|
Stratopause
The stratopause (formerly mesopeak) is the level of the atmosphere which is the boundary between two layers: the stratosphere and the mesosphere. In the stratosphere, the temperature increases with altitude, and the stratopause is the region where a maximum in the temperature occurs. This atmospheric feature is not exclusive to Earth, but also occurs on any other planet or moon with an atmosphere. According to James Kasting, planets whose atmospheres do not absorb shortwave sunlight, such as Venus and Mars, do not have a Stratosphere and thus have no Stratopause. On Earth, the stratopause is above sea level. The atmospheric pressure is around of the pressure at sea level. The temperature in the stratopause is . See also * Jet stream Jet streams are fast flowing, narrow thermal wind, air currents in the Earth's Atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere. The main jet streams are located near the altitude of the tropopause and are westerly winds, flowing west to east around the gl . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth's Atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is composed of a layer of gas mixture that surrounds the Earth's planetary surface (both lands and oceans), known collectively as air, with variable quantities of suspended aerosols and particulates (which create weather features such as clouds and hazes), all retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere serves as a protective buffer between the Earth's surface and outer space, shields the surface from most meteoroids and ultraviolet solar radiation, keeps it warm and reduces diurnal temperature variation (temperature extremes between day and night) through heat retention (greenhouse effect), redistributes heat and moisture among different regions via air currents, and provides the chemical and climate conditions allowing life to exist and evolve on Earth. By mole fraction (i.e., by quantity of molecules), dry air contains 78.08% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.04% carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other trace gases (see Composition below ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratosphere
The stratosphere () is the second-lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth, located above the troposphere and below the mesosphere. The stratosphere is composed of stratified temperature zones, with the warmer layers of air located higher (closer to outer space) and the cooler layers lower (closer to the planetary surface of the Earth). The increase of temperature with altitude is a result of the absorption of the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation by the ozone layer, where ozone is exothermically photolyzed into oxygen in a cyclical fashion. This temperature inversion is in contrast to the troposphere, where temperature decreases with altitude, and between the troposphere and stratosphere is the tropopause border that demarcates the beginning of the temperature inversion. Near the equator, the lower edge of the stratosphere is as high as , at mid-latitudes around , and at the poles about . Temperatures range from an average of near the tropopause to an average of ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesosphere
The mesosphere (; ) is the third layer of the atmosphere, directly above the stratosphere and directly below the thermosphere. In the mesosphere, temperature decreases as altitude increases. This characteristic is used to define limits: it begins at the top of the stratosphere (sometimes called the stratopause), and ends at the mesopause, which is the coldest part of Earth's atmosphere, with temperatures below . The exact upper and lower boundaries of the mesosphere vary with latitude and with season (higher in winter and at the tropics, lower in summer and at the poles), but the lower boundary is usually located at altitudes from above sea level, and the upper boundary (the mesopause) is usually from . The stratosphere and mesosphere are sometimes collectively referred to as the "middle atmosphere", which spans altitudes approximately between above Earth's surface. The mesopause, at an altitude of , separates the mesosphere from the thermosphere—the second-outermost la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making up a substance. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), with the third being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altitude
Altitude is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum (geodesy), datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context (e.g., aviation, geometry, geographical survey, sport, or atmospheric pressure). Although the term ''altitude'' is commonly used to mean the height above sea level of a location, in geography the term elevation is often preferred for this usage. In aviation, altitude is typically measured relative to mean sea level or above ground level to ensure safe navigation and flight operations. In geometry and geographical surveys, altitude helps create accurate topographic maps and understand the terrain's elevation. For high-altitude trekking and sports, knowing and adapting to altitude is vital for performance and safety. Higher altitudes mean reduced oxygen levels, which can lead to altitude sickness if proper acclimatization measures are not taken. Vertical distance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planet
A planet is a large, Hydrostatic equilibrium, rounded Astronomical object, astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets by the most restrictive definition of the term: the terrestrial planets Mercury (planet), Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, and the giant planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a young protostar orbited by a protoplanetary disk. Planets grow in this disk by the gradual accumulation of material driven by gravity, a process called accretion (astrophysics), accretion. The word ''planet'' comes from the Greek () . In Classical antiquity, antiquity, this word referred to the Sun, Moon, and five points of light visible to the naked eye that moved across the background of the stars—namely, Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Satellite
A natural satellite is, in the most common usage, an astronomical body that orbits a planet, dwarf planet, or small Solar System body (or sometimes another natural satellite). Natural satellites are colloquially referred to as moons, a derivation from the Moon of Earth. In the Solar System, there are six planetary satellite systems containing 418 known natural satellites altogether. Seven objects commonly considered dwarf planets by astronomers are also known to have natural satellites: , Pluto, Haumea, , Makemake, , and Eris. As of January 2022, there are 447 other minor planets known to have natural satellites. A planet usually has at least around 10,000 times the mass of any natural satellites that orbit it, with a correspondingly much larger diameter. The Earth–Moon system is a unique exception in the Solar System; at 3,474 kilometres (2,158 miles) across, the Moon is 0.273 times the diameter of Earth and about of its mass. The next largest ratios are the N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosphere is the outer region of a star, which includes the layers above the opaque photosphere; stars of low temperature might have outer atmospheres containing compound molecules. The atmosphere of Earth is composed of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), argon (0.9%), carbon dioxide (0.04%) and trace gases. Most organisms use oxygen for respiration; lightning and bacteria perform nitrogen fixation which produces ammonia that is used to make nucleotides and amino acids; plants, algae, and cyanobacteria use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. The layered composition of the atmosphere minimises the harmful effects of sunlight, ultraviolet radiation, solar wind, and cosmic rays and thus protects the organisms from genetic damage. The curr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Kasting
James Fraser Kasting (born January 2, 1953) is an American Earth science, geoscientist and Distinguished Professor of Geosciences at Penn State University. Kasting is active in NASA's search for habitable Exoplanet, extrasolar planets. He is considered a world leader in the field of planetary habitability, assessing habitable zones around stars. He was elected a member of the National Academy of Sciences in 2018. Kasting also serves on the Advisory Council of METI (Messaging Extraterrestrial Intelligence). Education Kasting grew up in Huntsville, Alabama, and credits the nearby Marshall Space Flight Center and the Mercury, Gemini, and Apollo rockets for inspiring his interests in space and science. Kasting received an Bachelor of Arts, A.B. from Harvard University in 1975. He then went to the University of Michigan, where he worked with Tom Donahue, receiving his M.S. in physics and atmospheric science in 1978, and his Ph.D. in atmospheric science in 1979. Research Kasting work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker and denser than Earth and any other rocky body in the Solar System. Its atmosphere is composed of mostly carbon dioxide (), with a global sulfuric acid cloud cover and no liquid water. At the mean surface level the atmosphere reaches a temperature of and a pressure 92 times greater than Earth's at sea level, turning the lowest layer of the atmosphere into a supercritical fluid. Venus is the third brightest object in Earth's sky, after the Moon and the Sun, and, like Mercury, appears always relatively close to the Sun, either as a "morning star" or an "evening star", resulting from orbiting closer ( inferior) to the Sun than Earth. The orbits of Venus and Earth make the two planets approach each other in synodic periods of 1.6 years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
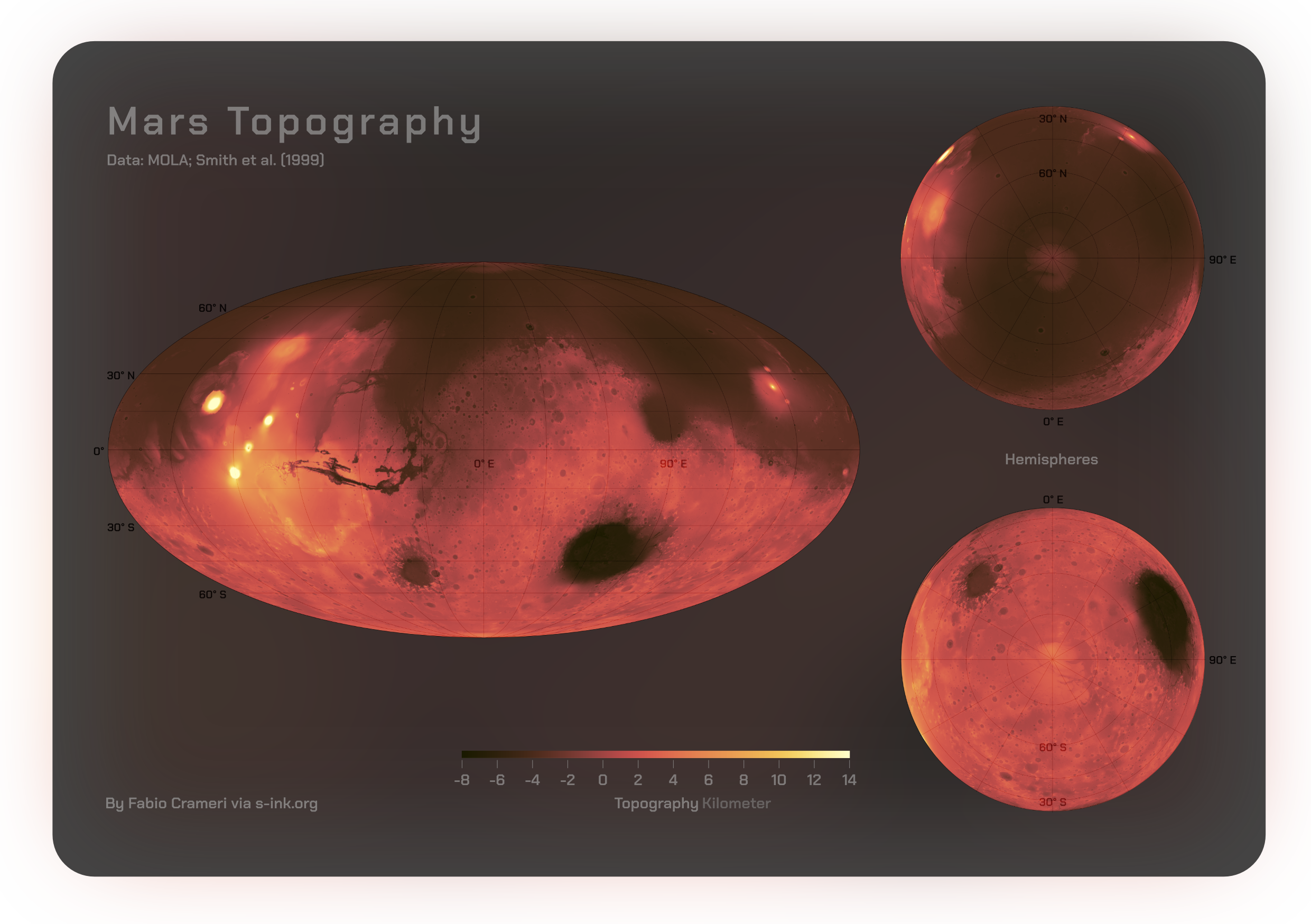
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmospheric pressure is a few thousandths of Earth's, atmospheric temperature ranges from and cosmic radiation is high. Mars retains some water, in the ground as well as thinly in the atmosphere, forming cirrus clouds, frost, larger polar regions of permafrost and ice caps (with seasonal snow), but no liquid surface water. Its surface gravity is roughly a third of Earth's or double that of the Moon. It is half as wide as Earth or twice the Moon, with a diameter of , and has a surface area the size of all the dry land of Earth. Fine dust is prevalent across the surface and the atmosphere, being picked up and spread at the low Martian gravity even by the weak wind of the tenuous atmosphere. The terrain of Mars roughly follows a north-south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all of Earth's water is contained in its global ocean, covering Water distribution on Earth, 70.8% of Earth's crust. The remaining 29.2% of Earth's crust is land, most of which is located in the form of continental landmasses within Earth's land hemisphere. Most of Earth's land is at least somewhat humid and covered by vegetation, while large Ice sheet, sheets of ice at Polar regions of Earth, Earth's polar polar desert, deserts retain more water than Earth's groundwater, lakes, rivers, and Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water combined. Earth's crust consists of slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's outer core, Earth has a liquid outer core that generates a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |