|
Soliton (optics)
In optics, the term soliton is used to refer to any optical field that does not change during propagation because of a delicate balance between nonlinear and dispersive effects in the medium. There are two main kinds of solitons: * spatial solitons: the nonlinear effect can balance the dispersion. The electromagnetic field can change the refractive index of the medium while propagating, thus creating a structure similar to a graded-index fiber. If the field is also a propagating mode of the guide it has created, then it will remain confined and it will propagate without changing its shape * temporal solitons: if the electromagnetic field is already spatially confined, it is possible to send pulses that will not change their shape because the nonlinear effects will balance the dispersion. Those solitons were discovered first and they are often simply referred as "solitons" in optics. *Spatial solitons* In order to understand how a spatial soliton can exist, we have to make som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of optical instruments, instruments that use or Photodetector, detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible light, visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation, and other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties. Most optical phenomena can be accounted for by using the Classical electromagnetism, classical electromagnetic description of light, however complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of Ray (optics), rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporal Soliton Explanation
{{disambiguation ...
Temporal may refer to: Entertainment * Temporal (band), an Australian metal band * ''Temporal'' (Radio Tarifa album), 1997 * ''Temporal'' (Love Spirals Downwards album), 2000 * ''Temporal'' (Isis album), 2012 * ''Temporal'' (video game), a 2008 freeware platform and puzzle game * ''Temporal'' (film), a 2022 Sri Lankan short film Philosophy * Temporality * Temporal actual entity, see Other * Temporal (anatomy), An alternative for lateral, in the head; towards the temporal bone * Temporality (ecclesiastical), or temporal goods, secular possessions of the Church * Temporal database See also * * Ephemeral * Impermanence * Temporal region (other) Temporal region may refer to: * Temporal lobe, one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals * Temple (anatomy) The temple, also known as the pterion, is a latch where four skull bones intersect: the frontal, pariet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves), phase'' on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, troughs, or zero crossings. Wavelength is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns. The multiplicative inverse, inverse of the wavelength is called the ''spatial frequency''. Wavelength is commonly designated by the Greek letter lambda (''λ''). For a modulated wave, ''wavelength'' may refer to the carrier wavelength of the signal. The term ''wavelength'' may also apply to the repeating envelope (mathematics), envelope of modulated waves or waves formed by Interference (wave propagation), interference of several sinusoids. Assuming a sinusoidal wave moving at a fixed phase velocity, wave speed, wavelength is inversely proportion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio signals (sound), radio waves, and light. The interval of time between events is called the period. It is the reciprocal of the frequency. For example, if a heart beats at a frequency of 120 times per minute (2 hertz), its period is one half of a second. Special definitions of frequency are used in certain contexts, such as the angular frequency in rotational or cyclical properties, when the rate of angular progress is measured. Spatial frequency is defined for properties that vary or cccur repeatedly in geometry or space. The unit of measurement of frequency in the International System of Units (SI) is the hertz, having the symbol Hz. Definitions and units For cyclical phenomena such as oscillations, waves, or for examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandwidth (signal Processing)
Bandwidth is the difference between the upper and lower Frequency, frequencies in a continuous Frequency band, band of frequencies. It is typically measured in unit of measurement, unit of hertz (symbol Hz). It may refer more specifically to two subcategories: ''Passband bandwidth'' is the difference between the upper and lower cutoff frequencies of, for example, a band-pass filter, a communication channel, or a signal spectrum. ''Baseband bandwidth'' is equal to the upper cutoff frequency of a low-pass filter or baseband signal, which includes a zero frequency. Bandwidth in hertz is a central concept in many fields, including electronics, information theory, digital communications, radio communications, signal processing, and spectroscopy and is one of the determinants of the capacity of a given communication channel. A key characteristic of bandwidth is that any band of a given width can carry the same amount of information, regardless of where that band is located in the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dispersion (optics)
Dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency. Sometimes the term chromatic dispersion is used to refer to optics specifically, as opposed to wave propagation in general. A medium having this common property may be termed a dispersive medium. Although the term is used in the field of optics to describe light and other electromagnetic waves, dispersion in the same sense can apply to any sort of wave motion such as acoustic dispersion in the case of sound and seismic waves, and in gravity waves (ocean waves). Within optics, dispersion is a property of telecommunication signals along transmission lines (such as microwaves in coaxial cable) or the Pulse (signal processing), pulses of light in optical fiber. In optics, one important and familiar consequence of dispersion is the change in the angle of refraction of different colors of light, as seen in the spectrum produced by a dispersive Prism (optics), prism and in chromatic aberration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Fibres
An optical fiber, or optical fibre, is a flexible glass or plastic fiber that can transmit light from one end to the other. Such fibers find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths (data transfer rates) than electrical cables. Fibers are used instead of metal wires because signals travel along them with less loss and are immune to electromagnetic interference. Fibers are also used for illumination and imaging, and are often wrapped in bundles so they may be used to carry light into, or images out of confined spaces, as in the case of a fiberscope. Specially designed fibers are also used for a variety of other applications, such as fiber optic sensors and fiber lasers. Glass optical fibers are typically made by drawing, while plastic fibers can be made either by drawing or by extrusion. Optical fibers typically include a core surrounded by a transparent cladding material with a lower index of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bit Rate
In telecommunications and computing, bit rate (bitrate or as a variable ''R'') is the number of bits that are conveyed or processed per unit of time. The bit rate is expressed in the unit bit per second (symbol: bit/s), often in conjunction with an SI prefix such as kilo (1 kbit/s = 1,000 bit/s), mega (1 Mbit/s = 1,000 kbit/s), giga (1 Gbit/s = 1,000 Mbit/s) or tera (1 Tbit/s = 1,000 Gbit/s). The non-standard abbreviation bps is often used to replace the standard symbol bit/s, so that, for example, 1 Mbps is used to mean one million bits per second. In most computing and digital communication environments, one byte per second (symbol: B/s) corresponds roughly to 8 bit/s. However if stop bits, start bits, and parity bits need to be factored in, a higher number of bits per second will be required to achieve a throughput of the same number of bytes. Prefixes When quantifying large or small bit rates, SI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confocal Cavity OS 2000
In geometry, confocal means having the same foci: confocal conic sections. * For an optical cavity consisting of two mirrors, confocal means that they share their foci. If they are identical mirrors, their radius of curvature, ''R''mirror, equals ''L'', where ''L'' is the distance between the mirrors. * In conic sections, it is said of two ellipses, two hyperbolas, or an ellipse and a hyperbola which share both foci with each other. If an ellipse and a hyperbola are confocal, they are perpendicular to each other. * In optics, it means that one focus or image point of one lens is the same as one focus of the next lens. See also *Confocal laser scanning microscopy *Confocal microscopy Confocal microscopy, most frequently confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) or laser scanning confocal microscopy (LSCM), is an optical imaging technique for increasing optical resolution and contrast (vision), contrast of a micrograph by me ... * {{set index article, mathematics Elementary geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematicon
In optics, a nematicon is a spatial soliton in nematic liquid crystals (NLC). The name was invented in 2003 by G. Assanto. and used thereafter Nematicons are generated by a special type of optical nonlinearity present in NLC: the light induced reorientation of the molecular director (''i.e.'' the average molecular orientation). This nonlinearity arises from the fact that the molecular director (i.e., the optic axis of the corresponding uniaxial) tends to align along the electric field of light. Nematicons are easy to generate (with mW optical power or less ) because the NLC dielectric medium exhibits the following properties: * A very large nonlinear response : the effective nonlinearity is typically eight orders of magnitude larger than that of carbon disulfide. This means that much lower optical powers are necessary to obtain the same refractive index variation (increase) or self-focusing to balance out diffraction. * A nonlocal response : the nonlinear response is not limite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
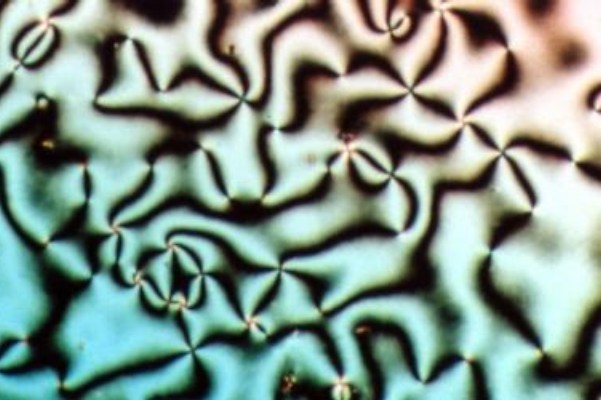
Liquid Crystal
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal can flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a common direction as in a solid. There are many types of LC Phase (matter), phases, which can be distinguished by their Optics, optical properties (such as Texture (crystalline), textures). The contrasting textures arise due to molecules within one area of material ("domain") being oriented in the same direction but different areas having different orientations. An LC material may not always be in an LC state of matter (just as water may be ice or water vapour). Liquid crystals can be divided into three main types: thermotropic, lyotropic, and #Metallotropic liquid crystals, metallotropic. Thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals consist mostly of organic molecules, although a few minerals are also known. Thermotropic LCs exhibit a phase transition into the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |