|
Spatha
The spatha was a type of straight and long sword, measuring between , with a handle length of between , in use in the territory of the Roman Empire during the 1st to 6th centuries AD. Later swords, from the 7th to 10th centuries, like the Viking swords, are recognizable derivatives and sometimes subsumed under the term ''spatha''. The Roman ''spatha'' was used in war and in gladiatorial fights. The ''spatha'' of literature appears in the Roman Empire in the 1st century AD as a weapon used by presumably Celtic auxiliaries and gradually became a standard heavy infantry weapon by the 3rd century AD, relegating the ''gladius'' to use as a light infantry weapon. The ''spatha'' apparently replaced the ''gladius'' in the front ranks, giving the infantry more reach when thrusting. While the infantry version had a long point, versions carried by the cavalry had a rounded tip that prevented accidental stabbing of the cavalryman's own foot or horse. Archaeologically many instances of the ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
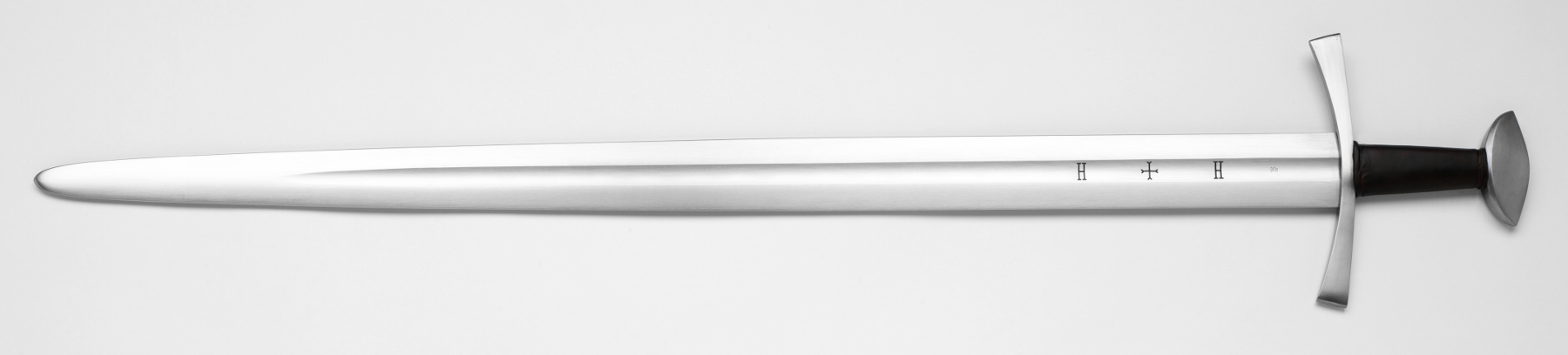
Knightly Sword
In the European High Middle Ages, the typical sword (sometimes academically categorized as the knightly sword, arming sword, or in full, knightly arming sword) was a straight, double-edged weapon with a single-handed, cruciform (i.e., cross-shaped) hilt and a blade length of about . This type is frequently depicted in period artwork, and numerous examples have been preserved archaeologically. The high medieval sword of the Romanesque period (10th to 13th centuries) developed gradually from the Viking sword of the 9th century. In the Late Medieval period (14th and 15th centuries), late forms of these swords continued to be used, but often as a sidearm, at that point called "arming swords" and contrasting with the two-handed, heavier longswords. Though the majority of late-medieval arming swords kept their blade properties from previous centuries, there are also surviving specimens from the 15th century that took the form of a late-medieval estoc, specialised for use against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
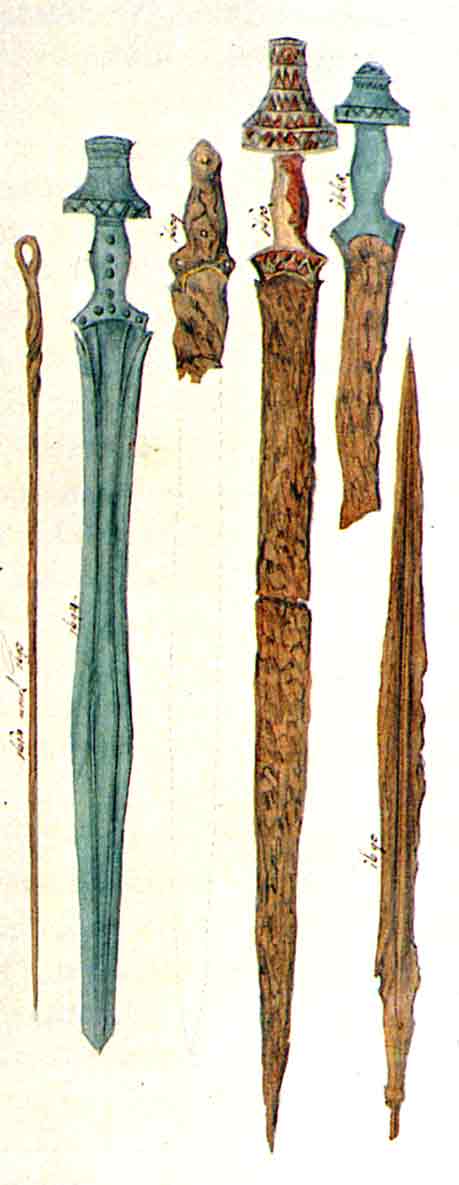
Iron Age Sword
Swords made of iron (as opposed to bronze) appear from the Early Iron Age ( century BC), but do not become widespread before the 8th century BC. Early Iron Age swords were significantly different from later steel swords. They were work-hardened, rather than quench-hardened, which made them about the same or only slightly better in terms of strength and hardness to earlier bronze swords. This meant that they could still be bent out of shape during use. The easier production, however, and the greater availability of the raw material allowed for much larger scale production. Eventually smiths learned of processes to refine smelted iron and make steel. By quenching (making the steel hard and brittle) and tempering (removing the brittleness), swords could be made that would suffer much less damage, and would spring back into shape if bent. It took a long time, however, before this was done consistently, and even until the end of the early medieval period, many swords were still u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanization
In linguistics, romanization is the conversion of text from a different writing system to the Latin script, Roman (Latin) script, or a system for doing so. Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written text, and transcription (linguistics), transcription, for representing the spoken word, and combinations of both. Transcription methods can be subdivided into ''phonemic orthography, phonemic transcription'', which records the phonemes or units of semantic meaning in speech, and more strict ''phonetic transcription'', which records speech sounds with precision. Methods There are many consistent or standardized romanization systems. They can be classified by their characteristics. A particular system's characteristics may make it better-suited for various, sometimes contradictory applications, including document retrieval, linguistic analysis, easy readability, faithful representation of pronunciation. * Source, or donor language – A system may be tai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homeric Greek
Homeric Greek is the form of the Greek language that was used in the ''Iliad'', ''Odyssey'', and ''Homeric Hymns''. It is a literary dialect of Ancient Greek consisting mainly of an archaic form of Ionic, with some Aeolic forms, a few from Arcadocypriot, and a written form influenced by Attic. It was later named Epic Greek because it was used as the language of epic poetry, typically in dactylic hexameter, by poets such as Hesiod and Theognis of Megara. Some compositions in Epic Greek date from as late as the 5th century D and it only fell out of use by the end of classical antiquity. Main features In the following description, only forms that differ from those of later Greek are discussed. Omitted forms can usually be predicted from patterns seen in Ionic Greek. Phonology Homeric Greek is like Ionic Greek, and unlike Classical Attic, in shifting almost all cases of long to . Exceptions include nouns like ("a goddess"), and the genitive plural of first-declension n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcaeus Of Mytilene
Alcaeus of Mytilene (; , ''Alkaios ho Mutilēnaios''; – BC) was a lyric poet from the Greek island of Lesbos who is credited with inventing the Alcaic stanza. He was included in the canonical list of nine lyric poets by the scholars of Hellenistic Alexandria. He was a contemporary of Sappho, with whom he may have exchanged poems. He was born into the aristocratic governing class of Mytilene, the main city of Lesbos, where he was involved in political disputes and feuds. Biography The broad outlines of the poet's life are well known. He was born into the aristocratic, warrior class that dominated Mytilene, the strongest city-state on the island of Lesbos and, by the end of the seventh century BC, the most influential of all the North Aegean Greek cities, with a strong navy and colonies securing its trade-routes in the Hellespont. The city had long been ruled by kings born to the Penthilid clan but, during the poet's life, the Penthilids were a spent force and rival arist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
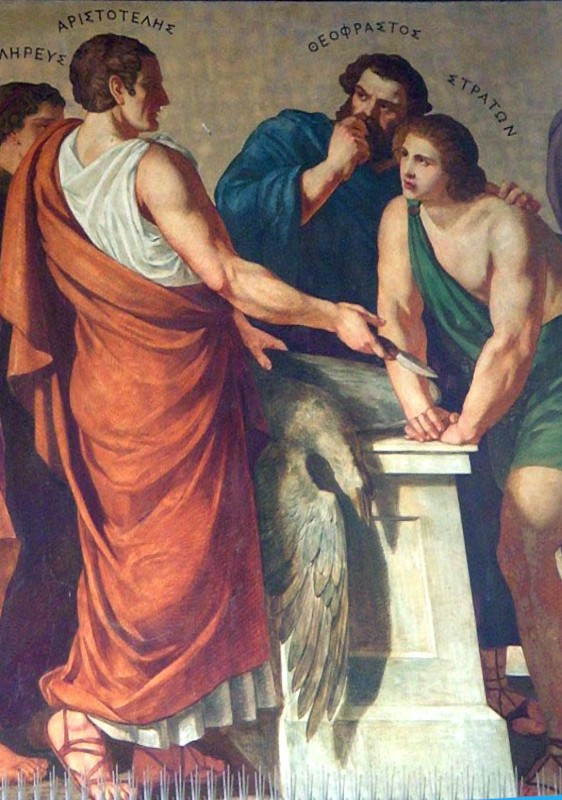
Theophrastus
Theophrastus (; ; c. 371 – c. 287 BC) was an ancient Greek Philosophy, philosopher and Natural history, naturalist. A native of Eresos in Lesbos, he was Aristotle's close colleague and successor as head of the Lyceum (classical), Lyceum, the Peripatetic school, Peripatetic school of philosophy in Athens. Theophrastus wrote numerous treatises across all areas of philosophy, working to support, improve, expand, and develop Aristotelian system, the Aristotelian system. He made significant contributions to various fields, including ethics, metaphysics, botany, and natural history. Often considered the "father of botany" for his groundbreaking works "Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus), Enquiry into Plants" () and "On the Causes of Plants", () Theophrastus established the foundations of Botany, botanical science. His given name was (Ancient Greek: ); the nickname Theophrastus ("divine speaker") was reputedly given to him by Aristotle in recognition of his eloquent style. He came to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
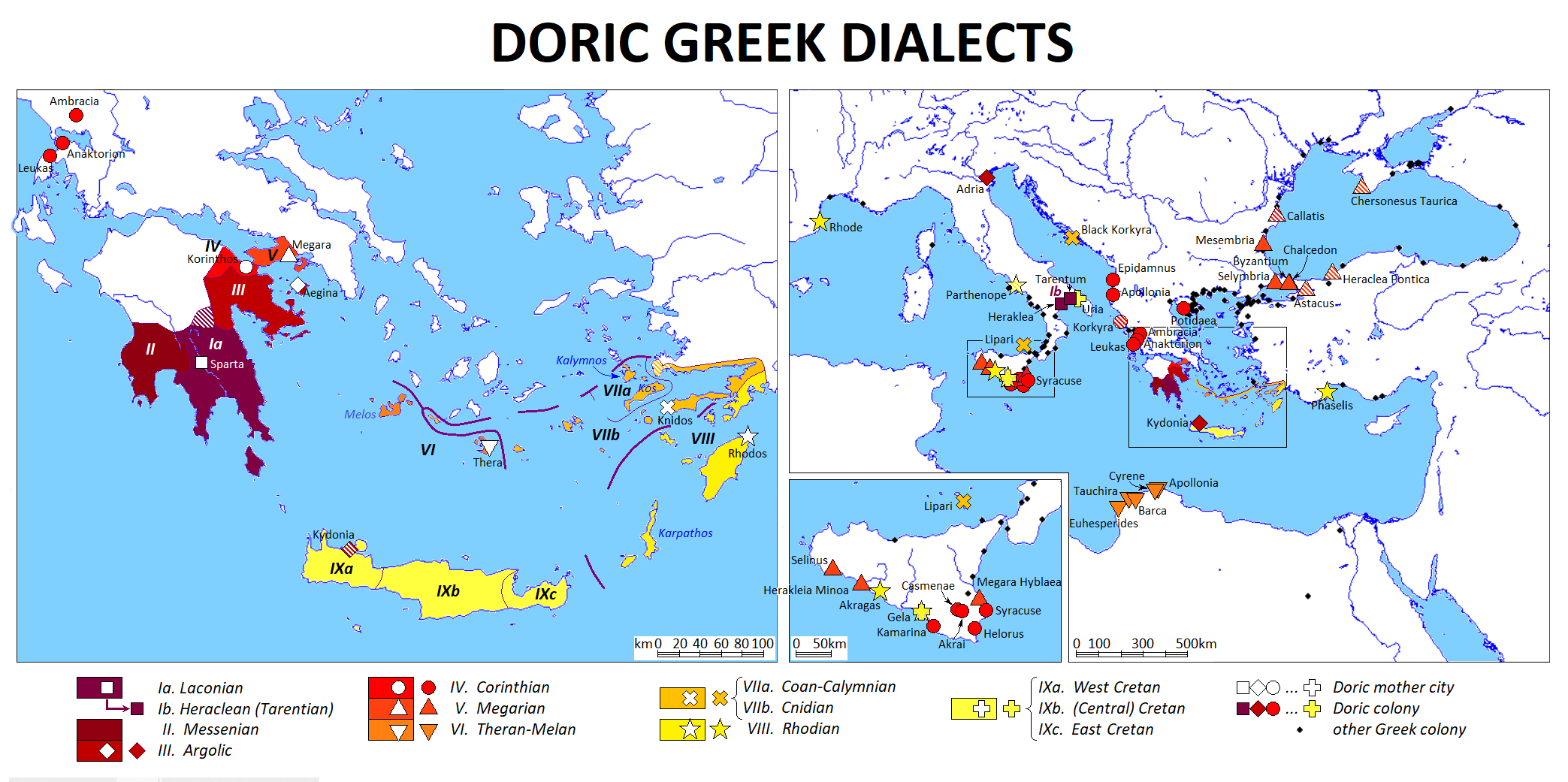
Doric Greek
Doric or Dorian (), also known as West Greek, was a group of Ancient Greek dialects; its Variety (linguistics), varieties are divided into the Doric proper and Northwest Doric subgroups. Doric was spoken in a vast area, including northern Greece (Acarnania, Aetolia, Epirus, Ozolian Locris, western and Opuntian Locris, eastern Locris, Phocis (ancient region), Phocis, Doris (Greece), Doris, and possibly Macedonia (ancient kingdom), ancient Macedonia), most of the Regions of ancient Greece#Peloponnese, Peloponnese (Achaea (ancient region), Achaea, Ancient Elis, Elis, Messenia (ancient region), Messenia, Laconia, Argolid, Aegina, Corinthia (ancient region), Corinthia, and Megara), the Southern Aegean (Kythira, Milos, Santorini, Thera, Crete, Karpathos, and Rhodes), as well as the colonies of some of those regions in Cyrene, Libya, Cyrene, Magna Graecia, the Greek colonisation#Black Sea and Propontis, Black Sea, Greek colonisation#Ionian Sea, Adriatic Sea, and Illyria, the Ionian Sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy (in Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, Caucasus, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the list of languages by first written accounts, longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting importance in the European canon. Greek is also the language in which many of the foundational texts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |