|
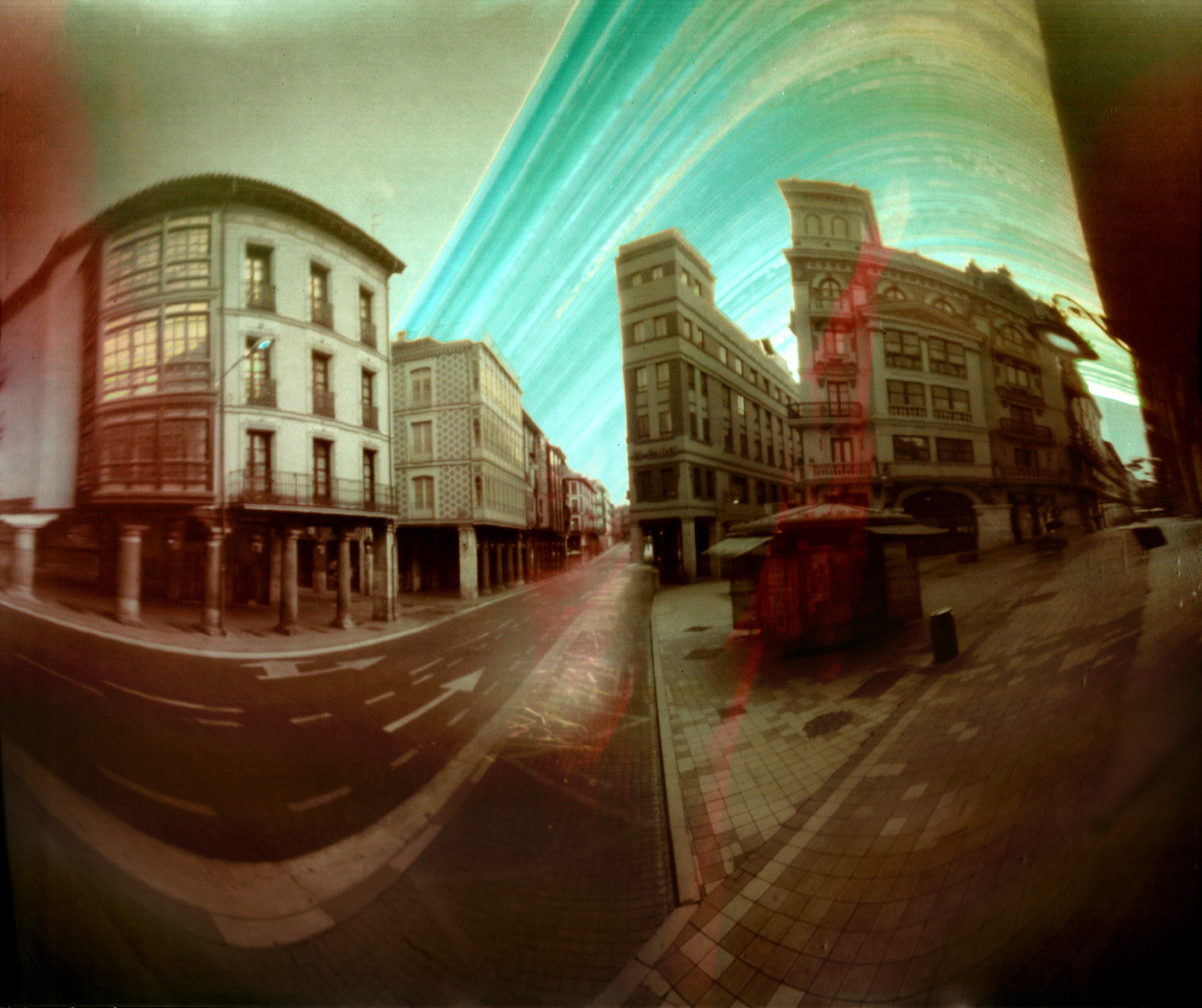
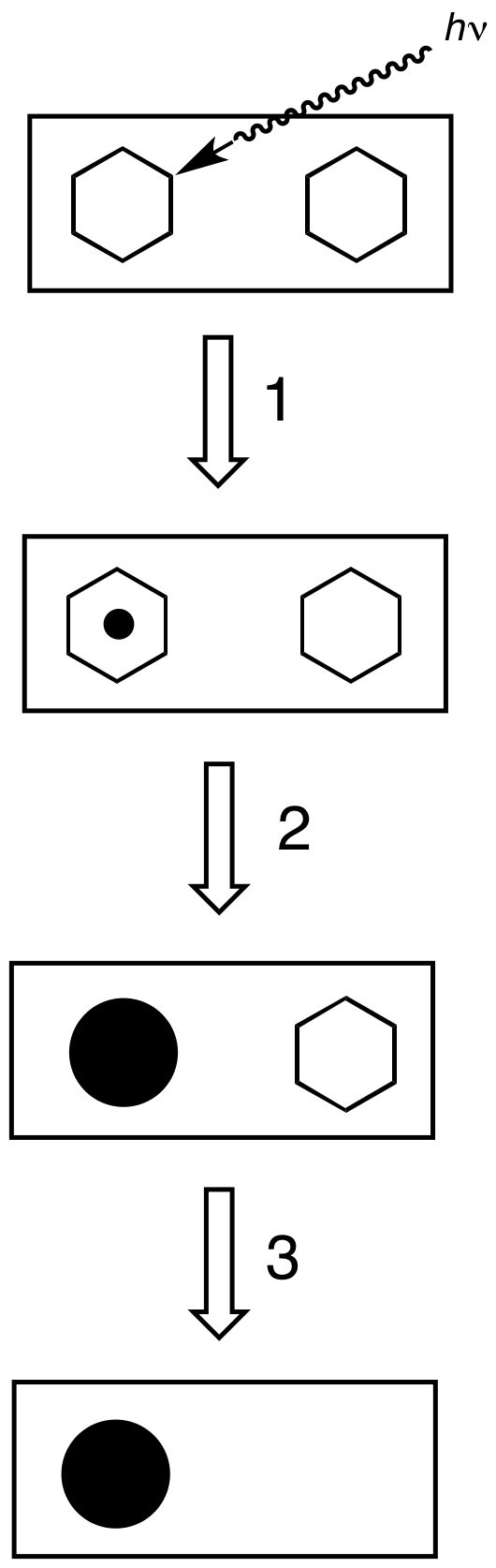
Solarigraphy
Solarigraphy is a concept and a photographic practice based on the observation of the sun path in the sky (different in each place on the Earth) and its effect on the landscape, captured by a specific procedure that combines Pinhole camera, pinhole photography and digital processing. Invented around 2000, solarigraphy (also known as wiktionary:solargraphy, solargraphy) uses photographic paper without Photographic processing, chemical processing, a pinhole camera and a scanner to create images that catch the daily journey of the sun along the sky with very long exposure times, from several hours to several years. The longest known solarigraph was captured over the course of eight years. Solarigraphy is an extreme case of long-exposure photography, and the non-conventional use of photosensitive materials is what makes it different to other methods of sun paths capture such as the Yamazaki's "heliographys". Beginnings Previous experiments with long exposures on photosensitive pap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long-exposure Photography
Long-exposure, time-exposure, or slow-shutter photography involves using a long-duration shutter speed to sharply capture the stationary elements of images while blurring, smearing, or obscuring the moving elements. Long-exposure photography captures one element that conventional photography does not: an extended period of time. The paths of bright moving objects become clearly visible—clouds form broad bands, vehicle lights draw bright streaks, stars leave trails in the sky, and water waves appear smooth. Only bright objects leave visible trails, whereas dark objects usually disappear. Boats in long exposures disappear during the daytime, but draw bright trails from their lights at night. Technique While there is no fixed definition of what constitutes "long", the intent is to create a photo that somehow shows the effect of passing time, be it smoother waters or light trails. A 30-minute photo of a static object and surrounding cannot be distinguished from a short exposu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Path
Sun path, sometimes also called day arc, refers to the diurnal motion, daily (sunrise to sunset) and seasonal arc (geometry), arc-like path that the Sun appears to follow across the sky as the Earth Earth's rotation, rotates and Earth's orbit, orbits the Sun. The Sun's path affects the length of daytime experienced and amount of daylight received along a certain latitude during a given season. The relative position of the Sun is a major factor in the solar gain, heat gain of buildings and in the performance of solar energy systems. Accurate location-specific knowledge of sun path and climatic conditions is essential for economic decisions about solar thermal collector, solar collector area, orientation, landscaping, summer shading, and the cost-effective use of solar trackers. Angles Effect of the Earth's axial tilt Sun paths at any latitude and any time of the year can be determined from basic geometry. The Earth's axis of Earth's rotation, rotation tilts about Axial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinhole Camera
A pinhole camera is a simple camera without a lens but with a tiny aperture (the so-called ''Pinhole (optics), pinhole'')—effectively a light-proof box with a small hole in one side. Light from a scene passes through the aperture and projects an inverted image on the opposite side of the box, which is known as the camera obscura effect. The size of the images depends on the distance between the object and the pinhole. A Worldwide Pinhole Photography Day is observed on the last Sunday of April, every year. History Camera obscura The camera obscura or pinhole image is a natural optical phenomenon. Early known descriptions are found in the Chinese Mozi (book), Mozi writings (circa 500 BCE) and the Aristotelian ''Problems (Aristotle), Problems'' (circa 300 BCE – 600 CE). Ibn al-Haytham (965–1039), an Physics in the medieval Islamic world, Arab physicist also known as Alhazen, described the camera obscura effect. Over the centuries others started to experiment with it, main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Processing
Photographic processing or photographic development is the chemical means by which photographic film or paper is treated after photographic exposure to produce a negative or positive image. Photographic processing transforms the latent image into a visible image, makes this permanent and renders it insensitive to light.Karlheinz Keller et al. "Photography" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. All processes based upon the gelatin silver process are similar, regardless of the film or paper's manufacturer. Exceptional variations include instant films such as those made by Polaroid and thermally developed films. Kodachrome required Kodak's proprietary K-14 process. Kodachrome film production ceased in 2009, and K-14 processing is no longer available as of December 30, 2010. Ilfochrome materials use the dye destruction process. Deliberately using the wrong process for a film is known as cross processing. Common processes All p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Editing
Image editing encompasses the processes of altering images, whether they are Digital photography, digital photographs, traditional Photographic processing, photo-chemical photographs, or illustrations. Traditional analog image editing is known as photo manipulation, photo retouching, using tools such as an airbrush to modify photographs or edit illustrations with any traditional art medium. Graphic software programs, which can be broadly grouped into vector graphics editors, raster graphics editors, and 3D modelers, are the primary tools with which a user may manipulate, enhance, and transform images. Many image editing programs are also used to artistic rendering, render or create computer art from scratch. The term "image editing" usually refers only to the editing of 2D images, not 3D ones. Basics of image editing Raster graphics, Raster images are stored on a computer in the form of a grid of picture elements, or pixels. These pixels contain the image's color and brightn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Film Speed
Film speed is the measure of a photographic film's sensitivity to light, determined by sensitometry and measured on various numerical scales, the most recent being the ISO system introduced in 1974. A closely related system, also known as ISO, is used to describe the relationship between exposure and output image lightness in digital cameras. Prior to ISO, the most common systems were ASA in the United States and DIN in Europe. The term ''speed'' comes from the early days of photography. Photographic emulsions that were more sensitive to light needed less time to generate an acceptable image and thus a complete exposure could be finished faster, with the subjects having to hold still for a shorter length of time. Emulsions that were less sensitive were deemed "slower" as the time to complete an exposure was much longer and often usable only for still life photography. Exposure times for photographic emulsions shortened from hours to fractions of a second by the late 19th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Processes
A list of photographic processing techniques. Color * Agfacolor ** Ap-41 process (pre-1978 Agfa color slides; 1978-1983 was a transition period when Agfa slowly changed their color slide films from AP-41 to E6) * Anthotype * Autochrome Lumière, 1903 *Carbon print, 1862 * Chromogenic positive ( Ektachrome) ** E-3 process ** E-4 process **E-6 process * Chromogenic negative ** C-41 process ** RA-4 process * Dufaycolor * Dye destruction ** Cibachrome ** Ilfochrome *Dye-transfer process * Finlaycolor *Heliochrome * Kinemacolor *Kodachrome ** K-12 process ** K-14 process * Lippmann plate, 1891 * One-light Black and white (monochrome) A * Abration tone * Acetate film * Albertype *Albumen print, 1850 * Algraphy *Ambrotype * Amphitype * Amylotype * Anaglyph * Anthotype * Anthrakotype * Archertype * Argentotype * Argyrotype * Aristo paper * Aristotype * Aristo * Artotype * Atrephograph * Atrograph * Aurotype * Autotype (photographic process) B * Barrieotype * Baryta coated paper * Baya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternative Photographic Processes
Alternative or alternate may refer to: Arts, entertainment and media * Alternative (''Kamen Rider''), a character in the Japanese TV series ''Kamen Rider Ryuki'' * Alternative comics, or independent comics are an alternative to mainstream superhero comics * Alternative fashion, fashion that stands apart from mainstream, commercial fashion. * Alternative manga, manga published outside the more commercial market, or which have different art styles, themes, and narratives to those found in the more popular manga magazines. * ''AlterNative'', academic journal * ''The Alternative'' (film), a 1978 Australian television film * ''The Alternative'', a radio show hosted by Tony Evans * ''120 Minutes'' (2004 TV program), an alternative rock music video program formerly known as ''The Alternative'' *''The American Spectator'', an American magazine formerly known as ''The Alternative: An American Spectator'' Music * Alternative dance, a musical genre that mixes alternative rock with elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |