|
Splice Site Mutation
A splice site mutation is a genetic mutation that inserts, deletes or changes a number of nucleotides in the specific site at which splicing takes place during the processing of precursor messenger RNA into mature messenger RNA. Splice site consensus sequences that drive exon recognition are located at the very termini of introns. The deletion of the splicing site results in one or more introns remaining in mature mRNA and may lead to the production of abnormal proteins. When a splice site mutation occurs, the mRNA transcript possesses information from these introns that normally should not be included. Introns are supposed to be removed, while the exons are expressed. The mutation must occur at the specific site at which intron splicing occurs: within non-coding sites in a gene, directly next to the location of the exon. The mutation can be an insertion, deletion, frameshift, etc. The splicing process itself is controlled by the given sequences, known as splice-donor and spl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinians, Augustinian friar working in the 19th century in Brno, was the first to study genetics scientifically. Mendel studied "trait inheritance", patterns in the way traits are handed down from parents to offspring over time. He observed that organisms (pea plants) inherit traits by way of discrete "units of inheritance". This term, still used today, is a somewhat ambiguous definition of what is referred to as a gene. Phenotypic trait, Trait inheritance and Molecular genetics, molecular inheritance mechanisms of genes are still primary principles of genetics in the 21st century, but modern genetics has expanded to study the function and behavior of genes. Gene structure and function, variation, and distribution are studied within the context of the Cell (bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Split Gene Theory
Split(s) or The Split may refer to: Places * Split, Croatia, the largest coastal city in Croatia * Split Island, Canada, an island in the Hudson Bay * Split Island, Falkland Islands * Split Island, Fiji, better known as Hạfliua Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Split'' (1989 film), a science fiction film * ''Split'' (2016 American film), a psychological horror thriller film * ''Split'' (2016 Canadian film), also known as ''Écartée'', a Canadian drama film directed by Lawrence Côté-Collins * ''Split'' (2016 South Korean film), a sports drama film * '' Split: A Divided America'', a 2008 documentary on American politics * ''The Split'' (film), a 1968 heist film * ''The Split'', or ''The Manster'', a U.S.-Japanese horror film Games * Split (poker), the division of winnings in the card game * Split (blackjack), a possible player decision in the card game Music Albums * ''Split'' (The Groundhogs album), 1971 * ''Split'' (Lush album), 1994 * ''Split'' (Patricia B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-thalassemia
Beta-thalassemia (β-thalassemia) is an inherited blood disorder, a form of thalassemia resulting in variable outcomes ranging from clinically asymptomatic to severe anemia individuals. It is caused by reduced or absent synthesis of the beta chains of hemoglobin, the molecule that carries oxygen in the blood. Symptoms depend on the extent to which hemoglobin is deficient, and include anemia, pallor, tiredness, enlargement of the spleen, jaundice, and gallstones. In severe cases death ensues. Beta thalassemia occurs due to a mutation of the HBB gene leading to deficient production of the hemoglobin subunit beta-globin; the severity of the disease depends on the nature of the mutation, and whether or not the mutation is homozygous. The body's inability to construct beta-globin leads to reduced or zero production of adult hemoglobin thus causing anemia. The other component of hemoglobin, alpha-globin, accumulates in excess leading to ineffective production of red blood cells, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Disease
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosome abnormality. Although polygenic disorders are the most common, the term is mostly used when discussing disorders with a single genetic cause, either in a gene or chromosome. The mutation responsible can occur spontaneously before embryonic development (a ''de novo'' mutation), or it can be inherited from two parents who are carriers of a faulty gene (autosomal recessive inheritance) or from a parent with the disorder (autosomal dominant inheritance). When the genetic disorder is inherited from one or both parents, it is also classified as a hereditary disease. Some disorders are caused by a mutation on the X chromosome and have X-linked inheritance. Very few disorders are inherited on the Y chromosome or mitochondrial DNA (due to their size). There are well over 6,000 known genetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
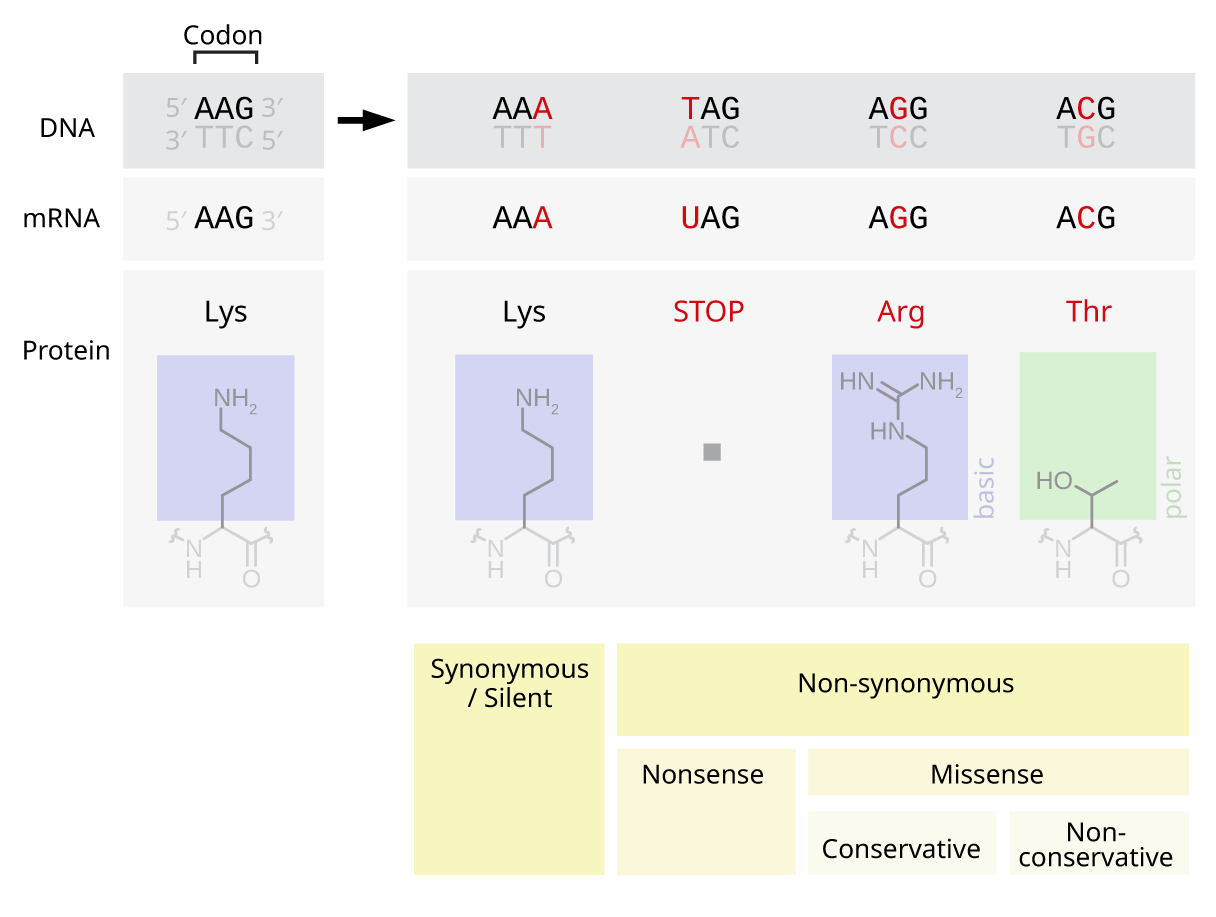
Point Mutation
A point mutation is a genetic mutation where a single nucleotide base is changed, inserted or deleted from a DNA or RNA sequence of an organism's genome. Point mutations have a variety of effects on the downstream protein product—consequences that are moderately predictable based upon the specifics of the mutation. These consequences can range from no effect (e.g. Synonymous substitution, synonymous mutations) to deleterious effects (e.g. frameshift mutations), with regard to protein production, composition, and function. Causes Point mutations usually take place during DNA replication. DNA replication occurs when one double-stranded DNA molecule creates two single strands of DNA, each of which is a template for the creation of the complementary strand. A single point mutation can change the whole DNA sequence. Changing one purine or pyrimidine may change the amino acid that the nucleotides code for. Point mutations may arise from spontaneous mutations that occur during DNA re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Febrile Seizures
A febrile seizure, also known as a fever fit or febrile convulsion, is a seizure associated with a high body temperature but without any serious underlying health issue. They most commonly occur in children between the ages of 6 months and 5 years. Most seizures are less than five minutes in duration, and the child is completely back to normal within an hour of the event. There are two types: simple febrile seizures and complex febrile seizures. Simple febrile seizures involve an otherwise healthy child who has at most one tonic-clonic seizure lasting less than 15 minutes in a 24-hour period. Complex febrile seizures have focal symptoms, last longer than 15 minutes, or occur more than once within 24 hours. About 80% are classified as simple febrile seizures. Febrile seizures are triggered by fever, typically due to a viral infection. They may run in families. The underlying mechanism is not fully known, but it is thought to involve genetics, environmental factors, brain immatu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transversion
Transversion, in molecular biology, refers to a point mutation in DNA in which a single (two ring) purine ( A or G) is changed for a (one ring) pyrimidine ( T or C), or vice versa. A transversion can be spontaneous, or it can be caused by ionizing radiation or alkylating agents. It can only be reversed by a spontaneous reversion. Ratio of transitions to transversions Although there are two possible transversions but only one possible transition per base, transition mutations are more likely than transversions because substituting a single ring structure for another single ring structure is more likely than substituting a double ring for a single ring. Also, transitions are less likely to result in amino acid substitutions (due to wobble base pair), and are therefore more likely to persist as "silent substitutions" in populations as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). A transversion usually has a more pronounced effect than a transition because the second and third nucle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystatin B
Cystatin-B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CSTB'' gene. The cystatin superfamily encompasses proteins that contain multiple cystatin-like sequences. Some of the members are active cysteine protease inhibitors, while others have lost or perhaps never acquired this inhibitory activity. There are three inhibitory families in the superfamily, including the type 1 cystatins (stefins), type 2 cystatins and kininogens. This gene encodes a stefin that functions as an intracellular cysteine protease inhibitor. The protein is able to form a dimer stabilized by noncovalent forces, inhibiting papain and cathepsins L, H and B. The protein is thought to play a role in protecting against the proteases leaking from lysosomes. Evidence indicates that mutations in this gene are responsible for the primary defects in patients with Unverricht–Lundborg disease, a form of progressive myoclonic epilepsy (EPM1). Interactions Cystatin B has been shown to interact with Cathepsin B. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stop Codon
In molecular biology, a stop codon (or termination codon) is a codon (nucleotide triplet within messenger RNA) that signals the termination of the translation process of the current protein. Most codons in messenger RNA correspond to the addition of an amino acid to a growing polypeptide chain, which may ultimately become a protein; stop codons signal the termination of this process by binding release factors, which cause the ribosomal subunits to disassociate, releasing the amino acid chain. While start codons need nearby sequences or initiation factors to start translation, a stop codon alone is sufficient to initiate termination. Properties Standard codons In the standard genetic code, there are three different termination codons: Alternative stop codons There are variations on the standard genetic code, and alternative stop codons have been found in the mitochondrial genomes of vertebrates, '' Scenedesmus obliquus'', and '' Thraustochytrium''. Reassigned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activation-induced Cytidine Deaminase
Activation-induced cytidine deaminase, also known as AICDA, AID and single-stranded DNA cytosine deaminase, is a 24 kDa enzyme which in humans is encoded by the ''AICDA'' gene. It creates mutations in DNA by deamination of cytosine base, which turns it into uracil (which is recognized as a thymine). In other words, it changes a C:G base pair into a U:G mismatch. The cell's DNA replication machinery recognizes the U as a T, and hence C:G is converted to a T:A base pair. During germinal center development of B lymphocytes, error-prone DNA repair following AID action also generates other types of mutations, such as C:G to A:T. AID is a member of the APOBEC family. In B cells in the lymph nodes, AID causes mutations that produce antibody diversity, but that same mutation process can also lead to B cell lymphoma. Function This gene encodes a DNA-editing deaminase that is a member of the cytidine deaminase family. The protein is involved in somatic hypermutation, gene conver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD79B
CD79b molecule, immunoglobulin-associated beta, also known as CD79B (Cluster of Differentiation 79B), is a human gene. It is associated with agammaglobulinemia-6. The B lymphocyte antigen receptor is a multimeric complex that includes the antigen-specific component, surface immunoglobulin (Ig). Surface Ig non-covalently associates with two other proteins, Ig-alpha and Ig-beta, which are necessary for expression and function of the B-cell antigen receptor. This gene encodes the Ig-beta protein of the B-cell antigen component. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described. See also * Cluster of differentiation The cluster of differentiation (also known as cluster of designation or classification determinant and often abbreviated as CD) is a protocol used for the identification and investigation of cell surface molecules providing targets for immunophe ... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BCL7A
B-cell CLL/lymphoma 7 protein family member A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BCL7A gene located in the chromosome 12 (Cytogenetic band'':'' 12q24.31). Function This gene codifies for a protein that belongs to the SWI/SNF chromatin remodelling complex, a complex that is able to modify the interations between DNA and histones using the energy of the ATP hydrolysis. It has found recurrently mutated in lymphomas and silenced by promoter hypermetylation in haematological malignancies. See also * B-cell lymphoma The B-cell lymphomas are types of lymphoma affecting B cells. Lymphomas are Tumors of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues, "blood cancers" in the lymph nodes. They develop more frequently in older adults and in immunocompromised individuals. ... References Further reading * * * * * * * {{gene-12-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |