|
Spring Hare
''Pedetes'' is a genus of rodent, the springhares, in the family Pedetidae. Members of the genus are distributed across southern and Eastern Africa. Species A number of species both extant and extinct are classified in the genus ''Pedetes''. They include: * South African springhare or ''springhaas'' (''Pedetes capensis'') * East African springhare (''Pedetes surdaster'') * ''Pedetes laetoliensis'' (Davies, 1987) (Pliocene fossil) Throughout the 20th century, the living species (and occasionally the prehistoric one) were merged into ''P. capensis'', making the genus monotypic. Ecology These rodents are generally nocturnal and sleep through the day in burrows they dig. They feed on foliage, roots and other vegetable matter, and occasionally arthropods. Outside the burrow they usually move around by hopping on their hind legs. When only one springhare species was recognized, it was listed as vulnerable by the IUCN in 1996 due to an approximately 20% decrease in the population o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South African Springhare
The South African springhare (''Pedetes capensis'') () is a medium-sized terrestrial and burrowing rodent. Despite the name, it is not a hare. It is one of two extant species in the genus '' Pedetes'', and is native to southern Africa. Formerly, the genus was considered monotypic and the East African springhare (''P. surdaster'') was included in ''P. capensis''. Springhares live throughout semi-arid areas in southern Africa, preferentially in sandy plains and pans with short grasses. In agricultural areas, springhares can be considered a pest due to their destructive feeding on crops. However, they are not currently considered under an impending risk of extinction. Etymology and taxonomy The springhare was named in English by William John Burchell in 1822, who derived "springhare" from the Afrikaans name . The generic name ''Pedetes'' comes from the Greek (Pidités), meaning "leaper or dancer". The specific name ''capensis'', a Latin word meaning "of the Cape", refers to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muridae
The Muridae, or murids, are either the largest or second-largest family of rodents and of mammals, containing approximately 870 species, including many species of mice, rats, and gerbils found naturally throughout Eurasia, Africa, and Australia. The name Muridae comes from the Latin ' (genitive '), meaning "mouse", since all true mice belong to the family, with the more typical mice belonging to the genus ''Mus (genus), Mus''. Distribution and habitat Murids are found nearly everywhere in the world, though many subfamilies have narrower ranges. Murids are not found in Antarctica or many oceanic islands. Although none of them are native to the Americas, a few species, notably the house mouse and black rat, have been introduced worldwide. Murids occupy a broad range of ecosystems from tropical forests to tundras. Fossorial, arboreal, and semiaquatic murid species occur, though most are terrestrial animals. The extensive list of niches filled by murids helps to explain their relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedetes
''Pedetes'' is a genus of rodent, the springhares, in the family Pedetidae. Members of the genus are distributed across southern and Eastern Africa. Species A number of species both extant and extinct are classified in the genus ''Pedetes''. They include: * South African springhare or ''springhaas'' (''Pedetes capensis'') * East African springhare (''Pedetes surdaster'') * ''Pedetes laetoliensis'' (Davies, 1987) (Pliocene fossil) Throughout the 20th century, the living species (and occasionally the prehistoric one) were merged into ''P. capensis'', making the genus monotypic. Ecology These rodents are generally nocturnal and sleep through the day in burrows they dig. They feed on foliage, roots and other vegetable matter, and occasionally arthropods. Outside the burrow they usually move around by hopping on their hind legs. When only one springhare species was recognized, it was listed as vulnerable by the IUCN in 1996 due to an approximately 20% decrease in the population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convergent Evolution
Convergent evolution is the independent evolution of similar features in species of different periods or epochs in time. Convergent evolution creates analogous structures that have similar form or function but were not present in the last common ancestor of those groups. The cladistic term for the same phenomenon is Cladogram#Homoplasies, homoplasy. The recurrent evolution of flight is a classic example, as flying pterygota, insects, birds, pterosaurs, and bats have independently evolved the useful capacity of flight. Functionally similar features that have arisen through convergent evolution are ''analogous'', whereas ''homology (biology), homologous'' structures or traits have a common origin but can have dissimilar functions. Bird, bat, and pterosaur wings are analogous structures, but their forelimbs are homologous, sharing an ancestral state despite serving different functions. The opposite of convergence is divergent evolution, where related species evolve different trai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marsupial
Marsupials are a diverse group of mammals belonging to the infraclass Marsupialia. They are natively found in Australasia, Wallacea, and the Americas. One of marsupials' unique features is their reproductive strategy: the young are born in a relatively undeveloped state and then nurtured within a pouch on their mother's abdomen. Extant marsupials encompass many species, including Kangaroo, kangaroos, Koala, koalas, Opossum, opossums, Phalangeriformes, possums, Tasmanian devil, Tasmanian devils, Wombat, wombats, Wallaby, wallabies, and Bandicoot, bandicoots. Marsupials constitute a clade stemming from the last common ancestor of extant Metatheria, which encompasses all mammals more closely related to marsupials than to Placentalia, placentals. The evolutionary split between placentals and marsupials occurred 125-160 million years ago, in the Middle Jurassic-Early Cretaceous period. Presently, close to 70% of the 334 extant marsupial species are concentrated on the Australian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kultarr
The kultarr (''Antechinomys laniger'') (also called the "jerboa-marsupial" or marsupial jerboa) is a small insectivorous nocturnal marsupial inhabiting the arid interior of Australia. Preferred habitat includes stony deserts, shrubland, woodland, grassland and open plains.Van Dyck, S., Strahan, R., 2008. The mammals of Australia / edited by Steve van Dyck and Ronald Strahan. The kultarr has a range of adaptations to help cope with Australia's harsh arid environment including torpor similar to hibernation that helps conserve energy. The species has declined across its former range since European settlement due to changes in land management practices and introduced predators.Menkhorst, P., 2004. A field guide to the mammals of Australia / Peter Menkhorst, Frank Knight. Description The kultarr is a small carnivorous marsupial of the family Dasyuridae with unique morphological features. It is nocturnal, hunting a variety of invertebrates including spiders, crickets and cockroaches. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heteromyid
Heteromyidae is a family of rodents consisting of kangaroo rats, kangaroo mice, pocket mice and spiny pocket mice. Most heteromyids live in complex burrows within the deserts and grasslands of western North America, though species within the genus ''Heteromys'' are also found in forests and their range extends as far south as northern South America. They feed mostly on seeds and other plant parts, which they carry in their fur-lined cheek pouches to their burrows. Although they are very different in physical appearance, the closest relatives of the heteromyids are pocket gophers in the family Geomyidae. Description There are about fifty-nine members of the family Heteromyidae divided among six genera. They are all small rodents, the largest being the giant kangaroo rat (''Dipodomys ingens'') with a body length of and a tail a little longer than this. In many species the tail is tufted and is mainly used for balance. Other adaptations include partially fused vertebrae in the nec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kangaroo Rat
Kangaroo rats, small mostly nocturnal rodents of genus ''Dipodomys'', are native to arid areas of western North America. The common name derives from their bipedal form. They hop in a manner similar to the much larger kangaroo, but developed this mode of locomotion independently, like several other clades of rodents (e.g., dipodids and hopping mice). Description Kangaroo rats are four or five-toed heteromyid rodents with big hind legs, small front legs, and relatively large heads. Adults typically weigh between Nader, I.A. 1978"Kangaroo rats: Intraspecific Variation in ''Dipodomus spectabilis'' Merriami and ''Dipodomys deserti'' Stephens" ''Illinois biological monographs''; 49: 1-116. Chicago, University of Illinois Press. The tail of a kangaroo rat is longer than its body and head combined. Another notable feature of kangaroo rats is their fur-lined cheek pouches, which are used for storing food. The coloration of kangaroo rats varies from cinnamon buff to dark gray, depend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kangaroo Mouse
A kangaroo mouse is either one of the two species of jumping mouse (genus ''Microdipodops'') native to the deserts of the southwestern United States, predominantly found in the state of Nevada. The name "kangaroo mouse" refers to the species' extraordinary jumping ability, similar to the much larger kangaroo. The two species are: * Dark kangaroo mouse – ''Microdipodops megacephalus'' * Pale kangaroo mouse – ''Microdipodops pallidus'' Both species of kangaroo mouse live in sandy desert ecosystems, and forage for seeds and vegetation amongst the scrub brush of their native habitat. The dark kangaroo mouse is also known to feed occasionally on insects and carrion. The mouse rarely drinks water, instead deriving it metabolically from the foods it eats. The kangaroo mouse collects food and maintains large caches in their burrows, which are excavated to a length of between 3 and 8 feet (1 to 2.5 meters). The burrow, the entrance to which the mouse covers during daylight hours, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jumping Mouse
Zapodidae, the jumping mice, is a family of mouse-like rodents in North America and China. Although mouse-like in general appearance, these rodents are distinguished by their elongated hind limbs, and, typically, by the presence of four pairs of cheek-teeth in each jaw. There are five toes to all the feet, but the first in the fore-feet is rudimentary, and furnished with a flat nail. The tail makes up about 60% of its body length and is used to gain balance while jumping. The cheeks have pouches. The Sichuan jumping "yeti" mouse ('' Eozapus setchuanus'') from China can be identified by the ‘Y’ marking on its belly. Jumping mice live in wooded areas, grassy fields and alpine meadows. When disturbed, they can leap eight to ten feet at a time, diminishing to three to four as they widen the gap between them and any pursuer. They are nocturnal and generally live alone. Nests are often found in clefts of rocks, among timber, or in hollow trees. Typically, they will have two to thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
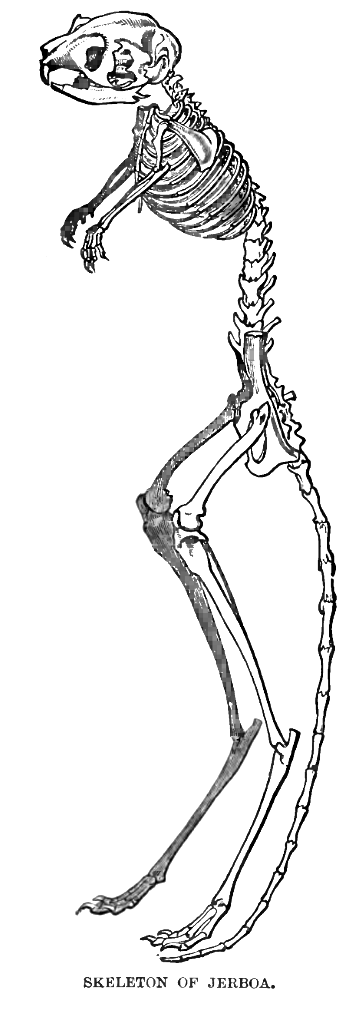
Dipodid
Jerboas () are the members of the family Dipodidae. They are hopping desert rodents found throughout North Africa and Asia. They tend to live in hot deserts. When chased, jerboas can run at up to . Some species are preyed on by little owls (''Athene noctua'') in central Asia. Most species of jerboas have excellent hearing that they use to avoid becoming the prey of nocturnal predators. The typical lifespan of a jerboa is around 2–3 years. Taxonomy Jerboas, as previously defined, were thought to be paraphyletic, with the jumping mice (Zapodidae) and birch mice (Sminthidae) also being classified in the family Dipodidae. However, phylogenetic analysis split all three as distinct families, leaving just the jerboas in Dipodidae and revealing them to be a monophyletic group. This animal has a body length (including the head) of between , with an additional of tail, which is always longer than the full body. Jerboa dental records reveal a slow increase in crown heights, which cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |