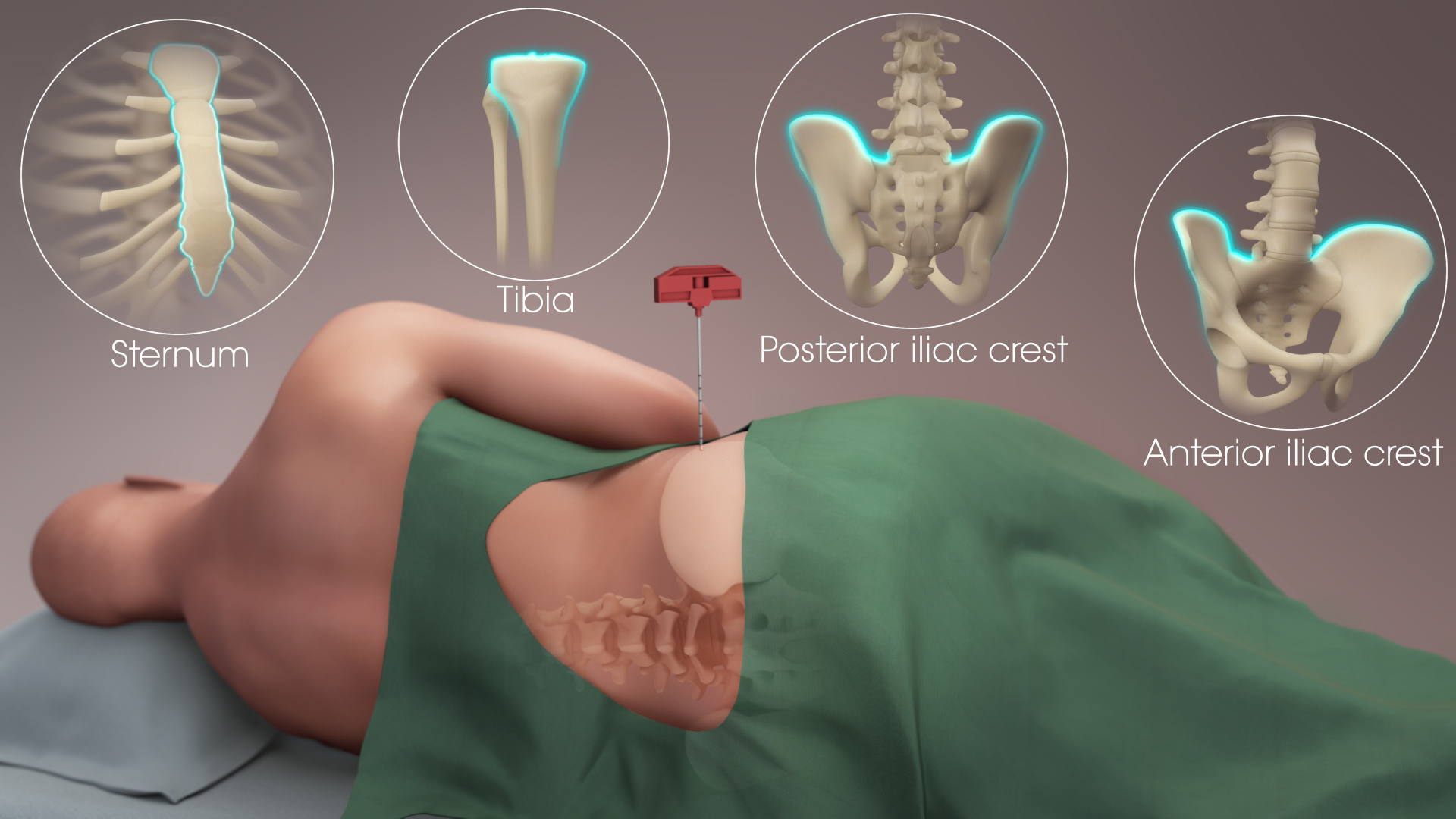
|
Splenectomy
A splenectomy is the surgical procedure that partially or completely removes the spleen. The spleen is an important organ in regard to immunological function due to its ability to efficiently destroy encapsulated bacteria. Therefore, removal of the spleen runs the risk of overwhelming post-splenectomy infection, a medical emergency and rapidly fatal disease caused by the inability of the body's immune system to properly fight infection following splenectomy or asplenia. Common indications for splenectomy include trauma, tumors, splenomegaly or for hematological disease such as sickle cell anemia or thalassemia. Indications The spleen is an organ located in the abdomen next to the stomach. It is composed of red pulp which filters the blood, removing foreign material, damaged and worn out red blood cells. It also functions as a storage site for iron, red blood cells and platelets. The rest (~25%) of the spleen is known as the white pulp and functions like a large lymph n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asplenia
Asplenia is the absence of normal spleen function and is associated with some serious infection risks. Hyposplenism is the condition of reduced ('hypo-'), but not absent, splenic functioning. ''Functional'' asplenia occurs when splenic tissue is present but does not work well (e.g. sickle-cell disease, polysplenia) such patients are managed as if asplenic while in ''anatomic'' asplenia, the spleen itself is absent. Causes Congenital * Congenital asplenia is rare. There are two distinct types of genetic disorders: heterotaxy syndromeOnline Mendelian Inheritance in Man. OMIM entry 208530: Right atrial isomerism; RAI. Johns Hopkins University/ref> and isolated congenital asplenia.Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man. Johns Hopkins UniversityOMIM entry 271400: Asplenia, isolated congenital; ICAS. * polysplenia Acquired Acquired asplenia occurs for several reasons: * Following splenectomy due to splenic rupture from trauma or because of tumor * After splenectomy with the ''goal'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overwhelming Post-splenectomy Infection
An overwhelming post-splenectomy infection (OPSI) is a rare but rapidly fatal infection occurring in individuals following removal (or permanent dysfunction) of the spleen. The infections are typically characterized by either meningitis or sepsis, and are caused by encapsulated organisms including ''Streptococcus pneumoniae''. It is a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment. Death has been reported to occur within 12 hours. The spleen is necessary for protection against encapsulated bacteria (see Mechanism) and as such when removed by splenectomy it can lead to rapid unchallenged infection by encapsulated bacteria. The rapid progression from mild viral symptoms to sepsis is one of the things that makes OPSI particularly dangerous. Another source of infection are species of ''Babesia'', which are tick-borne parasites that cause babesiosis. Signs and symptoms OPSI may initially present with mild viral symptoms such as fever or coughing, however later in infection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spleen
The spleen (, from Ancient Greek '' σπλήν'', splḗn) is an organ (biology), organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The spleen plays important roles in regard to red blood cells (erythrocytes) and the immune system. It removes old red blood cells and holds a reserve of blood, which can be valuable in case of Shock (circulatory), hemorrhagic shock, and also Human iron metabolism, recycles iron. As a part of the mononuclear phagocyte system, it metabolizes hemoglobin removed from senescent red blood cells. The globin portion of hemoglobin is degraded to its constitutive amino acids, and the heme portion is metabolized to bilirubin, which is removed in the liver. The spleen houses antibody-producing lymphocytes in its white pulp and monocytes which remove antibody-coated bacteria and antibody-coated blood cells by way of blood and lymph node circulation. These monocytes, upon moving to injured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splenomegaly
Splenomegaly is an enlargement of the spleen. The spleen usually lies in the left upper quadrant (LUQ) of the human abdomen. Splenomegaly is one of the four cardinal signs of ''hypersplenism'' which include: some reduction in number of circulating blood cells affecting granulocytes, erythrocytes or platelets in any combination; a compensatory proliferative response in the bone marrow; and the potential for correction of these abnormalities by splenectomy. Splenomegaly is usually associated with increased workload (such as in hemolytic anemias), which suggests that it is a response to hyperfunction. It is therefore not surprising that splenomegaly is associated with any disease process that involves abnormal red blood cells being destroyed in the spleen. Other common causes include congestion due to portal hypertension and infiltration by leukemias and lymphomas. Thus, the finding of an enlarged spleen, along with caput medusae, is an important sign of portal hypertension ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splenic Injury
A splenic injury, which includes a ruptured spleen, is any injury to the spleen. The rupture of a normal spleen can be caused by trauma, such as a traffic collision. Signs and symptoms In minor injuries with little bleeding, there may be abdominal pain, tenderness in the epigastrium and pain in the left flank. Often there is a sharp pain in the left shoulder, known as Kehr's sign. In larger injuries with more extensive bleeding, signs of hypovolemic shock are most prominent. This might include a rapid pulse, low blood pressure, rapid breathing, and paleness. Causes The most common cause of a ruptured spleen is blunt abdominal trauma, such as in traffic collisions or sports accidents. Direct, penetrating injuries, for example, stab or gunshot wounds are rare. Non-traumatic causes are less common. These include infectious diseases, medical procedures such as colonoscopy, haematological diseases, medications, and pregnancy. In less than one percent of cases of infectious mono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle cell disease (SCD), also simply called sickle cell, is a group of inherited Hemoglobinopathy, haemoglobin-related blood disorders. The most common type is known as sickle cell anemia. Sickle cell anemia results in an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying protein haemoglobin found in red blood cells. This leads to the red blood cells adopting an abnormal sickle-like shape under certain circumstances; with this shape, they are unable to deform as they pass through Capillary, capillaries, causing blockages. Problems in sickle cell disease typically begin around 5 to 6 months of age. A number of health problems may develop, such as attacks of pain (known as a sickle cell crisis) in joints, anemia, swelling in the hands and feet, bacterial infections, dizziness and stroke. The probability of severe symptoms, including long-term pain, increases with age. Without treatment, people with SCD rarely reach adulthood but with good healthcare, median life expectancy is between 58 and 66 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia; pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and produce high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or '' leukemia cells''. Symptoms may include bleeding and bruising, bone pain, fatigue, fever, and an increased risk of infections. These symptoms occur due to a lack of normal blood cells. Diagnosis is typically made by blood tests or bone marrow biopsy. The exact cause of leukemia is unknown. A combination of genetic factors and environmental (non-inherited) factors are believed to play a role. Risk factors include smoking, ionizing radiation, petrochemicals (such as benzene), prior chemotherapy, and Down syndrome. People with a family history of leukemia are also at higher risk. There are four main types of leukemia—acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and chronic myelo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platelet
Platelets or thrombocytes () are a part of blood whose function (along with the coagulation#Coagulation factors, coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping to form a thrombus, blood clot. Platelets have no cell nucleus; they are fragments of cytoplasm from megakaryocytes which reside in bone marrow or Lung, lung tissue, and then enter the circulation. Platelets are found only in mammals, whereas in other vertebrates (e.g. birds, amphibians), thrombocytes circulate as intact agranulocyte, mononuclear cells. One major function of platelets is to contribute to hemostasis: the process of stopping bleeding at the site where the lining of vessels (endothelium) has been interrupted. Platelets gather at the site and, unless the interruption is physically too large, they plug the hole. First, platelets attach to substances outside the interrupted endothelium: ''adhesion (medicine), adhesion''. Second, they change shape, turn on receptors and secret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalassemia
Thalassemias are a group of Genetic disorder, inherited blood disorders that manifest as the production of reduced hemoglobin. Symptoms depend on the type of thalassemia and can vary from none to severe, including death. Often there is mild to severe anemia (low red blood cells or hemoglobin) as thalassemia can affect the production of red blood cells and also affect how long the red blood cells live. Symptoms include fatigue (medical), tiredness, pallor, bone problems, an splenomegaly, enlarged spleen, jaundice, pulmonary hypertension, and dark urine. A child's growth and development may be slower than normal. Thalassemias are genetic disorders. Alpha thalassemia is caused by deficient production of the Hemoglobin subunit alpha, alpha globin component of hemoglobin, while beta thalassemia is a deficiency in the Hemoglobin subunit beta, beta globin component. The severity of alpha and beta thalassemia depends on how many of the four genes for alpha globin or two genes for beta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of Blood cell, hematopoietic cells, marrow adipose tissue, and supportive stromal cells. In adult humans, bone marrow is primarily located in the Rib cage, ribs, vertebrae, sternum, and Pelvis, bones of the pelvis. Bone marrow comprises approximately 5% of total body mass in healthy adult humans, such that a person weighing 73 kg (161 lbs) will have around 3.7 kg (8 lbs) of bone marrow. Human marrow produces approximately 500 billion blood cells per day, which join the Circulatory system, systemic circulation via permeable vasculature sinusoids within the medullary cavity. All types of Hematopoietic cell, hematopoietic cells, including both Myeloid tissue, myeloid and Lymphocyte, lymphoid lineages, are create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptococcus Pneumoniae
''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', or pneumococcus, is a Gram-positive, spherical bacteria, hemolysis (microbiology), alpha-hemolytic member of the genus ''Streptococcus''. ''S. pneumoniae'' cells are usually found in pairs (diplococci) and do not form Bacterial morphological plasticity, spores and are non motile. As a significant human pathogenic bacterium ''S. pneumoniae'' was recognized as a major cause of pneumonia in the late 19th century, and is the subject of many humoral immunity studies. ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' resides asymptomatically in healthy carriers typically colonizing the respiratory tract, sinuses, and nasopharynx, nasal cavity. However, in susceptible individuals with immunocompromised, weaker immune systems, such as the elderly and young children, the bacterium may become pathogenic and spread to other locations to cause disease. It spreads by direct person-to-person contact via respiratory droplets and by auto inoculation in persons carrying the bacteria in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, Epileptic seizure, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin 10 to 15 days after being bitten by an infected ''Anopheles'' mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial Immunity (medical), resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria. The mosquitoes themselves are harmed by malaria, causing reduced lifespans in those infected by it. Malaria is caused by protozoa, single-celled microorganisms of the genus ''Plasmodium''. It is spread exclusively through bites of infected female ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |