|
Stomodeum
The stomodeum, also called stomatodeum or stomatodaeum, is a depression between the brain and the pericardium in an embryo, and is the precursor to the mouth and the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. Development The mouth is developed partly from the stomodeum, and partly from the floor of the anterior portion of the fore-gut. By the growth of the head end of the embryo, and the formation of the cephalic flexure, the pericardial area and the buccopharyngeal membrane come to lie on the ventral surface of the embryo. With the further expansion of the brain, and the forward bulging of the pericardium, the buccopharyngeal membrane is depressed between these two prominences. This depression constitutes the stomodeum. No trace of the membrane is found in the adult; and the communication just mentioned must not be confused with the permanent isthmus faucium. The lips, teeth, and gums are formed from the walls of the stomodeum, but the tongue is developed in the floor of the pharyn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for special senses such as visual perception, vision, hearing, and olfaction. Being the most specialized organ, it is responsible for receiving information from the sensory nervous system, processing that information (thought, cognition, and intelligence) and the coordination of motor control (muscle activity and endocrine system). While invertebrate brains arise from paired segmental ganglia (each of which is only responsible for the respective segmentation (biology), body segment) of the ventral nerve cord, vertebrate brains develop axially from the midline dorsal nerve cord as a brain vesicle, vesicular enlargement at the rostral (anatomical term), rostral end of the neural tube, with centralized control over all body segments. All vertebr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
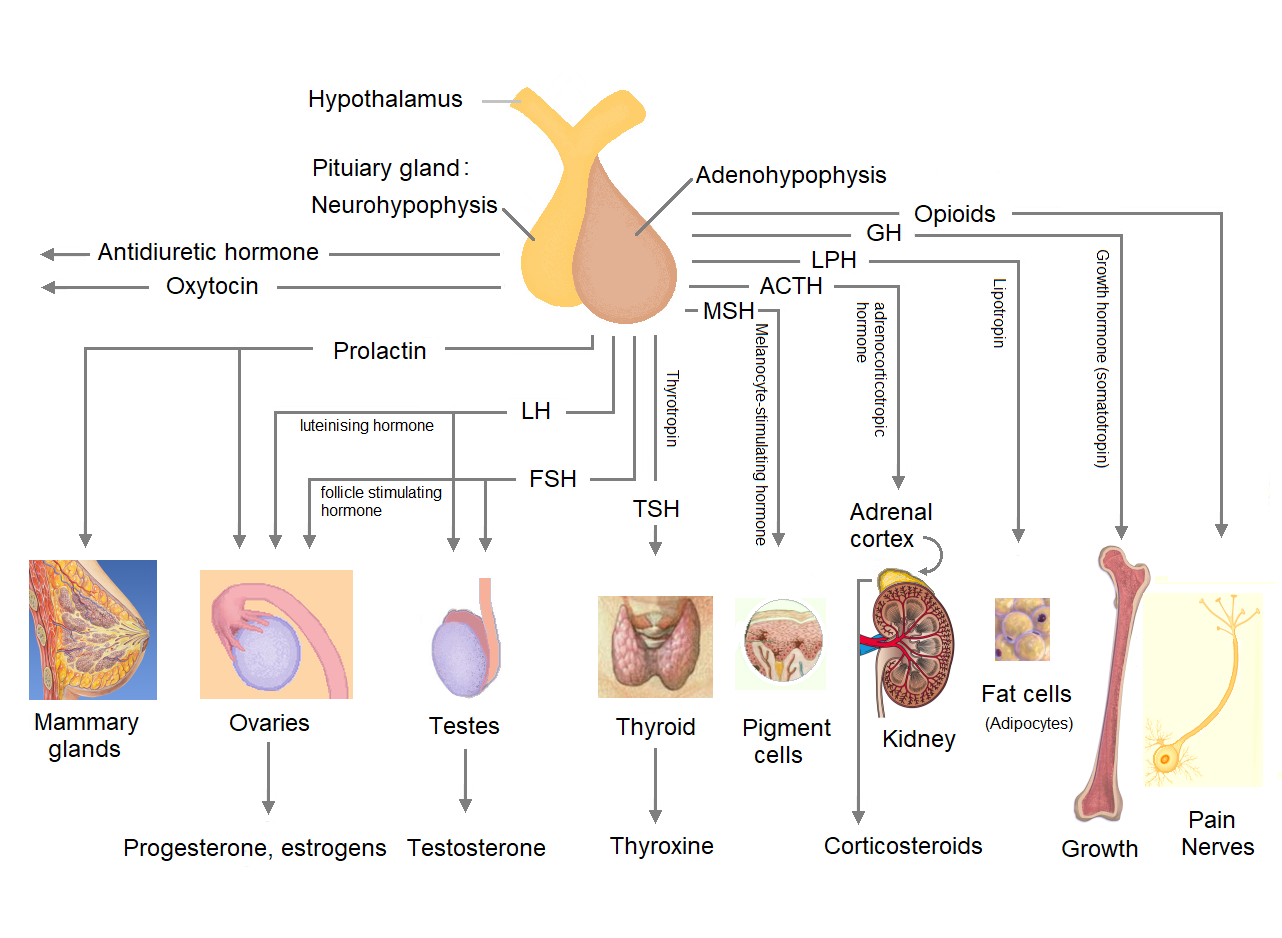
Pituitary Gland
The pituitary gland or hypophysis is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, the pituitary gland is located at the base of the human brain, brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus control much of the body's endocrine system. It is seated in part of the sella turcica a fossa (anatomy), depression in the sphenoid bone, known as the hypophyseal fossa. The human pituitary gland is ovoid, oval shaped, about 1 cm in diameter, in weight on average, and about the size of a kidney bean. Digital version. There are two main lobes of the pituitary, an anterior pituitary, anterior lobe, and a posterior pituitary, posterior lobe joined and separated by a small intermediate lobe. The anterior lobe (adenohypophysis) is the glandular part that produces and secretes several hormones. The posterior lobe (neurohypophysis) secretes neurohypophysial hormones produced in the hypothalamus. Both lobes have different origins and they are both co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tongue
The tongue is a Muscle, muscular organ (anatomy), organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for chewing and swallowing as part of the digestive system, digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste buds housed in numerous lingual papillae. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva and is richly supplied with nerves and blood vessels. The tongue also serves as a natural means of cleaning the teeth. A major function of the tongue is to enable speech in humans and animal communication, vocalization in other animals. The human tongue is divided into two parts, an oral cavity, oral part at the front and a pharynx, pharyngeal part at the back. The left and right sides are also separated along most of its length by a vertical section of connective tissue, fibrous tissue (the lingual septum) that results in a groove, the median sulcus, on the tongue's surface. There are two groups of glossal muscles. The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gums
The gums or gingiva (: gingivae) consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health. Structure The gums are part of the soft tissue lining of the mouth. They surround the teeth and provide a seal around them. Unlike the soft tissue linings of the lips and cheeks, most of the gums are tightly bound to the underlying bone which helps resist the friction of food passing over them. Thus when healthy, it presents an effective barrier to the barrage of periodontal insults to deeper tissue. Healthy gums are usually coral pink in light skinned people, and may be naturally darker with melanin pigmentation. Changes in color, particularly increased redness, together with swelling and an increased tendency to bleed, suggest an inflammation that is possibly due to the accumulation of bacterial plaque. Overall, the clinical appearance of the tissue reflects the underlying histology, both in hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teeth
A tooth (: teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tearing food, for defensive purposes, to intimidate other animals often including their own, or to carry prey or their young. The roots of teeth are covered by gums. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness that originate from the outermost embryonic germ layer, the ectoderm. The general structure of teeth is similar across the vertebrates, although there is considerable variation in their form and position. The teeth of mammals have deep roots, and this pattern is also found in some fish, and in crocodilians. In most teleost fish, however, the teeth are attached to the outer surface of the bone, while in lizards they are attached to the inner surface of the jaw by one side. In cartilaginous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buccopharyngeal Membrane
The region where the crescentic masses of the ectoderm and endoderm come into direct contact with each other constitutes a thin membrane, the buccopharyngeal membrane (or oropharyngeal membrane), which forms a septum between the primitive mouth and pharynx. In front of the buccopharyngeal area, where the lateral crescents of mesoderm fuse in the middle line, the pericardium The pericardium (: pericardia), also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong inelastic connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), ... is afterward developed, and this region is therefore designated the ''pericardial area''. The buccopharyngeal membranes serve as a respiratory surface in a wide variety of amphibians and reptiles. In this type of respiration, membranes in the mouth and throat are permeable to oxygen and carbon dioxide. In some species that remain submerged in water for long period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pericardial Area
The pericardium (: pericardia), also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong inelastic connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), and an inner layer made of serous membrane (serous pericardium). It encloses the pericardial cavity, which contains pericardial fluid, and defines the middle mediastinum. It separates the heart from interference of other structures, protects it against infection and blunt trauma, and lubricates the heart's movements. The English name originates from the Ancient Greek prefix ''peri-'' (περί) 'around' and the suffix ''-cardion'' (κάρδιον) 'heart'. Anatomy The pericardium is a tough fibroelastic sac which covers the heart from all sides except at the cardiac root (where the great vessels join the heart) and the bottom (where only the serous pericardium exists to cover the upper surface of the central tendon of diaphragm). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalic Flexure
Three flexures form in the part of the embryonic neural tube that develops into the brain. At four weeks gestational age in the human embryo, the neural tube has developed at the cranial end into three swellings – the primary brain vesicles. The space into which the cranial part of the neural tube is developing is limited. This limitation causes the neural tube to bend, or flex, at two ventral flexures – the rostral cephalic flexure, and the caudal cervical flexure. It also bends dorsally into the pontine flexure. These flexures have formed by the time that the primary brain vesicles have developed into five secondary brain vesicles in the fifth week. Flexure development The neural tube has a longitudinal axis called the neuraxis, from the future brain area at the cranial end, to the conus medullaris of the spinal cord at the caudal end. By the fourth week in the human embryo, at its cranial end, three swellings have formed as primary brain vesicles. These vesicles form the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fore-gut
The foregut in humans is the anterior part of the alimentary canal, from the distal esophagus to the first half of the duodenum, at the entrance of the bile duct. Beyond the stomach, the foregut is attached to the abdominal walls by mesentery. The foregut arises from the endoderm, developing from the folding primitive gut, and is developmentally distinct from the midgut and hindgut. Although the term “foregut” is typically used in reference to the anterior section of the primitive gut, components of the adult gut can also be described with this designation. Pain in the epigastric region, just below the intersection of the ribs, typically refers to structures in the adult foregut. Adult foregut Components * Esophagus * Respiratory tract (lower respiratory tract) * Stomach * Duodenum (up to ampulla of vater) * Liver * Gallbladder * Pancreas * Spleen – The spleen arises from the mesodermal dorsal mesentery (the foregut arises from the endoderm not mesoderm). But the spleen shar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mouth
A mouth also referred to as the oral is the body orifice through which many animals ingest food and animal communication#Auditory, vocalize. The body cavity immediately behind the mouth opening, known as the oral cavity (or in Latin), is also the first part of the alimentary canal, which leads to the pharynx and the gullet. In tetrapod vertebrates, the mouth is bounded on the outside by the lips and cheeks — thus the oral cavity is also known as the buccal cavity (from Latin ', meaning "cheek") — and contains the tongue on the inside. Except for some groups like birds and lissamphibians, vertebrates usually have teeth in their mouths, although some fish species have pharyngeal teeth instead of oral teeth. Most bilaterian phylum, phyla, including arthropods, molluscs and chordates, have a two-opening gut tube with a mouth at one end and an anus at the other. Which end forms first in ontogeny is a criterion used to classify bilaterian animals into protostomes and deuterostomes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the tissue, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the thorax, chest, called the mediastinum. In humans, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right Atrium (heart), atria and lower left and right Ventricle (heart), ventricles. Commonly, the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. In a healthy heart, blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent cardiac regurgitation, backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a sma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell. The resulting fusion of these two cells produces a single-celled zygote that undergoes many cell divisions that produce cells known as blastomeres. The blastomeres (4-cell stage) are arranged as a solid ball that when reaching a certain size, called a morula, (16-cell stage) takes in fluid to create a cavity called a blastocoel. The structure is then termed a blastula, or a blastocyst in mammals. The mammalian blastocyst hatches before implantating into the endometrial lining of the womb. Once implanted the embryo will continue its development through the next stages of gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis. Gastrulation is the formation of the three germ layers that will form all of the different parts of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |