared by treating sodium tosylate with thionyl chloride: Also a straw-colored liqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindered Base
As the name suggests, a non-nucleophilic base is a sterically hindered organic base that is a poor nucleophile. Normal bases are also nucleophiles, but often chemists seek the proton-removing ability of a base without any other functions. Typical non-nucleophilic bases are bulky, such that protons can attach to the basic center but alkylation and complexation is inhibited. Non-nucleophilic bases A variety of amines and nitrogen heterocycles are useful bases of moderate strength (pKa of conjugate acid around 10-13) * ''N'',''N''-Diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA, also called Hünig's Base), pKa = 10.75 *1,8-Diazabicycloundec-7-ene (DBU) - useful for E2 elimination reactions, pKa = 13.5 * 1,5-Diazabicyclo(4.3.0)non-5-ene (DBN) - comparable to DBU * 2,6-Di-tert-butylpyridine, a weak non-nucleophilic base pKa = 3.58 * Phosphazene bases, such as ''t''-Bu-P4''Activation in anionic polymerization: Why phosphazene bases are very exciting promoters'' S. Boileau, N. Illy Prog. Polym. Sci., 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allicin
Allicin is an organosulfur compound obtained from garlic and leeks. When fresh garlic is chopped or crushed, the enzyme alliinase converts alliin into allicin, which is responsible for the aroma of fresh garlic. Allicin is unstable and quickly changes into a series of other sulfur-containing compounds such as diallyl disulfide. Allicin is an antifeedant, i.e. the defense mechanism against attacks by pests on the garlic plant. Allicin is an oily, slightly yellow liquid that gives garlic its distinctive odor. It is a thioester of sulfenic acid. It is also known as allyl thiosulfinate. Its biological activity can be attributed to both its antioxidant activity and its reaction with thiol-containing proteins. Structure and occurrence Allicin features the thiosulfinate functional group, R-S-(O)-S-R. The compound is not present in garlic unless tissue damage occurs, and is formed by the action of the enzyme alliinase on alliin. Allicin is chiral but occurs naturally only as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiobenzophenone
Thiobenzophenone is an organosulfur compound with the formula (C6H5)2CS. It is the prototypical thioketone. Unlike other thioketones that tend to dimerize to form rings and polymers, thiobenzophenone is quite stable, although it photoxidizes in air back to benzophenone and sulfur. Thiobenzophenone is deep blue and dissolves readily in many organic solvents. Structure The C=S bond length of thiobenzophenone is 1.63 Å, which is comparable to 1.64 Å, the C=S bond length of thioformaldehyde, measured in the gas phase. Due to steric interactions, the phenyl groups are not coplanar and the dihedral angle SC-CC is 36°.Sustmann, R.; Sicking, W.; Huisgen, R. "A Computational Study of the Cycloaddition of Thiobenzophenone S-Methylide to Thiobenzophenone". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 14425-14434. A variety of thiones with structures and stability related to thiobenzophenone have also been prepared. Synthesis One of the first reported syntheses of thiobenzophenone involves the reaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |