|
Strobogrammatic
A strobogrammatic number is a number whose numeral is rotationally symmetric, so that it appears the same when rotated 180 degrees. In other words, the numeral looks the same right-side up and upside down (e.g., 69, 96, 1001). A strobogrammatic prime is a strobogrammatic number that is also a prime number, i.e., a number that is only divisible by one and itself (e.g., 11). It is a type of ambigram, words and numbers that retain their meaning when viewed from a different perspective, such as palindromes. Description When written using standard characters (ASCII), the numbers, 0, 1, 8 are symmetrical around the horizontal axis, and 6 and 9 are the same as each other when rotated 180 degrees. In such a system, the first few strobogrammatic numbers are: 0, 1, 8, 11, 69, 88, 96, 101, 111, 181, 609, 619, 689, 808, 818, 888, 906, 916, 986, 1001, 1111, 1691, 1881, 1961, 6009, 6119, 6699, 6889, 6969, 8008, 8118, 8698, 8888, 8968, 9006, 9116, 9696, 9886, 9966, ... The first few strobo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambigram
An ambigram is a calligraphic composition of glyphs (letters, numbers, symbols or other shapes) that can yield different meanings depending on the orientation of observation. Most ambigrams are visual palindromes that rely on some kind of symmetry, and they can often be interpreted as visual puns. The term was coined by Douglas Hofstadter in 1983–1984. Most often, ambigrams appear as visually symmetrical words. When flipped, they remain unchanged, or they mutate to reveal another meaning. "Half-turn" ambigrams undergo a point reflection (180-degree rotational symmetry) and can be read upside down (for example, the word "swims"), while mirror ambigrams have axial symmetry and can be read through a reflective surface like a mirror. Many other types of ambigrams exist. Ambigrams can be constructed in various languages and alphabets, and the notion often extends to numbers and other symbols. It is a recent interdisciplinary concept, combining art, literature, mathematics, cogni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dihedral Prime
A dihedral prime or dihedral calculator prime is a prime number that still reads like itself or another prime number when read in a seven-segment display, regardless of orientation (normally or upside down), and surface (actual display or reflection on a mirror). The first few decimal dihedral primes are : 2, 5, 11, 101, 181, 1181, 1811, 18181, 108881, 110881, 118081, 120121, 121021, 121151, 150151, 151051, 151121, 180181, 180811, 181081 . The smallest dihedral prime that reads differently with each orientation and surface combination is 120121 which becomes 121021 (upside down), 151051 (mirrored), and 150151 (both upside down and mirrored). The digits 0, 1 and 8 remain the same regardless of orientation or surface (the fact that 1 moves from the right to the left of the seven-segment cell when reversed is ignored). 2 and 5 remain the same when viewed upside down, and turn into each other when reflected in a mirror. In the display of a calculator that can handle hexadecimal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serif
In typography, a serif () is a small line or stroke regularly attached to the end of a larger stroke in a letter or symbol within a particular font or family of fonts. A typeface or "font family" making use of serifs is called a serif typeface (or serifed typeface), and a typeface that does not include them is sans-serif. Some typography sources refer to sans-serif typefaces as "grotesque" (in German language, German, ) or "Gothic" (although this often refers to blackletter type as well). In German usage, the term Antiqua (typeface class), Antiqua is used more broadly for serif types. Serif typefaces can be broadly classified into one of four subgroups: Serif#Old-style, Old-style, Serif#Transitional, Transitional, Serif#Didone, Didone, and Serif#Slab serif, Slab serif, in order of first emergence. Origins and etymology Serifs originated from the first official Greek writings on stone and in Latin alphabet with Roman square capitals, inscriptional lettering—words carved into s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mad Magazine
''Mad'' (stylized in all caps) is an American humor magazine which was launched in 1952 and currently published by DC Comics, a unit of the DC Entertainment subsidiary of Warner Bros. Discovery. ''Mad'' was founded by editor Harvey Kurtzman and publisher William Gaines, launched as a comic book series before it became a magazine. It was widely imitated and influential, affecting satirical media, as well as the cultural landscape of the late 20th century, with editor Al Feldstein increasing readership to more than two million during its 1973–1974 circulation peak. It is the last surviving strip in the EC Comics line, which sold ''Mad'' to Premier Industries in 1961, but closed in 1956. ''Mad'' publishes satire on all aspects of life and popular culture, politics, entertainment, and public figures. Its format includes TV and movie parodies, and satire articles about everyday occurrences that are changed to seem humorous. ''Mad''s mascot, Alfred E. Neuman, is usually on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leading Zero
A leading zero is any 0 digit that comes before the first nonzero digit in a number string in positional notation.. For example, James Bond's famous identifier, 007, has two leading zeros. Any zeros appearing to the left of the first non-zero digit ''before'' the decimal point do not affect its value, and can be omitted (or replaced with blanks) with no loss of information. Therefore, the usual decimal notation of integers does not use leading zeros except for the zero in the ones place, which would be denoted as an empty string otherwise. However, for digits ''after'' the decimal point, the leading zeros between the decimal point and the first nonzero digit are necessary for conveying the magnitude of a number and cannot be omitted (ex. 0.001), while trailing zeros – zeros occurring after the decimal point and after the last nonzero digit – can be omitted without changing the meaning (ex. 0.00100). Occurrence Often, leading zeros are found on non-electronic digital displ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
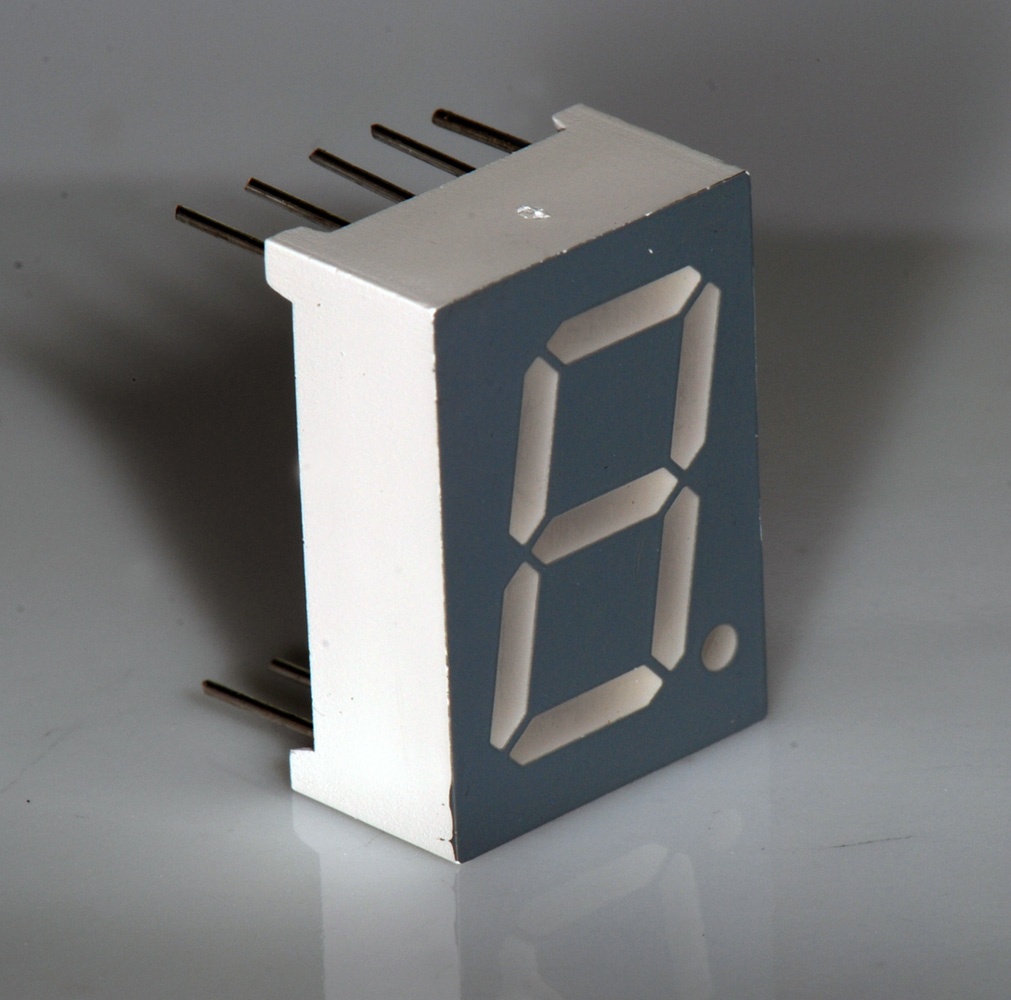
Seven-segment Display
A seven-segment display is a display device for Arabic numerals, less complex than a device that can show more characters such as dot matrix displays. Seven-segment displays are widely used in digital clocks, electronic meters, basic calculators, and other electronic devices that display numerical information. History Seven-segment representation of figures can be found in patents as early as 1903 (in ), when Carl Kinsley invented a method of telegraphically transmitting letters and numbers and having them printed on tape in a segmented format. In 1908, F. W. Wood invented an 8-segment display, which displayed the number 4 using a diagonal bar (). In 1910, a seven-segment display illuminated by incandescent bulbs was used on a power-plant boiler room signal panel. They were also used to show the dialed telephone number to operators during the transition from manual to automatic telephone dialing. They did not achieve widespread use until the advent of light-emitting diode, LEDs in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mersenne Numbers
In mathematics, a Mersenne prime is a prime number that is one less than a power of two. That is, it is a prime number of the form for some integer . They are named after Marin Mersenne, a French Minim friar, who studied them in the early 17th century. If is a composite number then so is . Therefore, an equivalent definition of the Mersenne primes is that they are the prime numbers of the form for some prime . The exponents which give Mersenne primes are 2, 3, 5, 7, 13, 17, 19, 31, ... and the resulting Mersenne primes are 3, 7, 31, 127, 8191, 131071, 524287, 2147483647, ... . Numbers of the form without the primality requirement may be called Mersenne numbers. Sometimes, however, Mersenne numbers are defined to have the additional requirement that should be prime. The smallest composite Mersenne number with prime exponent ''n'' is . Mersenne primes were studied in antiquity because of their close connection to perfect numbers: the Euclid–Euler th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Number
A binary number is a number expressed in the Radix, base-2 numeral system or binary numeral system, a method for representing numbers that uses only two symbols for the natural numbers: typically "0" (zero) and "1" (one). A ''binary number'' may also refer to a rational number that has a finite representation in the binary numeral system, that is, the quotient of an integer by a power of two. The base-2 numeral system is a positional notation with a radix of 2. Each digit is referred to as a bit, or binary digit. Because of its straightforward implementation in digital electronic circuitry using logic gates, the binary system is used by almost all modern computer, computers and computer-based devices, as a preferred system of use, over various other human techniques of communication, because of the simplicity of the language and the noise immunity in physical implementation. History The modern binary number system was studied in Europe in the 16th and 17th centuries by Thoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since 2023; and, since its independence in 1947, the world's most populous democracy. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is near Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations averag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gurmukhi
Gurmukhī ( , Shahmukhi: ) is an abugida developed from the Laṇḍā scripts, standardized and used by the second Sikh guru, Guru Angad (1504–1552). Commonly regarded as a Sikh script, Gurmukhi is used in Punjab, India as the official script of the Punjabi language. In the past, the script was also employed to write scientific and poetic literature from both Sanskritic and Persian traditions in the Braj language. The primary scripture of Sikhism, the Guru Granth Sahib, is written in Gurmukhī, in various dialects and languages often subsumed under the generic title '' Sant Bhasha'' or "saint language", in addition to other languages like Persian and various phases of Indo-Aryan languages. Modern Gurmukhī has thirty-five original letters, hence its common alternative term ''paintī'' or "the thirty-five", plus six additional consonants, nine vowel diacritics, two diacritics for nasal sounds, one diacritic that geminates consonants and three subscript characters. The sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |