|
Somatotropin
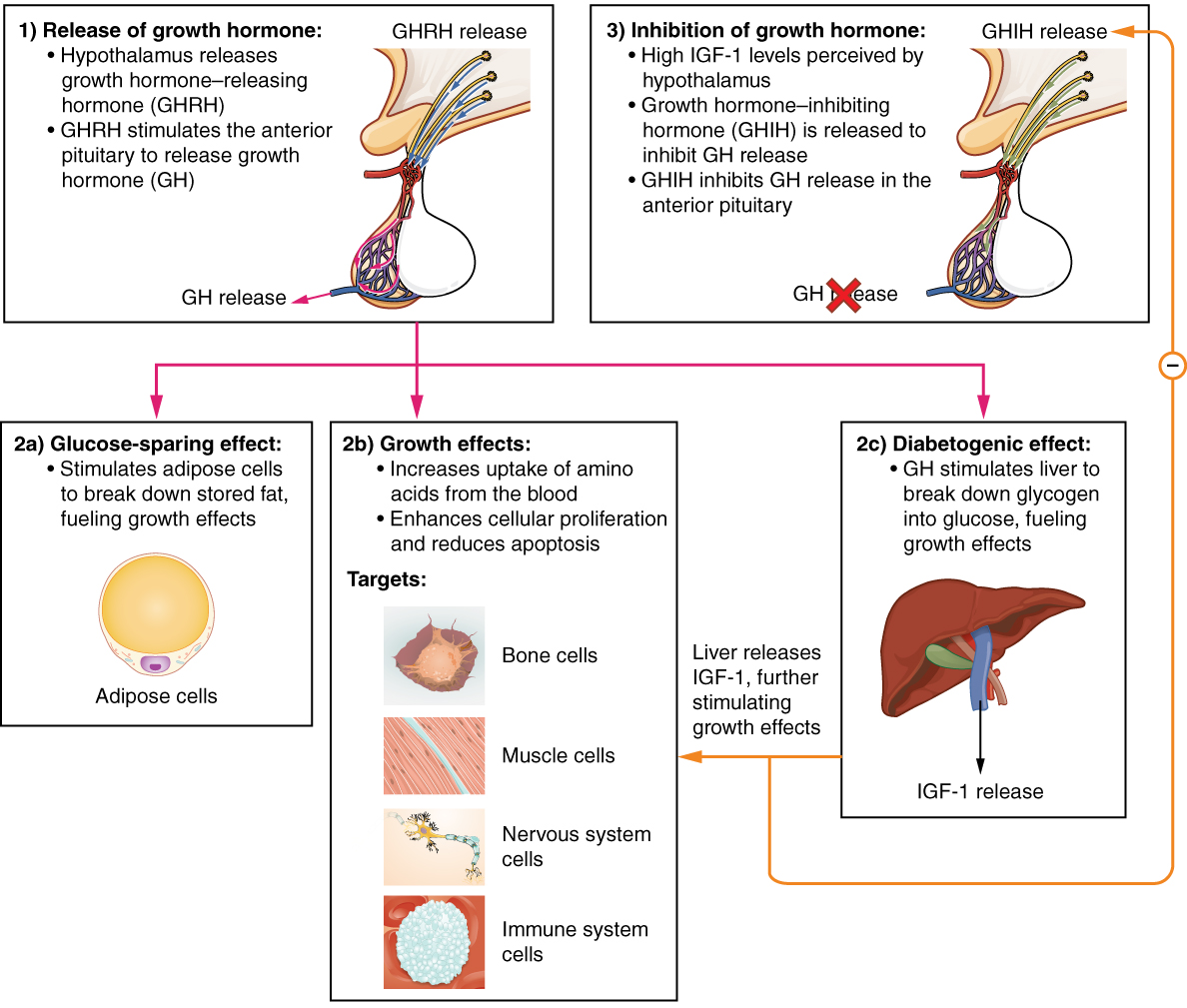
Growth hormone (GH) or somatotropin, also known as human growth hormone (hGH or HGH) in its human form, is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration in humans and other animals. It is thus important in human development. GH also stimulates production of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and increases the concentration of glucose and free fatty acids. It is a type of mitogen which is specific only to the receptors on certain types of cells. GH is a 191-amino acid, single-chain polypeptide that is synthesized, stored and secreted by somatotropic cells within the lateral wings of the anterior pituitary gland. A recombinant form of HGH called somatropin (INN) is used as a prescription drug to treat children's growth disorders and adult growth hormone deficiency. In the United States, it is only available legally from pharmacies by prescription from a licensed health care provider. In recent years in the United States, some health care pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bovine Somatotropin
Livestock Dairy industry Bovine somatotropin or bovine somatotrophin (abbreviated bST and BST), or bovine growth hormone (BGH), is a peptide hormone produced by cows' pituitary glands. Like other hormones, it is produced in small quantities and is used in regulating metabolic processes. Scientists created a bacterium that produces the hormone somatotropin which is produced by the cow's body after giving birth and increases milk production by around 10 percent. Recombinant bovine somatotropin (usually "rBST"), is a synthetic version of the bovine growth hormone given to dairy cattle by injection to increase milk production. Controversy over its safety for cows has led to it being banned in several countries, including the European Union since 1990, and Canada, Japan, Pakistan, Australia, New Zealand, and Argentina, as it has been found to increase health risks in cows. The Codex Alimentarius has not approved it as safe. The FDA approved it in 1993, and required that any mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Hormone 1
Growth hormone 1, also known as pituitary growth hormone or simply as growth hormone (GH) somatotropin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GH1'' gene In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei .... The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the somatotropin/prolactin family of hormones that play an important role in growth control. The gene, along with four other related genes, is located at the growth hormone locus on chromosome 17 where they are interspersed in the same transcriptional orientation, an arrangement thought to have evolved by a series of gene duplications. The five genes share a remarkably high degree of sequence identity. Alternative splicing generates additional isoforms of each of the five growth hormones, leading to further diversity and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Hormone 2
Growth hormone 2 (GH2), also known more commonly as placental growth hormone (PGH) or growth hormone variant (GH-V), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GH2'' gene. It is produced by and secreted from the placenta during pregnancy, and becomes the predominant form of growth hormone (GH) in the body during this time. Its cogener is growth hormone 1 (GH1), or ''pituitary growth hormone''. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the somatotropin/prolactin family of hormones, playing an important role in growth control. The gene, along with four other related genes, is located at the growth hormone locus on chromosome 17, where they are interspersed in the same transcriptional orientation, an arrangement that is thought to have evolved through a series of gene duplications. The five genes share a remarkably high degree of sequence identity. Alternative splicing generates additional isoforms of each of the five growth hormones, leading to further diversity and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recombinant DNA
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination (such as molecular cloning) that bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be found in the genome. Recombinant DNA is the general name for a piece of DNA that has been created by combining two or more fragments from different sources. Recombinant DNA is possible because DNA molecules from all organisms share the same chemical structure, differing only in the nucleotide sequence. Recombinant DNA molecules are sometimes called chimeric DNA because they can be made of material from two different species like the mythical chimera. rDNA technology uses palindromic sequences and leads to the production of sticky and blunt ends. The DNA sequences used in the construction of recombinant DNA molecules can originate from any species. For example, plant DNA can be joined to bacterial DNA, or human DNA can be joined with fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Pituitary
The anterior pituitary (also called the adenohypophysis or pars anterior) is a major Organ (anatomy), organ of the endocrine system. The anterior pituitary is the glandular, Anatomical terms of location#Usage in human anatomy, anterior lobe that together with the posterior pituitary (or neurohypophysis) makes up the pituitary gland (hypophysis) which, in humans, is located at the base of the Human brain, brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The anterior pituitary regulates several physiological processes, including stress (medicine), stress, Human development (biology), growth, reproduction, and lactation. Proper functioning of the anterior pituitary and of the organs it regulates can often be ascertained via blood tests that measure hormone levels. Structure The pituitary gland sits in a protective bony enclosure called the sella turcica (''Turkish chair/saddle''). It is composed of three lobes: the anterior, intermediate, and posterior lobes. In many animals, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Hormone Deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency (GHD), or hyposomatotropism, is a medical condition resulting from not enough growth hormone (GH). Generally the most noticeable symptom is that an individual attains a short height. Newborns may also present low blood sugar or a small penis size. In adults there may be decreased muscle mass, high cholesterol levels, or poor bone density. GHD can be present at birth or develop later in life. Causes may include genetics, trauma, infections, tumors, or radiation therapy. Genes that may be involved include '' GH1'', '' GHRHR'', or '' BTK''. In a third of cases no cause is apparent. The underlying mechanism generally involves problems with the pituitary gland. Some cases are associated with a lack of other pituitary hormones, in which case it is known as combined pituitary hormone deficiency. Diagnosis involves blood tests to measure growth hormone levels. Treatment is by growth hormone replacement using synthetic human growth hormone. The frequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptide Hormone
Peptide hormones are hormones composed of peptide molecules. These hormones influence the endocrine system of animals, including humans. Most hormones are classified as either amino-acid-based hormones (amines, peptides, or proteins) or steroid hormones. Amino-acid-based hormones are water-soluble and act on target cells via second messenger systems, whereas steroid hormones, being lipid-soluble, diffuse through plasma membranes to interact directly with intracellular receptors in the cell nucleus. Like all peptides, peptide hormones are synthesized in cell (biology), cells from amino acids based on Messenger RNA, mRNA transcripts, which are derived from DNA templates inside the cell nucleus. The initial precursors, known as preprohormones, undergo processing in the endoplasmic reticulum. This includes the removal of the N-terminal signal peptide and, in some cases, glycosylation, yielding prohormones. These prohormones are then packaged into secretory vesicle (biology), vesicles, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Hormone 1
Growth hormone 1, also known as pituitary growth hormone or simply as growth hormone (GH) somatotropin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GH1'' gene In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei .... The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the somatotropin/prolactin family of hormones that play an important role in growth control. The gene, along with four other related genes, is located at the growth hormone locus on chromosome 17 where they are interspersed in the same transcriptional orientation, an arrangement thought to have evolved by a series of gene duplications. The five genes share a remarkably high degree of sequence identity. Alternative splicing generates additional isoforms of each of the five growth hormones, leading to further diversity and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Agriculture
Industrial agriculture is a form of modern farming that refers to the industrialized production of crops and animals and animal products like eggs or milk. The methods of industrial agriculture include innovation in agricultural machinery and farming methods, genetic technology, techniques for achieving economies of scale in production, the creation of new markets for consumption, the application of patent protection to genetic information, and global trade. These methods are widespread in developed nations and increasingly prevalent worldwide. Most of the meat, dairy, eggs, fruits and vegetables available in supermarkets are produced in this way. Historical development and future prospects Industrial agriculture arose hand in hand with the Industrial Revolution in general. The identification of nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus (referred to by the acronym NPK) as critical factors in plant growth led to the manufacture of synthetic fertilizers, making possible more inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athens, Greece
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southernmost capital on the European mainland. With its urban area's population numbering over 3.6 million, it is the List of urban areas in the European Union, eighth-largest urban area in the European Union (EU). The Municipality of Athens (also City of Athens), which constitutes a small administrative unit of the entire urban area, had a population of 643,452 (2021) within its official limits, and a land area of . Athens is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, world's oldest cities, with its recorded history spanning over 3,400 years, and its earliest human presence beginning somewhere between the 11th and 7th millennia BCE. According to Greek mythology the city was named after Athena, the ancient Greek goddess of wisdom, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2004 Olympic Games
The 2004 Summer Olympics (), officially the Games of the XXVIII Olympiad (), and officially branded as Athens 2004 (), were an international multi-sport event held from 13 to 29 August 2004 in Athens, Greece. The Games saw 10,625 athletes compete, some 600 more than expected, accompanied by 5,501 team officials from 201 countries, with 301 medal events in 28 different sports. The 2004 Games marked the first time since the 1996 Summer Olympics that all countries with a National Olympic Committee were in attendance, and also marked the first time Athens hosted the Games since their first modern incarnation in 1896 as well as the return of the Olympic games to its birthplace. Athens became the fourth city to host the Summer Olympic Games on two occasions (together with Paris, London and Los Angeles). A new medal obverse was introduced at these Games, replacing the design by Giuseppe Cassioli that had been used since 1928. The new design features the Panathenaic Stadium in Ath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anabolic
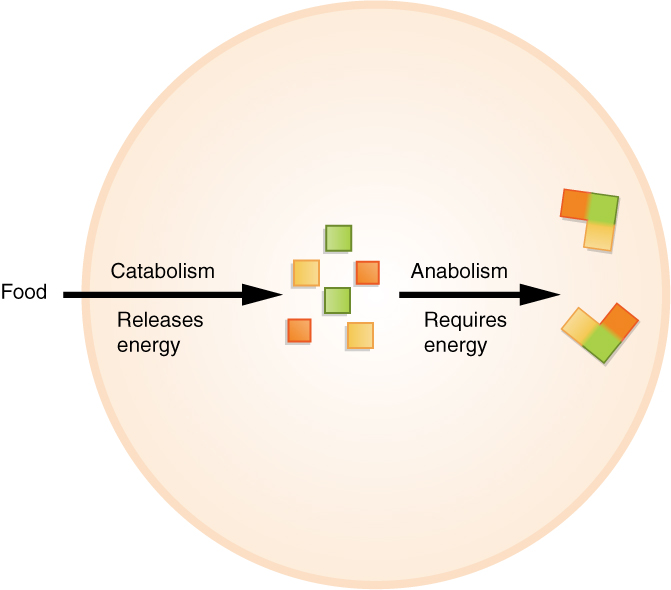
Anabolism () is the set of metabolic pathways that construct macromolecules like DNA or RNA from smaller units. These reactions require energy, known also as an endergonic process. Anabolism is the building-up aspect of metabolism, whereas catabolism is the breaking-down aspect. Anabolism is usually synonymous with biosynthesis. Pathway Polymerization, an anabolic pathway used to build macromolecules such as nucleic acids, proteins, and polysaccharides, uses condensation reactions to join monomers. Macromolecules are created from smaller molecules using enzymes and cofactors. Energy source Anabolism is powered by catabolism, where large molecules are broken down into smaller parts and then used up in cellular respiration. Many anabolic processes are powered by the cleavage of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Anabolism usually involves reduction and decreases entropy, making it unfavorable without energy input. The starting materials, called the precursor molecules, are joi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |