|
Sudden Unexpected Death Syndrome
Sudden arrhythmic death syndrome (SADS) is a sudden unexpected death of adolescents and adults caused by a cardiac arrest. However, the exact cause of the cardiac arrest, and thus the exact cause of death, is unknown. These deaths occur mainly during sleep or at rest. One type of conduction defect known as Brugada syndrome can be responsible. The syndrome is rare in most areas around the world but occurs in populations that are culturally and genetically distinct. It was first noted in 1977 among southeast Asian Hmong refugees in the United States and Canada. The syndrome was again noted in Singapore when a retrospective review of records showed that 230 otherwise healthy Thai foreign workers living in Singapore died suddenly of unexplained causes between 1982 and 1990. Causes Sudden death of a young person can be caused by heart disease (including cardiomyopathy, congenital heart disease, myocarditis, genetic connective tissue disorders) or conduction disease ( WPW syndro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
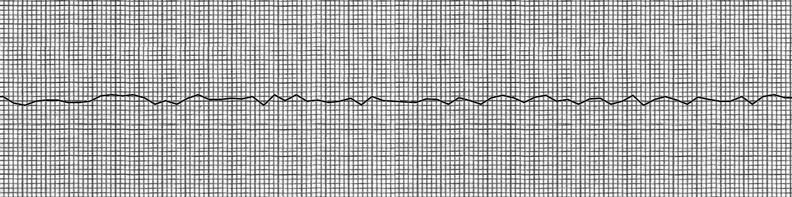
Ventricular Fibrillation
Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib or VF) is an abnormal heart rhythm in which the Ventricle (heart), ventricles of the heart Fibrillation, quiver. It is due to disorganized electrical conduction system of the heart, electrical activity. Ventricular fibrillation results in cardiac arrest with loss of consciousness and no pulse. This is followed by sudden cardiac death in the absence of treatment. Ventricular fibrillation is initially found in about 10% of people with cardiac arrest. Ventricular fibrillation can occur due to coronary heart disease, valvular heart disease, cardiomyopathy, Brugada syndrome, long QT syndrome, electric shock, or intracranial hemorrhage. Diagnosis is by an electrocardiogram (ECG) showing irregular unformed QRS complexes without any clear P wave (electrocardiography), P waves. An important differential diagnosis is torsades de pointes. Treatment is with cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and defibrillation. Defibrillation#Change to a biphasic waveform, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolff–Parkinson–White Syndrome
Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome (WPWS) is a disorder due to a specific type of problem with the electrical system of the heart involving an accessory pathway able to conduct electrical current between the atria and the ventricles, thus bypassing the atrioventricular node. About 60% of people with the electrical problem develop symptoms, which may include an abnormally fast heartbeat, palpitations, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, or syncope. Rarely, cardiac arrest may occur. The most common type of arrhythmia (abnormal heart rate) associated with WPWS is paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. The cause of WPW is typically unknown and is likely due to a combination of chance and genetic factors. A small number of cases are due to a mutation of the PRKAG2 gene which may be inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion. The underlying mechanism involves an accessory electrical conduction pathway between the atria and the ventricles. It is associated with other cond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCN5A
Sodium channel protein type 5 subunit alpha, also known as NaV1.5 is an integral membrane protein and tetrodotoxin-resistant voltage-gated sodium channel subunit. NaV1.5 is found primarily in cardiac muscle, where it mediates the fast influx of Na+-ions (INa) across the cell membrane, resulting in the fast depolarization phase of the cardiac action potential. As such, it plays a major role in impulse propagation through the heart. A vast number of cardiac diseases is associated with mutations in NaV1.5 (see paragraph genetics). ''SCN5A'' is the gene that encodes the cardiac sodium channel NaV1.5. Gene structure SCN5A is a highly conserved gene located on human chromosome 3, where it spans more than 100 kb. The gene consists of 28 exons, of which exon 1 and in part exon 2 form the 5' untranslated region ( 5’UTR) and exon 28 the 3' untranslated region ( 3’UTR) of the RNA. SCN5A is part of a family of 10 genes that encode different types of sodium channels, i.e. brain-type ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syncope (medicine)
Syncope , commonly known as fainting or passing out, is a loss of consciousness and muscle strength characterized by a fast onset, short duration, and spontaneous recovery. It is caused by a decrease in blood flow to the brain, typically from low blood pressure. There are sometimes symptoms before the loss of consciousness such as lightheadedness, sweating, pale skin, blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, or feeling warm. Syncope may also be associated with a short episode of muscle twitching. Psychiatric causes can also be determined when a patient experiences fear, anxiety, or panic; particularly before a stressful event, usually medical in nature. When consciousness and muscle strength are not completely lost, it is called presyncope. It is recommended that presyncope be treated the same as syncope. Causes range from non-serious to potentially fatal. There are three broad categories of causes: heart or blood vessel related; reflex, also known as neurally mediated; and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyspnea
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that consists of qualitatively distinct sensations that vary in intensity", and recommends evaluating dyspnea by assessing the intensity of its distinct sensations, the degree of distress and discomfort involved, and its burden or impact on the patient's activities of daily living. Distinct sensations include effort/work to breathe, chest tightness or pain, and "air hunger" (the feeling of not enough oxygen). The tripod position is often assumed to be a sign. Dyspnea is a normal symptom of heavy physical exertion but becomes pathological if it occurs in unexpected situations, when resting or during light exertion. In 85% of cases it is due to asthma, pneumonia, reflux/LPR, cardiac ischemia, COVID-19, interstitial lung disease, congestive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
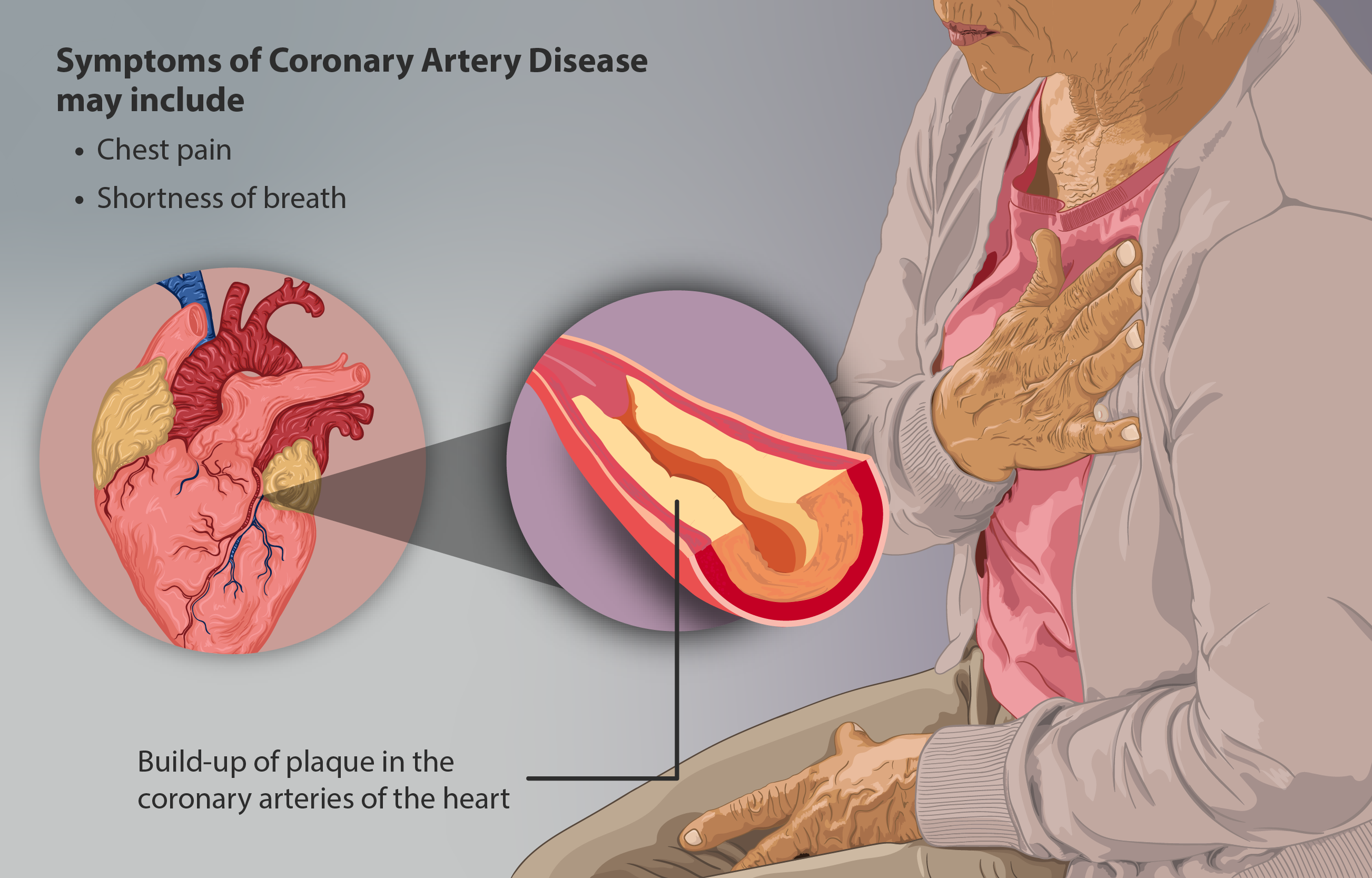
Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), or ischemic heart disease (IHD), is a type of cardiovascular disease, heart disease involving Ischemia, the reduction of blood flow to the cardiac muscle due to a build-up of atheromatous plaque in the Coronary arteries, arteries of the heart. It is the most common of the cardiovascular diseases. CAD can cause stable angina, unstable angina, myocardial ischemia, and myocardial infarction. A common symptom is angina, which is chest pain or discomfort that may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Occasionally it may feel like heartburn. In stable angina, symptoms occur with exercise or emotional Psychological stress, stress, last less than a few minutes, and improve with rest. Shortness of breath may also occur and sometimes no symptoms are present. In many cases, the first sign is a Myocardial infarction, heart attack. Other complications include heart failure or an Heart arrhythmia, abnormal h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM, or HOCM when obstructive) is a condition in which muscle tissues of the heart become thickened without an obvious cause. The parts of the heart most commonly affected are the interventricular septum and the ventricles. This results in the heart being less able to pump blood effectively and also may cause electrical conduction problems. Specifically, within the bundle branches that conduct impulses through the interventricular septum and into the Purkinje fibers, as these are responsible for the depolarization of contractile cells of both ventricles. People who have HCM may have a range of symptoms. People may be asymptomatic, or may have fatigue, leg swelling, and shortness of breath. It may also result in chest pain or fainting. Symptoms may be worse when the person is dehydrated. Complications may include heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, and sudden cardiac death. HCM is most commonly inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, are irregularities in the cardiac cycle, heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. Essentially, this is anything but normal sinus rhythm. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults – is called tachycardia, and a resting heart rate that is too slow – below 60 beats per minute – is called bradycardia. Some types of arrhythmias have no symptoms. Symptoms, when present, may include palpitations or feeling a pause between heartbeats. In more serious cases, there may be presyncope, lightheadedness, Syncope (medicine), passing out, shortness of breath, chest pain, or decreased level of consciousness. While most cases of arrhythmia are not serious, some predispose a person to complications such as stroke or heart failure. Others may result in cardiac arrest, sudden death. Arrhythmias are often categorized into four groups: premature heart beat, extra beats, supraventricular tachycard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia (American English), also spelled hypoglycaemia or hypoglycæmia (British English), sometimes called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes. It is defined as blood glucose below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L), symptoms associated with hypoglycemia, and resolution of symptoms when blood sugar returns to normal. Hypoglycemia may result in headache, tiredness, clumsiness, trouble talking, confusion, fast heart rate, sweating, shakiness, nervousness, hunger, loss of consciousness, seizures, or death. Symptoms typically come on quickly. Symptoms can remain even soon after raised blood level. The most common cause of hypoglycemia is diabetes medication, medications used to treat diabetes such as insulin (medication), insulin, sulfonylureas, and biguanides. Risk is greater in diabetics who have eaten less than usual, recently exe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short QT Syndrome
Short QT syndrome (SQT) is a very rare genetics, genetic disease of the electrical system of the heart, and is associated with an increased risk of Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythms and sudden cardiac death. The syndrome gets its name from a characteristic feature seen on an Electrocardiography, electrocardiogram (ECG) – a shortening of the QT interval. It is caused by mutations in genes encoding ion channels that shorten the cardiac action potential, and appears to be inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. The condition is diagnosed using a Electrocardiography, 12-lead ECG. Short QT syndrome can be treated using an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator or medications including quinidine. Short QT syndrome was first described in 2000, and the first genetic mutation associated with the condition was identified in 2004. Signs and symptoms Those affected by short QT syndrome (SQT) have an increased risk of developing Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythms. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benign Early Repolarization
Benign early repolarization (BER) or early repolarization is found on an electrocardiogram (ECG) in about 1% of those with chest pain. It is diagnosed based on an elevated J-point / ST elevation with an end-QRS notch or end-QRS slur and where the ST segment concave up. It is believed to be a normal variant. Benign early repolarization that occurs as some patterns is associated with ventricular fibrillation. The association, revealed by research performed in the late 2000s, is very small. Types Benign early repolarization, very prevalent in younger people and healthy male athletes, can be divided into 3 subtypes: * Type 1 – BER pattern seen in lateral precordial leads. * Type 2 – BER pattern seen in inferior or inferolateral leads. * Type 3 – BER pattern seen globally (inferior, lateral, right precordial leads). Associations with serious conditions Research in the late 2000s has linked this finding to ventricular fibrillation, particularly in those who have fainted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progressive Cardiac Conduction Defect
Progressive cardiac conduction defect (PCCD) is a hereditary cardiac condition marked by a progressive delay in impulse conduction via the His-Purkinje system, resulting in right or left bundle branch block (RBBB or LBBB), syncope, and occasionally sudden cardiac death. Cause Diagnosis When progressive conduction abnormalities in people under 50 with structurally normal hearts are present but skeletal myopathies are absent, progressive cardiac conduction defect is primarily diagnosed, particularly if there is a family history of PCCD. Treatment At the moment, implanting an implantable pacemaker A pacemaker, also known as an artificial cardiac pacemaker, is an implanted medical device that generates electrical pulses delivered by electrodes to one or more of the chambers of the heart. Each pulse causes the targeted chamber(s) to co ... is the only proven treatment for PCCD, regardless of the underlying cause. References Further reading * External links {{M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |