|
Stericated 6-orthoplex
In six-dimensional geometry, a stericated 6-orthoplex is a convex uniform 6-polytope, constructed as a sterication (4th order truncation) of the regular 6-orthoplex. There are 16 unique sterications for the 6-orthoplex with permutations of truncations, cantellations, and runcinations. Eight are better represented from the stericated 6-cubes. Stericated 6-orthoplex Alternate names * Small cellated hexacontatetrapeton (Acronym: scag) (Jonathan Bowers) Images Steritruncated 6-orthoplex Alternate names * Cellitruncated hexacontatetrapeton (Acronym: catog) (Jonathan Bowers) Images Stericantellated 6-orthoplex Alternate names * Cellirhombated hexacontatetrapeton (Acronym: crag) (Jonathan Bowers) Images Stericantitruncated 6-orthoplex Alternate names * Celligreatorhombated hexacontatetrapeton (Acronym: cagorg) (Jonathan Bowers) Images Steriruncinated 6-orthoplex Alternate names * Celliprismated hexacontatetrapeton (Acronym: copog) (Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6-cube T5
In geometry, a 6-cube is a six-dimensional hypercube with 64 Vertex (geometry), vertices, 192 Edge (geometry), edges, 240 square Face (geometry), faces, 160 cubic Cell (mathematics), cells, 60 tesseract 4-faces, and 12 5-cube 5-faces. It has Schläfli symbol , being composed of 3 5-cubes around each 4-face. It can be called a hexeract, a portmanteau of tesseract (the ''4-cube'') with ''hex'' for six (dimensions) in Greek language, Greek. It can also be called a regular dodeca-6-tope or dodecapeton, being a 6-polytope, 6-dimensional polytope constructed from 12 regular Facet (geometry), facets. Related polytopes It is a part of an infinite family of polytopes, called hypercubes. The Dual polytope, dual of a 6-cube can be called a 6-orthoplex, and is a part of the infinite family of cross-polytopes. It is composed of various 5-cubes, at perpendicular angles on the u-axis, forming coordinates (x,y,z,w,v,u). Applying an ''Alternation (geometry), alternation'' operation, deleting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-simplex T01234
In five-dimensional geometry, a 5-simplex is a self-dual regular 5-polytope. It has six vertices, 15 edges, 20 triangle faces, 15 tetrahedral cells, and 6 5-cell facets. It has a dihedral angle of cos−1(), or approximately 78.46°. The 5-simplex is a solution to the problem: ''Make 20 equilateral triangles using 15 matchsticks, where each side of every triangle is exactly one matchstick.'' Alternate names It can also be called a hexateron, or hexa-5-tope, as a 6- facetted polytope in 5-dimensions. The name ''hexateron'' is derived from ''hexa-'' for having six facets and '' teron'' (with ''ter-'' being a corruption of ''tetra-'') for having four-dimensional facets. By Jonathan Bowers, a hexateron is given the acronym hix. As a configuration This configuration matrix represents the 5-simplex. The rows and columns correspond to vertices, edges, faces, cells and 4-faces. The diagonal numbers say how many of each element occur in the whole 5-simplex. The nondiagonal n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stericated 5-simplexes
In five-dimensional geometry, a stericated 5-simplex is a convex uniform 5-polytope with fourth-order Truncation (geometry), truncations (sterication) of the regular 5-simplex. There are six unique sterications of the 5-simplex, including permutations of truncations, cantellations, and runcinations. The simplest stericated 5-simplex is also called an expanded 5-simplex, with the first and last nodes ringed, for being constructible by an Expansion (geometry), expansion operation applied to the regular 5-simplex. The highest form, the ''steriruncicantitruncated 5-simplex'' is more simply called an #Omnitruncated 5-simplex, omnitruncated 5-simplex with all of the nodes ringed. Stericated 5-simplex A stericated 5-simplex can be constructed by an Expansion (geometry), expansion operation applied to the regular 5-simplex, and thus is also sometimes called an expanded 5-simplex. It has 30 Vertex (geometry), vertices, 120 Edge (geometry), edges, 210 Face (geometry), faces (120 triang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-simplex T012
In geometry, a tetrahedron (: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertices. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ordinary convex polyhedra. The tetrahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a Euclidean simplex, and may thus also be called a 3-simplex. The tetrahedron is one kind of pyramid, which is a polyhedron with a flat polygon base and triangular faces connecting the base to a common point. In the case of a tetrahedron, the base is a triangle (any of the four faces can be considered the base), so a tetrahedron is also known as a "triangular pyramid". Like all convex polyhedra, a tetrahedron can be folded from a single sheet of paper. It has two such nets. For any tetrahedron there exists a sphere (called the circumsphere) on which all four vertices lie, and another sphere (the insphere) tangent to the tetrahedron's faces. Reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-cube
In geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral. It has four straight sides of equal length and four equal angles. Squares are special cases of rectangles, which have four equal angles, and of rhombuses, which have four equal sides. As with all rectangles, a square's angles are right angles (90 degrees, or /2 radians), making adjacent sides perpendicular. The area of a square is the side length multiplied by itself, and so in algebra, multiplying a number by itself is called squaring. Equal squares can tile the plane edge-to-edge in the square tiling. Square tilings are ubiquitous in tiled floors and walls, graph paper, image pixels, and game boards. Square shapes are also often seen in building floor plans, origami paper, food servings, in graphic design and heraldry, and in instant photos and fine art. The formula for the area of a square forms the basis of the calculation of area and motivates the search for methods for squaring the circle by compass and straightedge, now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
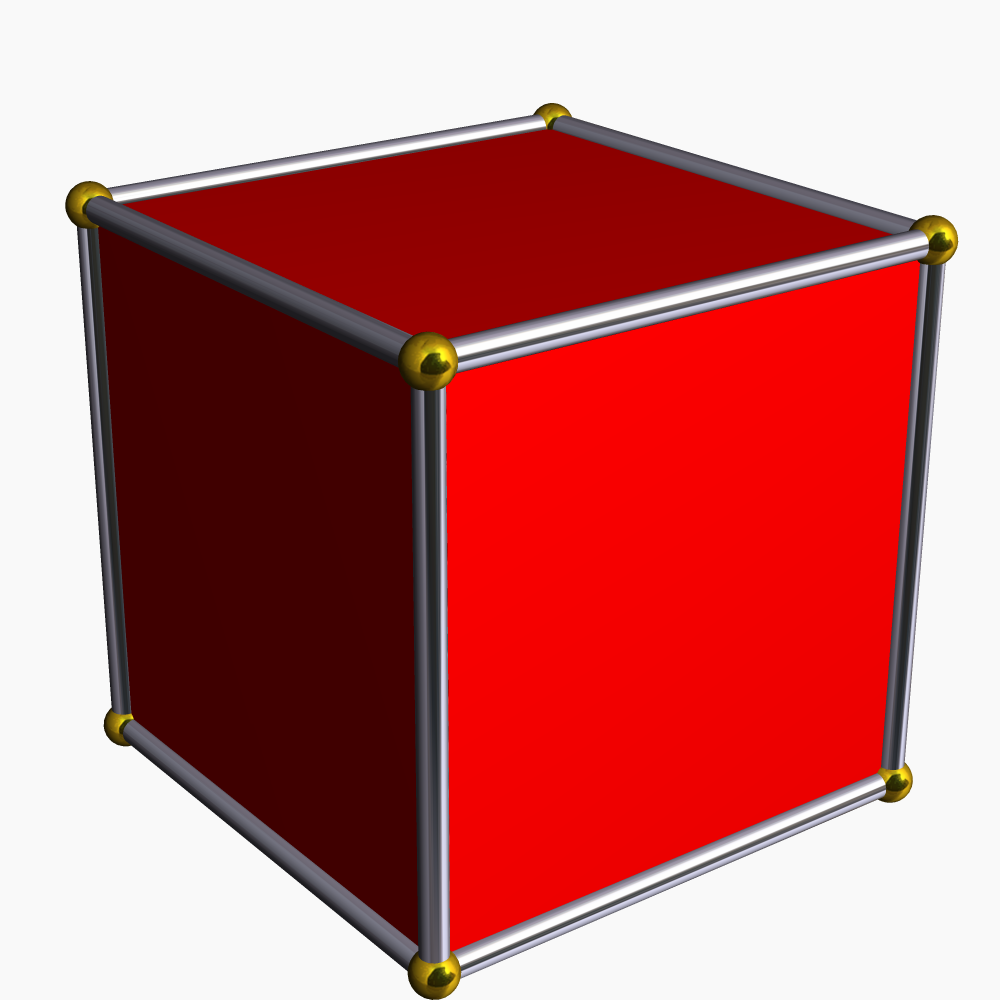
3-cube T12 B2
A cube or regular hexahedron is a three-dimensional solid object in geometry, which is bounded by six congruent square faces, a type of polyhedron. It has twelve congruent edges and eight vertices. It is a type of parallelepiped, with pairs of parallel opposite faces, and more specifically a rhombohedron, with congruent edges, and a rectangular cuboid, with right angles between pairs of intersecting faces and pairs of intersecting edges. It is an example of many classes of polyhedra: Platonic solid, regular polyhedron, parallelohedron, zonohedron, and plesiohedron. The dual polyhedron of a cube is the regular octahedron. The cube can be represented in many ways, one of which is the graph known as the cubical graph. It can be constructed by using the Cartesian product of graphs. The cube is the three-dimensional hypercube, a family of polytopes also including the two-dimensional square and four-dimensional tesseract. A cube with unit side length is the canonical unit of volume in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-cube T123
In geometry, a tesseract or 4-cube is a four-dimensional hypercube, analogous to a two-dimensional square and a three-dimensional cube. Just as the perimeter of the square consists of four edges and the surface of the cube consists of six square faces, the hypersurface of the tesseract consists of eight cubical cells, meeting at right angles. The tesseract is one of the six convex regular 4-polytopes. The tesseract is also called an 8-cell, C8, (regular) octachoron, or cubic prism. It is the four-dimensional measure polytope, taken as a unit for hypervolume. Coxeter labels it the polytope. The term ''hypercube'' without a dimension reference is frequently treated as a synonym for this specific polytope. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' traces the word ''tesseract'' to Charles Howard Hinton's 1888 book '' A New Era of Thought''. The term derives from the Greek ( 'four') and ( 'ray'), referring to the four edges from each vertex to other vertices. Hinton originally s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complete Graph K2
Complete may refer to: Logic * Completeness (logic) * Completeness of a theory, the property of a theory that every formula in the theory's language or its negation is provable Mathematics * The completeness of the real numbers, which implies that there are no "gaps" in the real numbers * Complete metric space, a metric space in which every Cauchy sequence converges * Complete uniform space, a uniform space where every Cauchy net in converges (or equivalently every Cauchy filter converges) * Complete measure, a measure space where every subset of every null set is measurable * Completion (algebra), at an ideal * Completeness (cryptography) * Completeness (statistics), a statistic that does not allow an unbiased estimator of zero * Complete graph, an undirected graph in which every pair of vertices has exactly one edge connecting them * Complete tree (abstract data type), a tree with every level filled, except possibly the last * Complete category, a category ''C'' where every di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-cube T1234
In five-dimensional geometry, a 5-cube is a name for a five-dimensional hypercube with 32 vertices, 80 edges, 80 square faces, 40 cubic cells, and 10 tesseract 4-faces. It is represented by Schläfli symbol or , constructed as 3 tesseracts, , around each cubic ridge. Related polytopes It is a part of an infinite hypercube family. The dual of a 5-cube is the 5-orthoplex, of the infinite family of orthoplexes. Applying an '' alternation'' operation, deleting alternating vertices of the 5-cube, creates another uniform 5-polytope, called a 5-demicube, which is also part of an infinite family called the demihypercubes. The 5-cube can be seen as an ''order-3 tesseractic honeycomb'' on a 4-sphere. It is related to the Euclidean 4-space (order-4) tesseractic honeycomb and paracompact hyperbolic honeycomb order-5 tesseractic honeycomb. As a configuration This configuration matrix represents the 5-cube. The rows and columns correspond to vertices, edges, faces, cells, and 4-face ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runcinated 5-orthoplexes
In five-dimensional geometry, a runcinated 5-orthoplex is a convex uniform 5-polytope with 3rd order truncation (runcination) of the regular 5-orthoplex. There are 8 runcinations of the 5-orthoplex with permutations of truncations, and cantellations. Four are more simply constructed relative to the 5-cube. Runcinated 5-orthoplex Alternate names * Runcinated pentacross * Small prismated triacontiditeron (Acronym: spat) (Jonathan Bowers) Coordinates The vertices of the can be made in 5-space, as permutations and sign combinations of: : (0,1,1,1,2) Images Runcitruncated 5-orthoplex Alternate names * Runcitruncated pentacross * Prismatotruncated triacontiditeron (Acronym: pattit) (Jonathan Bowers) Coordinates Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of a runcitruncated 5-orthoplex, centered at the origin, are all 80 vertices are sign (4) and coordinate (20) permutations of : (±3,±2,±1,±1,0) Images Runcicantellated 5-orthoplex Alternate names * Runcicantellated pent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |