|
Strawberry Poison Frog
The strawberry poison frog, strawberry poison-dart frog or blue jeans poison frog (''Oophaga pumilio'', formerly ''Dendrobates pumilio'') is a species of small poison dart frog found in Central America. It is common throughout its range, which extends from eastern central Nicaragua through Costa Rica and northwestern Panama. The species is often found in humid lowlands and premontane forest, but large populations are also found in disturbed areas such as plantations.Savage, J. M. 2002. The Amphibians and Reptiles of Costa Rica. University of Chicago Press, Chicago and London. The strawberry poison frog is perhaps most famous for its widespread variation in coloration, comprising approximately 15–30 color morphs, most of which are presumed to be true-breeding. ''O. pumilio'', while not the most poisonous of the dendrobatids, is the most toxic member of its genus. Diet The diet of ''O. pumilio'' causes the skin of the amphibian to become toxic in nature when certain subspec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eduard Oscar Schmidt
Eduard Oscar Schmidt (21 February 1823, in Torgau – 17 January 1886, in Kappelrodeck) was a German zoologist and phycologist. Biography He initially studied mathematics and science at Halle, then continued his education in Berlin, where he came under the influence of Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg and Johannes Peter Müller. In 1847 he received his habilitation at the University of Jena, becoming an associate professor during the following year. In 1855 was he appointed professor of zoology at the University of Cracow. Later he taught classes at the Universities of Graz (from 1857) and Strasbourg (from 1872). Schmidt was an early proponent of Darwinian evolutionary thought. He is remembered for his research of Porifera (sponges), particularly species from the Adriatic Sea. Schmidt also made contributions in the field of phycology. As far back as 1862 Oscar Schmidt showed that "cuttings" of sponges will attach themselves and grow. This idea was followed through in the exper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diurnality
Diurnality is a form of plant and animal behavior characterized by activity during daytime, with a period of sleeping or other inactivity at night. The common adjective used for daytime activity is "diurnal". The timing of activity by an animal depends on a variety of environmental factors such as the temperature, the ability to gather food by sight, the risk of predation, and the time of year. Diurnality is a cycle of activity within a 24-hour period; cyclic activities called circadian rhythms are endogenous cycles not dependent on external cues or environmental factors except for a zeitgeber. Animals active during twilight are crepuscular, those active during the night are nocturnal and animals active at sporadic times during both night and day are cathemeral. Plants that open their flowers during the daytime are described as diurnal, while those that bloom during nighttime are nocturnal. The timing of flower opening is often related to the time at which preferred pollinators ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aposematism
Aposematism is the Advertising in biology, advertising by an animal to potential predation, predators that it is not worth attacking or eating. This unprofitability may consist of any defences which make the prey difficult to kill and eat, such as toxicity, venom, foul taste or smell, sharp spines, or aggressive nature. These advertising signals may take the form of conspicuous animal coloration, coloration, sounds, odours, or other perception, perceivable characteristics. Aposematic signals are beneficial for both predator and prey, since both avoid potential harm. The term was coined in 1877 by Edward Bagnall Poulton for Alfred Russel Wallace's concept of warning coloration. Aposematism is exploited in Müllerian mimicry, where species with strong defences evolve to resemble one another. By mimicking similarly coloured species, the warning signal to predators is shared, causing them to learn more quickly at less of a cost. A genuine aposematic signal that a species actually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Drift
Genetic drift, also known as allelic drift or the Wright effect, is the change in the frequency of an existing gene variant (allele) in a population due to random chance. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation. It can also cause initially rare alleles to become much more frequent and even fixed. When few copies of an allele exist, the effect of genetic drift is more notable, and when many copies exist, the effect is less notable. In the middle of the 20th century, vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, population geneticist Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russell Lande
Russell Scott Lande (born 1951) is an American evolutionary biologist and ecologist, and an International Chair Professor at Centre for Biodiversity Dynamics at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU). He is a fellow of the Royal Society and a member of the United States National Academy of Sciences. Education and career He received his Ph.D. in 1976 from Harvard University where he was a student of Richard Lewontin, and completed his Postdoctoral work at the University of Wisconsin under James F. Crow. He then held positions at the University of Chicago, University of Oregon, University of California, San Diego, and Imperial College London. In 2016 he was employed as an International Chair Professor at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU). Work Lande is best known for his early work extending quantitative genetics theory to the context of evolutionary biology in natural populations. In particular, he developed a stochastic theory for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
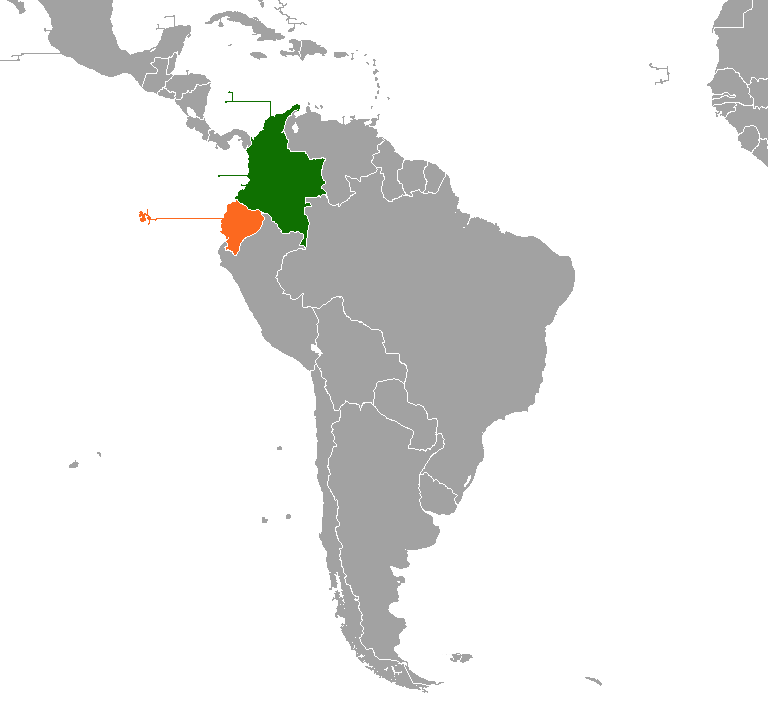
Oophaga Sylvatica ''Oophaga sylvatica'', sometimes known as its Spanish name diablito, is a species of frog in the family Dendrobatidae found in Southwestern Colombia and Northwestern Ecuador. Its natural habitat is lowland and submontane rainforest; it can, however, survive in moderately degraded areas, at least in the more humid parts of its range. It is a very common frog |