|
Stargazing Darter
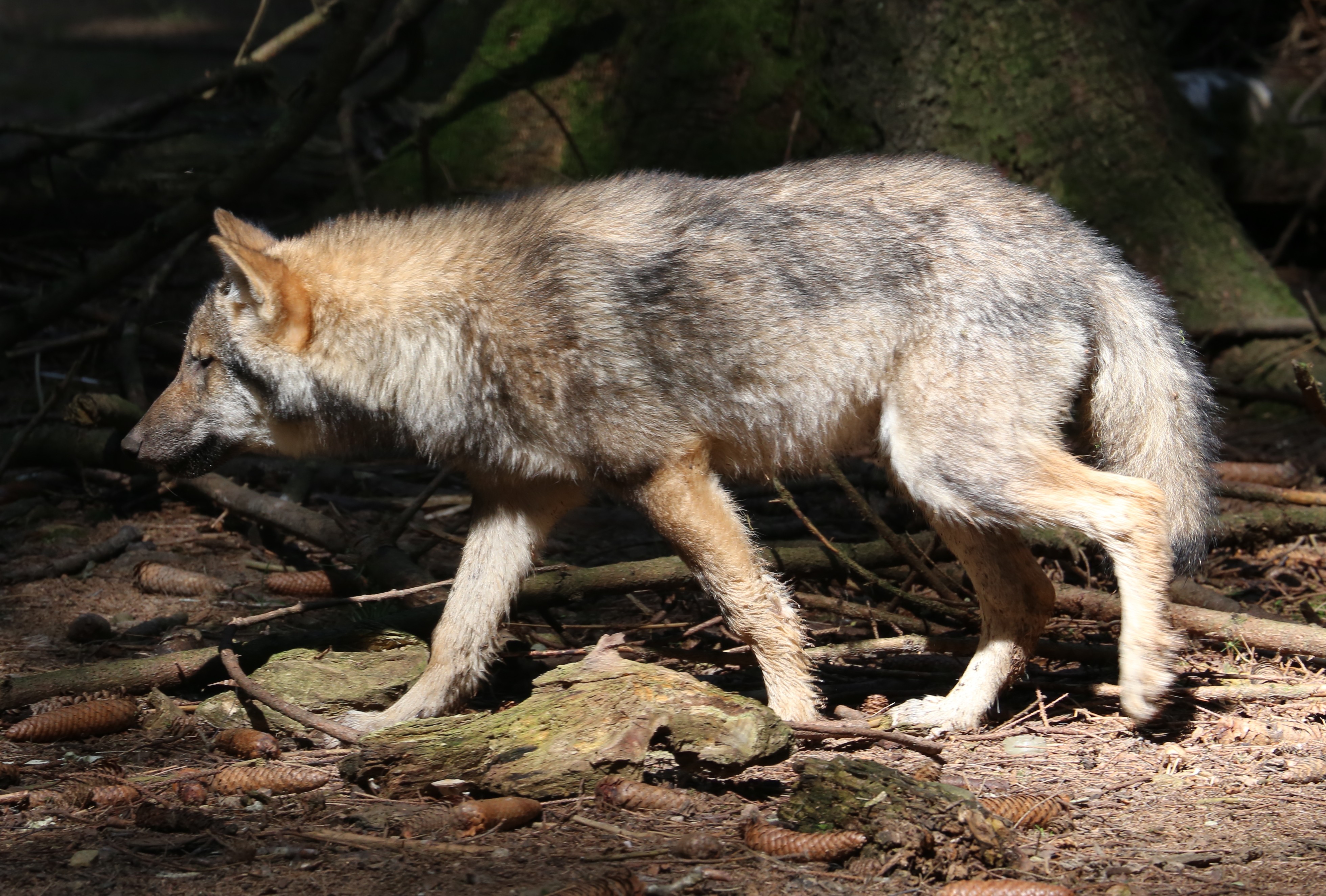
The stargazing darter (''Percina uranidea'') is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish, a darter from the subfamily Etheostomatinae, part of the Family (biology), family Percidae, which also contains the perches, Gymnocephalus, ruffes and Sander (fish), pikeperches. It is Endemism, endemic to the United States. In 2025, the snail darter (''Percina tanasi''), known for its political significance in the snail darter controversy, was determined to be an Allopatric speciation, allopatric eastern population of ''Percina uranidea''. This would expand the distribution of the stargazing darter to the eastern Tennessee River drainage. Geographic distribution Found in the St. Francis River, St. Francis, White River (Arkansas), White and Ouachita River drainages in Missouri, Arkansas and Louisiana; formerly in lower the Wabash River in Indiana and Illinois, where now Local extinction, extirpated. If the snail darter also belongs to this species, as determined by phylogenetic studies, then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Starr Jordan
David Starr Jordan (January 19, 1851 – September 19, 1931) was the founding president of Stanford University, serving from 1891 to 1913. He was an ichthyologist during his research career. Prior to serving as president of Stanford University, he served as president of Indiana University Bloomington, Indiana University from 1885 to 1891. Jordan was also a strong supporter of eugenics, and his published views expressed a fear of "race-degeneration", asserting that cattle and human beings are "governed by the same laws of selection". He was an antimilitarist since he believed that war killed off the best members of the gene pool, and he initially opposed American involvement in World War I. Early life and education Jordan was born in Gainesville (town), New York, Gainesville, New York, and grew up on a farm in upstate New York. His parents made an unorthodox decision to educate him at a local girls' high school. His middle name, Starr, does not appear in early census records, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allopatric Speciation
Allopatric speciation () – also referred to as geographic speciation, vicariant speciation, or its earlier name the dumbbell model – is a mode of speciation that occurs when biological populations become geographically isolated from each other to an extent that prevents or interferes with gene flow. Various geographic changes can arise such as the continental drift, movement of continents, and the formation of mountains, islands, bodies of water, or glaciers. Human activity such as agriculture or developments can also change the distribution of species populations. These factors can substantially alter a region's geography, resulting in the separation of a species population into isolated subpopulations. The vicariant populations then undergo Genetics, genetic changes as they become subjected to different Natural selection, selective pressures, experience genetic drift, and accumulate different mutations in the separated populations' gene pools. The barriers prevent t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By David Starr Jordan
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion, especially in the context of rank-based (" Linnaean") nomenclature (much less so under phylogenetic nomenclature). If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were presumably set forth in prehistoric times by hunter-gatherers, as suggested by the fairly sophisticated folk taxonomies. Much later, Aristotle, and later still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Described In 1887
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fins and a hard skull, but lacking limbs with digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all living cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single class (Pisces), modern phylogenetics views fish as a paraphyletic group. Most fish are cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large active swimmers like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature. Many fish can communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship displays. The study of fish is known as ichthyology. The earliest fish appeared during the Cambrian as small filter feeders; they continued to evolve through the Paleozoic, diversifying into many forms. The earliest fish wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percina
''Percina'' is a genus of small freshwater ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Etheostomatinae, which is part of the family Percidae. The Percidae family also includes the perches, ruffes and pikeperches from North America. Along with similar fishes in other genera, members of ''Percina'' are commonly known as " darters". More specifically, the genus as a whole is known as roughbelly darters, while certain species of ''Percina'' displaying vertical bars on their flanks are called logperches. Species There are currently 49 recognized species in this genus: * '' Percina antesella'' J. D. Williams & Etnier, 1978 (Amber darter) * '' Percina apristis'' C. L. Hubbs & Hubbs, 1954 (Guadalupe darter) * '' Percina aurantiaca'' Cope, 1868 (Tangerine darter) * '' Percina aurolineata'' Suttkus & Ramsey, 1967 (Goldline darter) * '' Percina aurora'' Suttkus & B. A. Thompson, 1994 (Pearl darter) * '' Percina austroperca'' B. A. Thompson, 1995 (Southern logperch) * '' Percina bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freshwater Fish Of The United States
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salt (chemistry), salts and other total dissolved solids. The term excludes seawater and brackish water, but it does include non-salty mineral water, mineral-rich waters, such as chalybeate springs. Fresh water may encompass frozen water, frozen and meltwater in ice sheets, ice caps, glaciers, snowfields and icebergs, natural precipitations such as rainfall, snowfall, hail/ice pellets, sleet and graupel, and surface runoffs that form inland bodies of water such as wetlands, ponds, lakes, rivers, streams, as well as groundwater contained in aquifers, subterranea (geography), subterranean subterranean river, rivers and underground lake, lakes. Water is critical to the survival of all living organisms. Many organisms can thrive on salt water, but the great majority of vascular plants and most insects, amphibians, reptiles, mammals and birds need fresh water to sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endangered Species Act Of 1973
The Endangered Species Act of 1973 (ESA; 16 U.S.C. § 1531 et seq.) is the primary law in the United States for protecting and conserving imperiled species. Designed to protect critically imperiled species from extinction as a "consequence of economic growth and development untempered by adequate concern and conservation", the ESA was signed into law by President Presidency of Richard Nixon#Environmental policy, Richard Nixon on December 28, 1973. The Supreme Court of the United States described it as "the most comprehensive legislation for the preservation of endangered species enacted by any nation"."Tennessee Valley Authority v. Hill" 437 U.S. 153 (1978) Retrieved 24 November 2015. The purposes of the ESA are two-fold: to prevent extinction and to recover species to the point wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Extinction
Local extinction, also extirpation, is the termination of a species (or other taxon) in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with extinction, global extinctions. Local extinctions mark a change in the ecology of an area. It has sometimes been followed by a replacement of the species taken from other locations, such as with wolf reintroduction. Discussion Glacial period, Glaciation is one factor that leads to local extinction. This was the case during the Quaternary glaciation, Pleistocene glaciation event in North America. During this period, most of the native North American species of earthworm were killed in places covered by glaciation. This left them open for colonization by European earthworms brought over in soil from Europe. Species naturally become extinct from islands over time; this can be either local extinction if the species also occurs elsewhere, or in cases of endemism, island endemism, outright ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wabash River
The Wabash River () is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed May 13, 2011 river that drains most of the state of Indiana, and a significant part of Illinois, in the United States. It flows from the headwaters in Ohio, near the Indiana border, then southwest across northern Indiana turning south near the Illinois border, where the southern portion forms the Indiana-Illinois border before flowing into the Ohio River. It is the largest northern tributary of the Ohio River and third largest overall, behind the Cumberland River, Cumberland and Tennessee River, Tennessee rivers. From the dam near Huntington, Indiana, to its terminus at the Ohio River, the Wabash flows freely for The Tippecanoe River, White River (Indiana), White River, Embarras River (Illinois), Embarras River and Little Wabash River are major tributaries. The river's name comes from a Miami-Illinois language, Miami word meaning "water over whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ouachita River
The Ouachita River ( ) is a river that runs south and east through the United States, U.S. U.S. state, states of Arkansas and Louisiana, joining the Tensas River to form the Black River (Louisiana), Black River near Jonesville, Louisiana. It is the List of longest rivers of the United States (by main stem), 25th-longest river in the United States (by main stem). Course The Ouachita River begins in the Ouachita Mountains near Mena, Arkansas. It flows east into Lake Ouachita, a reservoir created by Blakely Mountain Dam. The North Fork and South Fork of the Ouachita flow into Lake Ouachita to join the main stream. Portions of the river in this region flow through the Ouachita National Forest. From the lake, the Ouachita flows south into Lake Hamilton and Lake Catherine, Lake Hamilton, a reservoir created by Carpenter Dam, named after Flavius Josephus Carpenter. The city of Hot Springs, Arkansas, Hot Springs lies on the north side of Lake Hamilton. Another reservoir, Lake Hamilton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White River (Arkansas)
White River may refer to: Bodies of water Africa * Bakoy River, in West Africa, called the White River over a portion of its length Canada * White River (British Columbia) * White River (Vancouver Island), a river in the Discovery Passage–Johnstone Strait watersheds of British Columbia ** White River Provincial Park * White River (Nass River), a river in the Marcus Passage watershed of British Columbia * White River (Quebec) * White River (Yukon) * White River (Ontario) China * White River (China), an old name for the Hai River Dominica * White River (Dominica) Estonia * Valgejõgi, or "white river", in northern Estonia Iran * Sefīd-Rūd, or "the white river", in Gilan province Jamaica * White River (Jamaica), a river New Zealand * White River, New Zealand, a river in the South Island Montserrat * White River, Montserrat, a former river in Montserrat United Kingdom * St Austell River, a river in Cornwall also known as the White River Unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yale University
Yale University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in New Haven, Connecticut, United States. Founded in 1701, Yale is the List of Colonial Colleges, third-oldest institution of higher education in the United States, and one of the nine colonial colleges chartered before the American Revolution. Yale was established as the Collegiate School in 1701 by Congregationalism in the United States, Congregationalist clergy of the Connecticut Colony. Originally restricted to instructing ministers in theology and sacred languages, the school's curriculum expanded, incorporating humanities and sciences by the time of the American Revolution. In the 19th century, the college expanded into graduate and professional instruction, awarding the first Doctor of Philosophy, PhD in the United States in 1861 and organizing as a university in 1887. Yale's faculty and student populations grew rapidly after 1890 due to the expansion of the physical campus and its scientif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |