|
Subwavelength-diameter Optical Fibre
A subwavelength-diameter optical fibre (SDF or SDOF) is an optical fibre whose diameter is less than the wavelength of the light being propagated through it. An SDF usually consists of long thick parts (same as conventional optical fibres) at both ends, transition regions (tapers) where the fibre diameter gradually decreases down to the subwavelength value, and a subwavelength-diameter waist, which is the main acting part. Due to such a strong geometrical confinement, the guided electromagnetic field in an SDF is restricted to a Single-mode optical fiber, single transverse spatial Mode (electromagnetism), mode called ''fundamental''. Name There is no general agreement on how these optical elements are to be named; different groups prefer to emphasize different properties of such fibres, sometimes even using different terms. The names in use include subwavelength waveguide, subwavelength optical wire, subwavelength-diameter silica wire, subwavelength diameter fibre taper, (photonic) w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stripping (fiber)
Stripping is the act of removing the protective polymer coating around optical fiber in preparation for fusion splicing. The splicing process begins by preparing both fiber ends for fusion, which requires that all protective coating is removed or stripped from the ends of each fiber. Fiber optical stripping can be done using a special stripping and preparation unit that uses hot sulfuric acid or a controlled flow of hot air to remove the coating. There are also mechanical tools used for stripping fiber which are similar to copper wire strippers. Fiber optical stripping and preparation equipment used in fusion splicing is commercially available through a small number of specialized companies, which usually also design machines used for fiber optical recoating. See also *Optical communication Optical communication, also known as optical telecommunication, is communication at a distance using light to carry information. It can be performed visually or by using electronic dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
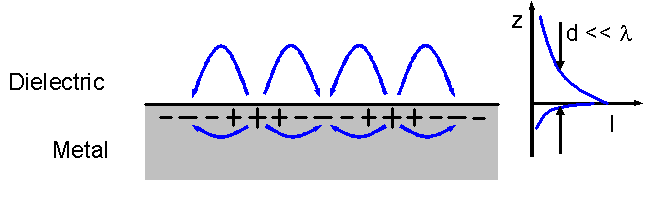
Evanescent Field
In electromagnetics, an evanescent field, or evanescent wave, is an oscillating electric and/or magnetic field that does not propagate as an electromagnetic wave but whose energy is spatially concentrated in the vicinity of the source (oscillating charges and currents). Even when there is a propagating electromagnetic wave produced (e.g., by a transmitting Antenna (radio), antenna), one can still identify as an evanescent field the component of the electric or magnetic field that cannot be attributed to the propagating wave observed at a distance of many wavelengths (such as the far field of a transmitting antenna). A hallmark of an evanescent field is that there is no net energy flow in that region. Since the net flow of electromagnetic energy is given by the average Poynting vector, this means that the Poynting vector in these regions, as averaged over a complete oscillation cycle, is zero. Use of the term In many cases one cannot simply say that a field is or is not "evane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scattering
In physics, scattering is a wide range of physical processes where moving particles or radiation of some form, such as light or sound, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by localized non-uniformities (including particles and radiation) in the medium through which they pass. In conventional use, this also includes deviation of reflected radiation from the angle predicted by the law of reflection. Reflections of radiation that undergo scattering are often called ''diffuse reflections'' and unscattered reflections are called ''specular'' (mirror-like) reflections. Originally, the term was confined to light scattering (going back at least as far as Isaac Newton in the 17th century). As more "ray"-like phenomena were discovered, the idea of scattering was extended to them, so that William Herschel could refer to the scattering of "heat rays" (not then recognized as electromagnetic in nature) in 1800. John Tyndall, a pioneer in light scattering research, noted the connecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dust
Dust is made of particle size, fine particles of solid matter. On Earth, it generally consists of particles in the atmosphere that come from various sources such as soil lifted by wind (an aeolian processes, aeolian process), Types of volcanic eruptions, volcanic eruptions, and pollution. Dust in homes is composed of about 20–50% dead skin Cell (biology), cells. The rest, and in offices and other built environments, is composed of small amounts of plant pollen, human hairs, animal fur, textile fibers, paper fibers, minerals from outdoor soil, burnt meteorite particles, and many other materials which may be found in the local environment. Atmospheric Atmospheric or wind-borne fugitive dust, also known as ''aeolian dust'', comes from dry regions where high-speed winds can remove mostly silt-sized material, abrading susceptible surfaces. This includes areas where grazing, ploughing, vehicle use, and other human behaviors have further destabilized the land, though not all so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UV Curing
UV curing (ultraviolet curing) is the process by which ultraviolet light initiates a photochemical reaction that generates a crosslinked network of polymers through radical polymerization or cationic polymerization. UV curing is adaptable to inkjet printing, printing, coating, decorating, stereolithography, and in the assembly of a variety of products and materials. UV curing is a low-temperature, high speed, and solventless process as curing occurs via polymerization. Originally introduced in the 1960s, this technology has streamlined and increased automation in many industries in the manufacturing sector. Applications UV curing is used for converting or curing Ink, inks, Adhesive, adhesives, and Coating, coatings. UV-cured adhesive has become a high speed replacement for two-part adhesives, eliminating the need for solvent removal, ratio mixing, and potential life concern. It is used in flexography, flexographic, offset printing, offset, pad printing, pad, and screen printin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epoxy
Epoxy is the family of basic components or Curing (chemistry), cured end products of epoxy Resin, resins. Epoxy resins, also known as polyepoxides, are a class of reactive prepolymers and polymers which contain epoxide groups. The epoxide functional group is also collectively called ''epoxy''. The IUPAC name for an epoxide group is an oxirane. Epoxy resins may be reacted (cross-linked) either with themselves through catalytic homopolymerisation, or with a wide range of co-reactants including polyfunctional amines, acids (and acid anhydrides), phenols, alcohols and thiols (sometimes called mercaptans). These co-reactants are often referred to as hardeners or curatives, and the cross-linking reaction is commonly referred to as Curing (chemistry), curing. Reaction of polyepoxides with themselves or with polyfunctional hardeners forms a thermosetting polymer, often with favorable mechanical properties and high thermal and chemical resistance. Epoxy has a wide range of application ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rayleigh Scattering
Rayleigh scattering ( ) is the scattering or deflection of light, or other electromagnetic radiation, by particles with a size much smaller than the wavelength of the radiation. For light frequencies well below the resonance frequency of the scattering medium (normal dispersion relation, dispersion regime), the amount of scattering is inversely proportional to the fourth power of the wavelength (e.g., a blue color is scattered much more than a red color as light propagates through air). The phenomenon is named after the 19th-century British physicist Lord Rayleigh (John William Strutt). Rayleigh scattering results from the electric polarizability of the particles. The oscillating electric field of a light wave acts on the charges within a particle, causing them to move at the same frequency. The particle, therefore, becomes a small radiating dipole whose radiation we see as scattered light. The particles may be individual atoms or molecules; it can occur when light travels throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Power Meter
An optical power meter (OPM) is a device used to measure the power in an optical signal. The term usually refers to a device for testing average power in fiber optic systems. Other general purpose light power measuring devices are usually called radiometers, photometers, laser power meters (can be photodiode sensors or thermopile laser sensors), light meters or lux meters. A typical optical power meter consists of a calibrated sensor, measuring amplifier and display. The sensor primarily consists of a photodiode selected for the appropriate range of wavelengths and power levels. On the display unit, the measured optical power and set wavelength is displayed. Power meters are calibrated using a traceable calibration standard. A traditional optical power meter responds to a broad spectrum of light, however, the calibration is wavelength dependent. This is not normally an issue, since the test wavelength is usually known, however, it has a couple of drawbacks. Firstly, the user must s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milliradian
A milliradian (International System of Units, SI-symbol mrad, sometimes also abbreviated mil) is an SI derived unit for angular measurement which is defined as a thousandth of a radian (0.001 radian). Milliradians are used in adjustment of firearm sights by adjusting the angle of the sight compared to the barrel (up, down, left, or right). Milliradians are also used for comparing shot groupings, or to compare the difficulty of hitting different sized shooting targets at different distances. When using a scope with both mrad adjustment and a reticle with mrad markings (called an "mrad/mrad scope"), the shooter can use the reticle as a ruler to count the number of mrads a shot was off-target, which directly translates to the sight adjustment needed to hit the target with a follow-up shot. Optics with mrad markings in the reticle can also be used to make a stadiametric rangefinding, range estimation of a known size target, or vice versa, to determine a target size if the distan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adiabatic Theorem
The adiabatic theorem is a concept in quantum mechanics. Its original form, due to Max Born and Vladimir Fock (1928), was stated as follows: :''A physical system remains in its instantaneous eigenstate if a given perturbation is acting on it slowly enough and if there is a gap between the eigenvalue and the rest of the Hamiltonian's spectrum.'' In simpler terms, a quantum mechanical system subjected to gradually changing external conditions adapts its functional form, but when subjected to rapidly varying conditions there is insufficient time for the functional form to adapt, so the spatial probability density remains unchanged. Adiabatic pendulum At the 1911 Solvay conference, Einstein gave a lecture on the quantum hypothesis, which states that E = nh \nu for atomic oscillators. After Einstein's lecture, Hendrik Lorentz commented that, classically, if a simple pendulum is shortened by holding the wire between two fingers and sliding down, it seems that its energy will change ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |