|
Spongiome
A contractile vacuole (CV) is a sub-cellular structure (organelle) involved in osmoregulation. It is found predominantly in protists, including unicellular algae. It was previously known as pulsatile or pulsating vacuole. Overview The contractile vacuole is a specialized type of vacuole that regulates the quantity of water inside a cell. In freshwater environments, the concentration of solutes is hypotonic, lower outside than inside the cell. Under these conditions, osmosis causes water to accumulate in the cell from the external environment. The contractile vacuole acts as part of a protective mechanism that prevents the cell from absorbing too much water and possibly lysing (rupturing) through excessive internal pressure. The contractile vacuole, as its name suggests, expels water out of the cell by contracting. The growth (water gathering) and contraction (water expulsion) of the contractile vacuole are periodical. One cycle takes several seconds, depending on the species an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protists
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any Eukaryote, eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, Embryophyte, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a Clade, natural group, or clade, but are a Paraphyly, paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancestor excluding land plants, animals, and fungi. Protists were historically regarded as a separate taxonomic rank, taxonomic kingdom (biology), kingdom known as Protista or Protoctista. With the advent of phylogenetic analysis and electron microscopy studies, the use of Protista as a formal taxon was gradually abandoned. In modern classifications, protists are spread across several eukaryotic clades called supergroup (biology), supergroups, such as Archaeplastida (photoautotrophs that includes land plants), SAR supergroup, SAR, Obazoa (which includes fungi and animals), Amoebozoa and "Excavata". Protists represent an extremely large genetic diversity, genetic and ecological diversity in all environments, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
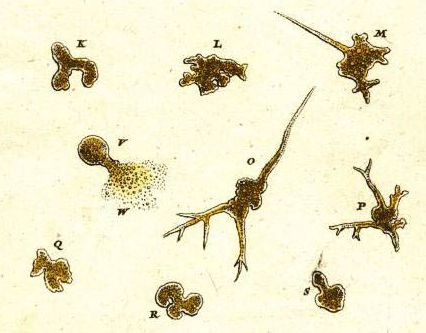
Vacuole
A vacuole () is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in Plant cell, plant and Fungus, fungal Cell (biology), cells and some protist, animal, and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic molecules including enzymes in Solutes, solution, though in certain cases they may contain solids which have been engulfed. Vacuoles are formed by the fusion of multiple membrane Vesicle (biology), vesicles and are effectively just larger forms of these. The organelle has no basic shape or size; its structure varies according to the requirements of the cell. Discovery Antonie van Leeuwenhoek described the plant vacuole in 1676. Contractile vacuoles ("stars") were first observed by Spallanzani (1776) in protozoa, although mistaken for respiratory organs. Félix Dujardin, Dujardin (1841) named these "stars" as ''vacuoles''. In 1842, Matthias Jakob Schleiden, Schleiden applied the term for plant cells, to dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paramecium Contractile Vacuoles
''Paramecium'' ( , , plural "paramecia" only when used as a Common name, vernacular name) is a genus of eukaryotic, unicellular ciliates, widespread in freshwater, brackish, and Ocean, marine environments. Paramecia are often abundant in stagnant basins and ponds. Because some species are readily cultivated and easily induced to sexual conjugation, conjugate and divide, they have been widely used in classrooms and laboratories to study biological processes. ''Paramecium'' species are commonly studied as model organisms of the ciliate group and have been characterized as the "laboratory rat, white rats" of the phylum Ciliophora. Historical background ''Paramecium'' were among the first ciliates to be observed by microscopy, microscopists, in the late 17th century. They were most likely known to the Dutch pioneer of protozoology, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, and were clearly described by his contemporary Christiaan Huygens in a letter from 1678. The earliest known illustration of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoeba (genus)
''Amoeba'' is a genus of single-celled amoeboids in the family Amoebidae. The type species of the genus is '' Amoeba proteus'', a common freshwater organism, widely studied in classrooms and laboratories. History and classification The earliest record of an organism resembling ''Amoeba'' was produced in 1755 by August Johann Rösel von Rosenhof, who named his discovery "''der kleine Proteus''" ("the little Proteus"), after Proteus, the shape-shifting sea-god of Greek Mythology. While Rösel's illustrations show a creature similar in appearance to the one now known as ''Amoeba proteus, ''his "little Proteus'' cannot be identified confidently with any modern species. The term "Proteus animalcule" remained in use throughout the 18th and 19th centuries, as an informal name for any large, free-living amoeboid. In 1758, apparently without seeing Rösel's "Proteus" for himself, Carl Linnaeus included the organism in his own system of classification, under the name ''Volvox cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multicellular
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell (biology), cell, unlike unicellular organisms. All species of animals, Embryophyte, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially uni- and partially multicellular, like slime molds and social Amoeba, amoebae such as the genus ''Dictyostelium''. Multicellular organisms arise in various ways, for example by cell division or by aggregation of many single cells. Colonial organisms are the result of many identical individuals joining together to form a colony (biology), colony. However, it can often be hard to separate colonial protists from true multicellular organisms, because the two concepts are not distinct; colonial protists have been dubbed "pluricellular" rather than "multicellular". There are also macroscopic organisms that are multinucleate though technically unicellular, such as the Xenophyophorea that can reach 20 cm. Evolutionary history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution
Evolution is the change in the heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, resulting in certain characteristics becoming more or less common within a population over successive generations. The process of evolution has given rise to biodiversity at every level of biological organisation. The scientific theory of evolution by natural selection was conceived independently by two British naturalists, Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace, in the mid-19th century as an explanation for why organisms are adapted to their physical and biological environments. The theory was first set out in detail in Darwin's book ''On the Origin of Species''. Evolution by natural selection is established by observable facts about living organisms: (1) more offspring are often produced than can possibly survive; (2) phenotypic variatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Wall
A cell wall is a structural layer that surrounds some Cell type, cell types, found immediately outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. Primarily, it provides the cell with structural support, shape, protection, and functions as a selective barrier. Another vital role of the cell wall is to help the cell withstand osmotic pressure and mechanical stress. While absent in many eukaryotes, including animals, cell walls are prevalent in other organisms such as fungi, algae and plants, and are commonly found in most Prokaryote, prokaryotes, with the exception of Mollicutes, mollicute bacteria. The composition of cell walls varies across taxonomic groups, species, cell type, and the cell cycle. In Embryophyte, land plants, the primary cell wall comprises Polysaccharide, polysaccharides like cellulose, hemicelluloses, and pectin. Often, other Polymer, polymers such as lignin, suberin or cutin are anchored to or embedded in plant cell walls. Algae exhibit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasite
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson characterised parasites' way of feeding as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as Armillaria mellea, honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the Orobanchaceae, broomrapes. There are six major parasitic Behavioral ecology#Evolutionarily stable strategy, strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), wikt:trophic, trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic scale, microscopic size, which may exist in its unicellular organism, single-celled form or as a Colony (biology)#Microbial colonies, colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from antiquity, with an early attestation in Jain literature authored in 6th-century BC India. The scientific study of microorganisms began with their observation under the microscope in the 1670s by Anton van Leeuwenhoek. In the 1850s, Louis Pasteur found that microorganisms caused food spoilage, debunking the theory of spontaneous generation. In the 1880s, Robert Koch discovered that microorganisms caused the diseases tuberculosis, cholera, diphtheria, and anthrax. Microorganisms are extremely diverse, representing most unicellular organisms in all three domains of life: two of the three domains, Archaea and Bacteria, only contain microorganisms. The third domain, Eukaryota, includes all multicellular o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, water, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms. Some scientific definitions distinguish dirt from ''soil'' by restricting the former term specifically to displaced soil. Soil consists of a solid collection of minerals and organic matter (the soil matrix), as well as a porous phase that holds gases (the soil atmosphere) and water (the soil solution). Accordingly, soil is a three- state system of solids, liquids, and gases. Soil is a product of several factors: the influence of climate, relief (elevation, orientation, and slope of terrain), organisms, and the soil's parent materials (original minerals) interacting over time. It continually undergoes development by way of numerous physical, chemical and biological processes, which include weathering with associated erosion. Given its complexity and strong internal connectedness, soil ecologists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine (ocean)
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of Earth. The ocean is conventionally divided into large bodies of water, which are also referred to as ''oceans'' (the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Antarctic/Southern, and Arctic Ocean),"Ocean." ''Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary'', Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/ocean . Accessed March 14, 2021. and are themselves mostly divided into seas, gulfs and subsequent bodies of water. The ocean contains 97% of [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have been proposed to define what an organism is. Among the most common is that an organism has autonomous reproduction, Cell growth, growth, and metabolism. This would exclude viruses, despite the fact that they evolution, evolve like organisms. Other problematic cases include colonial organisms; a colony of eusocial insects is organised adaptively, and has Germ-Soma Differentiation, germ-soma specialisation, with some insects reproducing, others not, like cells in an animal's body. The body of a siphonophore, a jelly-like marine animal, is composed of organism-like zooids, but the whole structure looks and functions much like an animal such as a jellyfish, the parts collaborating to provide the functions of the colonial organism. The evolutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |