|
Suctoria
Suctoria are ciliates that become sessility (zoology), sessile in their developed stage and then lose their redundant cilia. They feed by extracellular digestion. They were originally thought to feed by suction – hence their name. In fact, they use specialized microtubules to ensnare and manipulate their prey. They live in both freshwater and marine environments, including some that live on the surface of aquatic animals, and typically feed on other ciliates. Instead of a single cytostome, each cell feeds by means of several specialized tentacles. These are supported by microtubules and phyllae, and have toxic extrusomes called haptocysts at the tip, which they attach to prey. They then suck the prey's cytoplasm directly into a food vacuole inside the cell, where they digest and absorb its contents. Most suctoria are around 15-30 μm in size, with a non-contractile stalk and often a Lorica (biology), lorica or shell. Suctoria reproduce primarily by budding, producing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phyllopharyngea
The Phyllopharyngea are a class of ciliates, some of which are extremely specialized. Motile cells typically have cilia restricted to the ventral surface, or some part thereof, arising from monokinetids with a characteristic ultrastructure. In both chonotrichs and suctoria, however, only newly formed cells are motile and the sessile adults have undergone considerable modifications of form and appearance. Chonotrichs, found mainly on crustaceans, are vase-shaped, with cilia restricted to a funnel leading down into the mouth. Mature suctorians lack cilia altogether, and initially were not classified as ciliates. The mouths of Phyllopharyngea are characteristically surrounded by microtubular ribbons, called ''phyllae''. Nematodesmata, rods found in several other classes of ciliates, occur among the subclass Phyllopharyngia, most of which are free-living. In others, the mouth is often modified to form an extensible tentacle, with toxic extrusomes at the tip. These are espec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
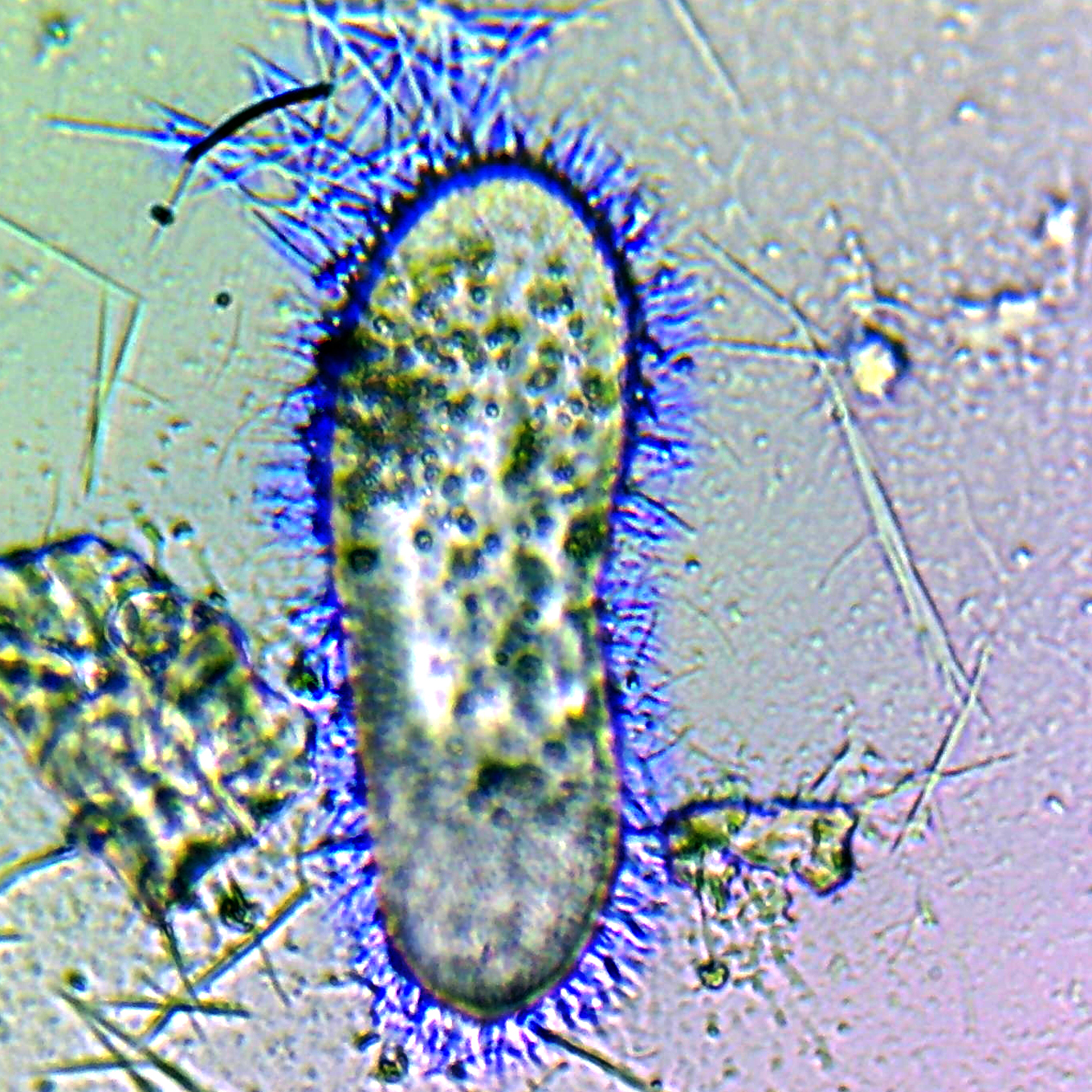
Ciliate
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to flagellum, eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different wikt:undulating, undulating pattern than flagella. Cilia occur in all members of the group (although the peculiar Suctoria only have them for part of their biological life cycle, life cycle) and are variously used in swimming, crawling, attachment, feeding, and sensation. Ciliates are an important group of protists, common almost anywhere there is water—in lakes, ponds, oceans, rivers, and soils, including anoxic and oxygen-depleted habitats. About 4,500 unique free-living species have been described, and the potential number of extant species is estimated at 27,000–40,000. Included in this number are many Ectosymbiosis, ectosymbiotic and endosymbiotic species, as well as some Obligate parasite, obligate and Facultative paras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
René-Édouard Claparède
René-Édouard Claparède (; 24 April 1832, Chancy – 31 May 1871, Siena) was a Swiss anatomist. The Claparède family was Protestant and originally from Languedoc. They moved to Geneva after Louis XIV's Edict of Fontainebleau in 1685. He received his education in Geneva and University of Berlin, Berlin, where he attended lectures given by Johannes Peter Müller. Later on, he served as an assistant to François Jules Pictet de la Rive at the University of Geneva, Geneva Academy, where in 1862 he became a professor of comparative anatomy. He was a regular contributor to th''Archives des sciences physiques et naturelles''Claparède, René-Edouard Historischen Lexikon der Schweiz His main research dealt with the structure of infusoria, the anatomy of annelids, the histology of earthworms, the embryology of arthropods and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lachmann (biologist)
Lachmann (also Lachman, Lachemann, Lackman, or Lackmann) is a family name of German origin. Notable people with the surname include: Lachmann * Clara Lachmann (1864–1920), Danish-Swedish patron of the arts * Erich Lachmann (1909–1972), Nazi SS officer at Sobibor extermination camp * Esther Lachmann, later Pauline Thérèse Lachmann, later Mme Villoing, later Mme la Marquise de Païva, later Countess Henckel von Donnersmarck, courtesan * Georges Lachmann, World War I flying ace and General officer * Gustav Lachmann, engineer * Hans Lachmann-Mosse, publisher * Karl Lachmann, classic philologist, Germanist * Ludwig Lachmann, Austrian economist * Peter Lachmann, British immunologist and nephew of Robert Lachmann * Richard Lachmann, American political scientist and international relations theorist. * Robert Lachmann, German ethnomusicologist and musicologist Lachman * Darryl Lachman (born 1989), Curaçaoan professional footballer * Dichen Lachman (born 1982), Austral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sessility (zoology)
Sessility is the biological property of an animal describing its lack of a means of self-locomotion. Sessile animals for which natural ''motility'' is absent are normally immobile. This is distinct from the botanical concept of sessility, which refers to an organism or biological structure attached directly by its base without a stalk. Sessile animals can move via external forces (such as water currents), but are usually permanently attached to something. Organisms such as corals lay down their own substrate from which they grow. Other organisms grow from a solid object, such as a rock, a dead tree trunk, or a human-made object such as a buoy or ship's hull. Mobility Sessile animals typically have a motile phase in their development. Sponges have a motile larval stage and become sessile at maturity. Conversely, many jellyfish develop as sessile polyps early in their life cycle. In the case of the cochineal, it is in the nymph stage (also called the crawler stage) that the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytostome
A cytostome (from ''cyto-'', cell and ''stome-'', mouth) or cell mouth is a part of a cell specialized for phagocytosis, usually in the form of a microtubule-supported funnel or groove. Food is directed into the cytostome, and sealed into vacuoles. Only certain groups of protozoa, such as the Ciliophora and Excavata, have cytostomes. An example is '' Balantidium coli'', a ciliate. In other protozoa, and in cells from multicellular organisms, phagocytosis takes place at any point on the cell or feeding takes place by absorption. Structure The cytostome forms an invagination on the cell surface and is typically directed towards the nucleus of the cell.Okuda, Kendi, et al. "The cytostome of Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes is associated with the flagellar complex." Experimental parasitology 92.4 (1999): 223-231. The cytostome is often labeled as the entire invagination, but in fact the cytostome only constitutes the opening of the invagination at the surface of the cell. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extrusome
Extrusomes are membrane-bound organelles found in eukaryotic cells that are capable of discharging material contained within to the exterior of the cell. Due to the diversity in structure and function, it is unlikely that different types of extrusomes are homologous. Some notable extrusomes include mucocysts, which discharge a mucous mass sometimes used in cyst formation, and trichocysts, which discharge a fibrous rod. Nematocysts, the stinging structure found in Cnidarian animals, could be considered extrusomes as well, though those functions are performed by differentiated cells rather than organelles. Other extrusomes include the ancoracyst, a specialized extrusome found in the Provoran eukaryote ''Ancoracysta twista'' used to immobilize prey. Extrusomes and their functions are currently not well understood; many of their supposed functions are in doubt. Function Ciliates Within the ciliates group, numerous extrusomes–primarily trichocysts–are distributed all ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuole
A vacuole () is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in Plant cell, plant and Fungus, fungal Cell (biology), cells and some protist, animal, and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic molecules including enzymes in Solutes, solution, though in certain cases they may contain solids which have been engulfed. Vacuoles are formed by the fusion of multiple membrane Vesicle (biology), vesicles and are effectively just larger forms of these. The organelle has no basic shape or size; its structure varies according to the requirements of the cell. Discovery Antonie van Leeuwenhoek described the plant vacuole in 1676. Contractile vacuoles ("stars") were first observed by Spallanzani (1776) in protozoa, although mistaken for respiratory organs. Félix Dujardin, Dujardin (1841) named these "stars" as ''vacuoles''. In 1842, Matthias Jakob Schleiden, Schleiden applied the term for plant cells, to dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorica (biology)
In biology, a lorica is a shell-like protective outer covering, often reinforced with sand grains and other particles that some protozoans and loriciferan animals secrete. Usually it is tubular or conical in shape, with a loose case that is closed at one end. An example is the protozoan genus '' Stentor'', in which the lorica is trumpet-shaped. In the tintinnids, the lorica is frequently transparent and is used as a domicile. '' Halofolliculina corallasia'' has a lorica that is attached as an outer structure, and into which it retracts when disturbed. Formation process There are three phases in the formation of lorica: agglomeration in a natural cast; helical extension; and stabilization. Agglomeration During agglomeration, the organism collects and assembles particles from its environment. These particles are then used to construct the initial framework of the lorica. Helical extension In the helical extension phase, the lorica is extended and shaped, often with a hel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |