|
Spinach Aptamer
The need for fluorescently tracking RNA rose as its roles in complex cellular functions has grown to not only include mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA, but also RNAi, siRNA, snoRNA, and lncRNA, among others. Spinach is a synthetically derived RNA aptamer born out of the need for a way of studying the role of RNAs at the cellular level. This aptamer was created using Systematic Evolution for Ligands by EXponential enrichment, or SELEX, which is also known as in vitro evolution. The aptamer was designed to be an RNA mimic of green fluorescent protein (GFP); similar to GFP for proteins, Spinach can be used for the fluorescently labeling RNA and tracking it in vivo. A method for inserting the Spinach sequence after an RNA sequence of interest is readily available. GFP’s fluorophore is made up of three cyclized amino acids within the beta-barrel structure: Serine65-Tyrosine66-Glycine67. This structure, 4-hydroxybenzylidene imidazolinone (HBI) was the basis for the synthetic analogue used in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein. mRNA is created during the process of transcription, where an enzyme ( RNA polymerase) converts the gene into primary transcript mRNA (also known as pre-mRNA). This pre-mRNA usually still contains introns, regions that will not go on to code for the final amino acid sequence. These are removed in the process of RNA splicing, leaving only exons, regions that will encode the protein. This exon sequence constitutes mature mRNA. Mature mRNA is then read by the ribosome, and, utilising amino acids carried by transfer RNA (tRNA), the ribosome creates the protein. This process is known as translation. All of these processes form part of the central dogma of molecular biology, which describes the flow of genetic information in a biological system. As in DNA, gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorophore
A fluorophore (or fluorochrome, similarly to a chromophore) is a fluorescent chemical compound that can re-emit light upon light excitation. Fluorophores typically contain several combined aromatic groups, or planar or cyclic molecules with several π bonds. Fluorophores are sometimes used alone, as a tracer in fluids, as a dye for staining of certain structures, as a substrate of enzymes, or as a probe or indicator (when its fluorescence is affected by environmental aspects such as polarity or ions). More generally they are covalently bonded to a macromolecule, serving as a marker (or dye, or tag, or reporter) for affine or bioactive reagents ( antibodies, peptides, nucleic acids). Fluorophores are notably used to stain tissues, cells, or materials in a variety of analytical methods, i.e., fluorescent imaging and spectroscopy. Fluorescein, via its amine-reactive isothiocyanate derivative fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), has been one of the most popular fluorophor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Imaging
Cell most often refers to: * Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life Cell may also refer to: Locations * Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery with only a few monks or nuns * Prison cell, a room used to hold people in prisons Groups of people * Cell, a group of people in a cell group, a form of Christian church organization * Cell, a unit of a clandestine cell system, a penetration-resistant form of a secret or outlawed organization * Cellular organizational structure, such as in business management Science, mathematics, and technology Computing and telecommunications * Cell (EDA), a term used in an electronic circuit design schematics * Cell (microprocessor), a microprocessor architecture developed by Sony, Toshiba, and IBM * Memory cell (computing), the basic unit of (volatile or non-volatile) computer memory * Cell, a unit in a database table or spreadsheet, formed by the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G-quadruplex
In molecular biology, G-quadruplex secondary structures (G4) are formed in nucleic acids by sequences that are rich in guanine. They are helical in shape and contain guanine tetrads that can form from one, two or four strands. The unimolecular forms often occur naturally near the ends of the chromosomes, better known as the telomeric regions, and in transcriptional regulatory regions of multiple genes, both in microbes and across vertebrates including oncogenes in humans. Four guanine bases can associate through Hoogsteen hydrogen bonding to form a square planar structure called a guanine tetrad (G-tetrad or G-quartet), and two or more guanine tetrads (from G-tracts, continuous runs of guanine) can stack on top of each other to form a G-quadruplex. The placement and bonding to form G-quadruplexes is not random and serve very unusual functional purposes. The quadruplex structure is further stabilized by the presence of a cation, especially potassium, which sits in a central c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photobleaching
In optics, photobleaching (sometimes termed fading) is the photochemical alteration of a dye or a fluorophore molecule such that it is permanently unable to fluoresce. This is caused by cleaving of covalent bonds or non-specific reactions between the fluorophore and surrounding molecules. Such irreversible modifications in covalent bonds are caused by transition from a singlet state to the triplet state of the fluorophores. The number of excitation cycles to achieve full bleaching varies. In microscopy, photobleaching may complicate the observation of fluorescent molecules, since they will eventually be destroyed by the light exposure necessary to stimulate them into fluorescing. This is especially problematic in time-lapse microscopy. However, photobleaching may also be used prior to applying the (primarily antibody-linked) fluorescent molecules, in an attempt to quench autofluorescence. This can help improve the signal-to-noise ratio. Photobleaching may also be exploited to st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinach (RNA)
Spinach (''Spinacia oleracea'') is a leafy green flowering plant native to central and Western Asia. It is of the order Caryophyllales, family Amaranthaceae, subfamily Chenopodioideae. Its leaves are a common edible vegetable consumed either fresh, or after storage using preservation techniques by canning, freezing, or dehydration. It may be eaten cooked or raw, and the taste differs considerably; the high oxalate content may be reduced by steaming. It is an annual plant (rarely biennial), growing as tall as . Spinach may overwinter in temperate regions. The leaves are alternate, simple, ovate to triangular, and very variable in size: long and broad, with larger leaves at the base of the plant and small leaves higher on the flowering stem. The flowers are inconspicuous, yellow-green, in diameter, and mature into a small, hard, dry, lumpy fruit cluster across containing several seeds. In 2021, world production of spinach was 32 million tonnes, with China alone accounting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Yield
The quantum yield (Φ) of a radiation-induced process is the number of times a specific event occurs per photon absorbed by the system. Applications Fluorescence spectroscopy The fluorescence quantum yield is defined as the ratio of the number of photons emitted to the number of photons absorbed.Lakowicz, Joseph R. ''Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy'' (Kluwer Academic / Plenum Publishers 1999) p.10. Fluorescence quantum yield is measured on a scale from 0 to 1.0, but is often represented as a percentage. A quantum yield of 1.0 (100%) describes a process where each photon absorbed results in a photon emitted. Substances with the largest quantum yields, such as rhodamines, display the brightest emissions; however, compounds with quantum yields of 0.10 are still considered quite fluorescent. Quantum yield is defined by the fraction of excited state fluorophores that decay through fluorescence: where \Phi_ is the fluorescence quantum yield, k_ is the rate constant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3,5-difluoro-4-hydroxybenzylidene Imidazolinone
3,5-Difluoro-4-hydroxybenzylidene imidazolidinone or DFHBI is an imidazolidinone fluorophore used in various biochemical studies. The benzene ring of DFHBI can freely rotate around the single bond but when it is fixed in planar conformation, DFHBI floresces. It is a synthetic analog of the GFP GFP may refer to: Organisations * Gaelic Football Provence, a French Gaelic Athletic Association club * Geheime Feldpolizei, the German secret military police during the Second World War * French Group for the Study of Polymers and their Applicat ... fluorophore. References {{organic-compound-stub Imidazolidinones Fluoroarenes Phenols ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Fluorescent Protein
The green fluorescent protein (GFP) is a protein that exhibits bright green fluorescence when exposed to light in the blue to ultraviolet range. The label ''GFP'' traditionally refers to the protein first isolated from the jellyfish '' Aequorea victoria'' and is sometimes called ''avGFP''. However, GFPs have been found in other organisms including corals, sea anemones, zoanithids, copepods and lancelets. The GFP from ''A. victoria'' has a major excitation peak at a wavelength of 395 nm and a minor one at 475 nm. Its emission peak is at 509 nm, which is in the lower green portion of the visible spectrum. The fluorescence quantum yield (QY) of GFP is 0.79. The GFP from the sea pansy (''Renilla reniformis'') has a single major excitation peak at 498 nm. GFP makes for an excellent tool in many forms of biology due to its ability to form an internal chromophore without requiring any accessory cofactors, gene products, or enzymes / substrates other tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RRNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal DNA (rDNA) and then bound to ribosomal proteins to form small and large ribosome subunits. rRNA is the physical and mechanical factor of the ribosome that forces transfer RNA (tRNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA) to process and translate the latter into proteins. Ribosomal RNA is the predominant form of RNA found in most cells; it makes up about 80% of cellular RNA despite never being translated into proteins itself. Ribosomes are composed of approximately 60% rRNA and 40% ribosomal proteins by mass. Structure Although the primary structure of rRNA sequences can vary across organisms, base-pairing within these sequences commonly forms stem-loop configurations. The length and position of these rRNA stem-loops allow them to create thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
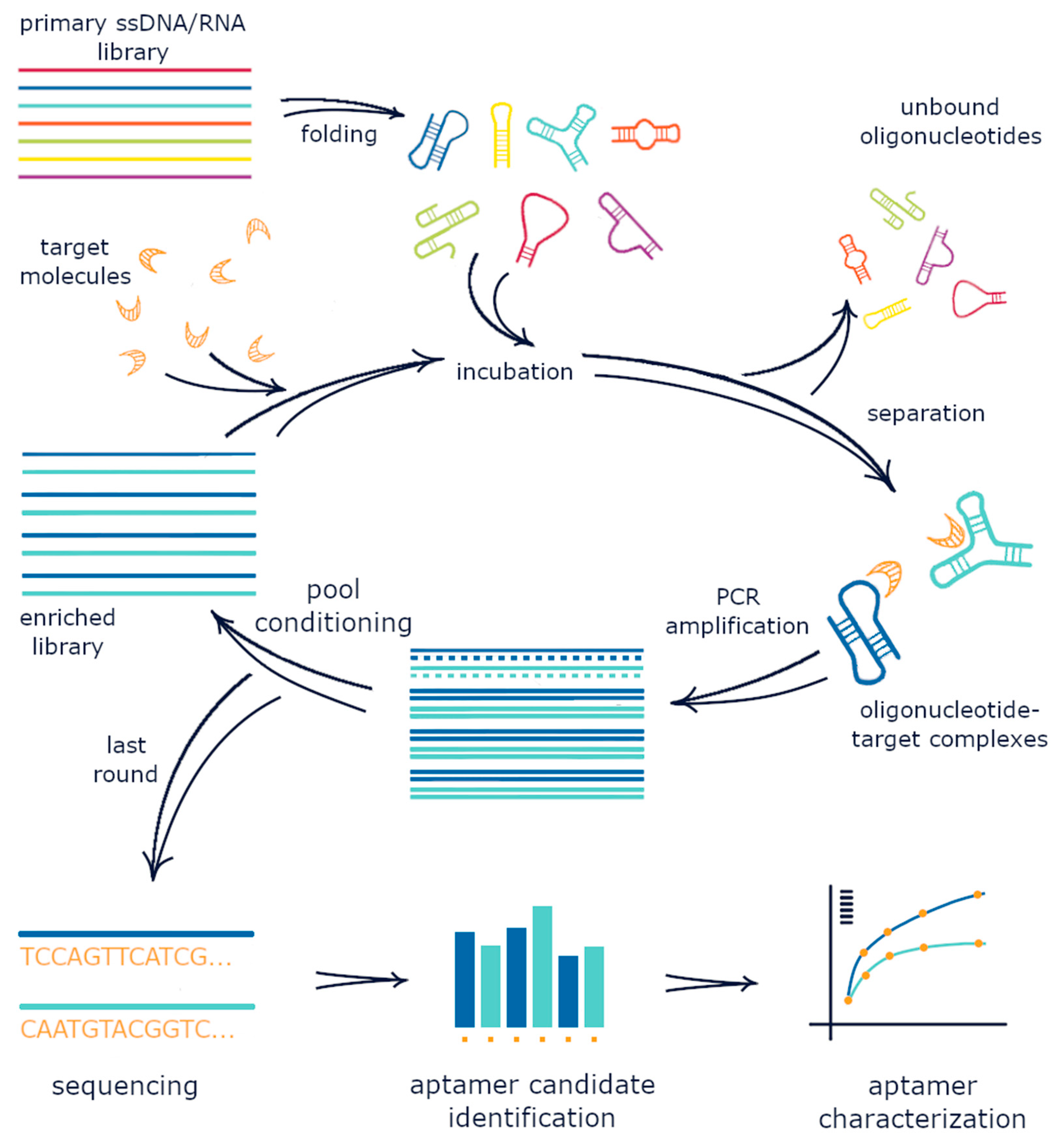
Systematic Evolution Of Ligands By Exponential Enrichment
Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment (SELEX), also referred to as '' in vitro selection'' or '' in vitro evolution'', is a combinatorial chemistry technique in molecular biology for producing oligonucleotides of either single-stranded DNA or RNA that specifically bind to a target ligand or ligands. These single-stranded DNA or RNA are commonly referred to as aptamers. Although SELEX has emerged as the most commonly used name for the procedure, some researchers have referred to it as SAAB (selected and amplified binding site) and CASTing (cyclic amplification and selection of targets) SELEX was first introduced in 1990. In 2015, a special issue was published in the Journal of Molecular Evolution in the honor of quarter century of the discovery of SELEX. The process begins with the synthesis of a very large oligonucleotide library, consisting of randomly generated sequences of fixed length flanked by constant 5' and 3' ends. The constant ends serve as pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |