|
Sodium Estrone Sulfate
Estrone sulfate (E1S) is an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone. It is used in menopausal hormone therapy among other indications. As the sodium salt (sodium estrone sulfate), it is the major estrogen component of conjugated estrogens (Premarin) and esterified estrogens (Estratab, Menest). In addition, E1S is used on its own as the piperazine salt estropipate (piperazine estrone sulfate; Ogen). The compound also occurs as a major and important metabolite of estradiol and estrone. E1S is most commonly taken by mouth, but in the form of Premarin can also be taken by parenteral routes such as transdermal, vaginal, and injection. Medical uses E1S is used in menopausal hormone therapy among other indications. Pharmacology Pharmacodynamics E1S itself is essentially biologically inactive, with less than 1% of the relative binding affinity of estradiol for the estrogen receptors (ERs), ERα and ERβ. The compound acts as a prodrug of estrone and more import ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration whereby a substance is taken through the Human mouth, mouth, swallowed, and then processed via the digestive system. This is a common route of administration for many medications. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes of administration, such as Injection (medicine), injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth". The expression is used in medicine to describe a treatment that is taken orally (but not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
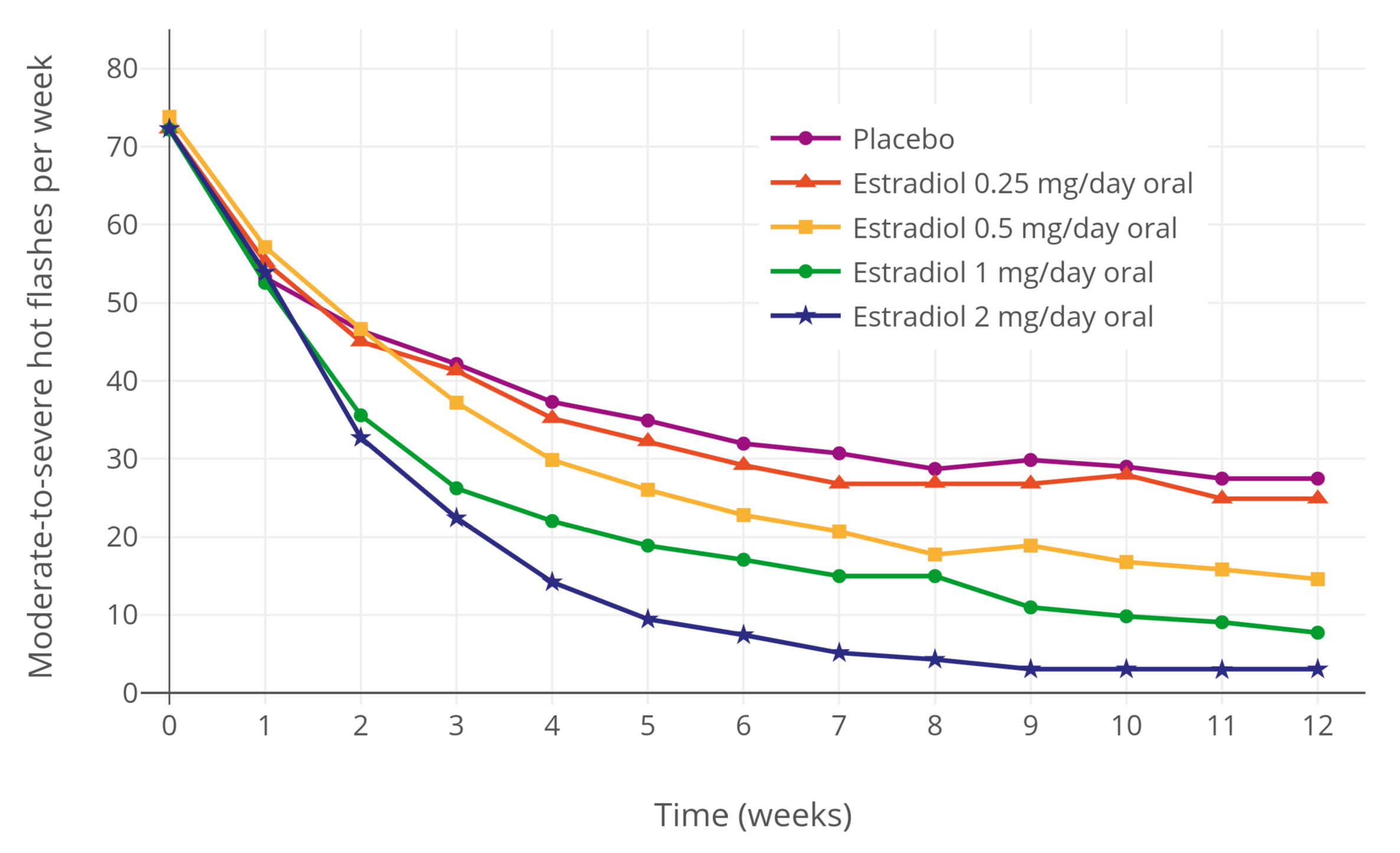
Estradiol (medication)
Estradiol (E2) is a medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone. It is an estrogen and is used mainly in menopausal hormone therapy and to treat hypogonadism, low sex hormone levels in women. It is also used in hormonal contraception, hormonal birth control for women, in feminizing hormone therapy for transgender women and some Non-binary gender, non-binary individuals, and in the treatment of hormone-sensitive cancers like prostate cancer in men and breast cancer in women, among other uses. Estradiol can be taken oral administration, by mouth, sublingual administration, held and dissolved under the tongue, as a gel or transdermal patch, patch that is transdermal, applied to the skin, intravaginal administration, in through the vagina, by intramuscular injection, injection into muscle or subcutaneous injection, fat, or through the use of an subcutaneous implant, implant that is placed into fat, among other route of administration, routes. Side effects of estradiol in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potency (pharmacology)
In pharmacology, potency or biological potency is a measure of a drug's biological activity expressed in terms of the dose required to produce a pharmacological effect of given intensity. A highly potent drug (e.g., fentanyl, clonazepam, risperidone, benperidol, bumetanide) evokes a given response at low concentrations, while a drug of lower potency (e.g. morphine, alprazolam, ziprasidone, haloperidol, furosemide) evokes the same response only at higher concentrations. Higher potency does not necessarily mean greater effectiveness nor more side effects nor less side effects. Types of potency The International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology (IUPHAR) has stated that "potency is an imprecise term that should always be further defined", and lists of types of potency as follows: Miscellaneous Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) is one of the most potent psychoactive drug A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, mind-altering drug, consciousness-altering drug, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prodrug
A prodrug is a pharmacologically inactive medication or compound that, after intake, is metabolized (i.e., converted within the body) into a pharmacologically active drug. Instead of administering a drug directly, a corresponding prodrug can be used to improve how the drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted (ADME). Prodrugs are often designed to improve bioavailability when a drug itself is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. A prodrug may be used to improve how selectively the drug interacts with cells or processes that are not its intended target. This reduces adverse or unintended effects of a drug, especially important in treatments like chemotherapy, which can have severe unintended and undesirable side effects. History Many herbal extracts historically used in medicine contain glycosides (sugar derivatives) of the active agent, which are hydrolyzed in the intestines to release the active and more bioavailable aglycone. For example, sal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ERβ
Estrogen receptor beta (ERβ) also known as NR3A2 (nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group A, member 2) is one of two main types of estrogen receptor—a nuclear receptor which is activated by the sex hormone estrogen. In humans ERβ is encoded by the ''ESR2'' gene. Function ERβ is a member of the family of estrogen receptors and the superfamily of nuclear receptor transcription factors. The gene product contains an N-terminus, N-terminal DNA binding domain and C-terminus, C-terminal ligand binding domain and is localized to the nucleus, cytoplasm, and mitochondria. Upon binding to 17-β-estradiol, estriol or related ligands, the encoded protein forms homo-dimers or hetero-dimers with estrogen receptor alpha, estrogen receptor α that interact with specific DNA sequences to activate transcription. Some isoforms dominantly inhibit the activity of other estrogen receptor family members. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been described, but the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ERα
Estrogen receptor alpha (ERα), also known as NR3A1 (nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group A, member 1), is one of two main types of estrogen receptor, a nuclear receptor (mainly found as a chromatin-binding protein) that is activated by the sex hormone estrogen. In humans, ERα is encoded by the gene ''ESR1'' (EStrogen Receptor 1). Structure The estrogen receptor (ER) is a ligand-activated transcription factor composed of several domains important for hormone binding, DNA binding, and activation of transcription. Alternative splicing results in several ESR1 mRNA transcripts, which differ primarily in their 5-prime untranslated regions. The translated receptors show less variability. Ligands Agonists Non-selective * Endogenous estrogens (e.g., estradiol, estrone, estriol, estetrol) * Natural estrogens (e.g., conjugated equine estrogens) * Synthetic estrogens (e.g., ethinylestradiol, diethylstilbestrol) Selective Agonists of ERα selective over ERβ in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estrogen Receptor
Estrogen receptors (ERs) are proteins found in cell (biology), cells that function as receptor (biochemistry), receptors for the hormone estrogen (17β-estradiol). There are two main classes of ERs. The first includes the intracellular estrogen receptors, namely ERα and ERβ, which belong to the nuclear receptor family. The second class consists of membrane estrogen receptors (mERs), such as GPER (GPR30), ER-X, and Gq-mER, Gq-mER, which are primarily G protein-coupled receptors. This article focuses on the nuclear estrogen receptors (ERα and ERβ). Upon activation by estrogen, intracellular ERs undergo protein targeting, translocation to the nucleus where they bind to specific DNA sequences. As DNA-binding transcription factors, they regulate the activity of various genes. However, ERs also exhibit functions that are independent of their DNA-binding capacity. These non-genomic actions contribute to the diverse effects of estrogen signaling in cells. Estrogen receptors (ERs) b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relative Binding Affinity
In biochemistry and pharmacology, a ligand is a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose. The etymology stems from Latin ''ligare'', which means 'to bind'. In protein-ligand binding, the ligand is usually a molecule which produces a signal by binding to a site on a target protein. The binding typically results in a change of conformational isomerism (conformation) of the target protein. In DNA-ligand binding studies, the ligand can be a small molecule, ion, or protein which binds to the DNA double helix. The relationship between ligand and binding partner is a function of charge, hydrophobicity, and molecular structure. Binding occurs by intermolecular forces, such as ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds and Van der Waals forces. The association or docking is actually reversible through dissociation. Measurably irreversible covalent bonding between a ligand and target molecule is atypical in biological systems. In contrast to the definition of l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Activity
In pharmacology, biological activity or pharmacological activity describes the beneficial or adverse effects of a drug on living matter. When a drug is a complex chemical mixture, this activity is exerted by the substance's active ingredient or pharmacophore but can be modified by the other constituents. Among the various properties of chemical compounds, pharmacological/biological activity plays a crucial role since it suggests uses of the compounds in the medical applications. However, chemical compounds may show some adverse and toxic effects which may prevent their use in medical practice. Biological activity is usually measured by a bioassay and the activity is generally dosage-dependent, which is investigated via dose-response curves. Further, it is common to have effects ranging from beneficial to adverse for one substance when going from low to high doses. Activity depends critically on fulfillment of the ADME criteria. To be an effective drug, a compound not only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Injection (medicine)
An injection (often and usually referred to as a "shot" in US English, a "jab" in UK English, or a "jag" in Scottish English and Scots) is the act of administering a liquid, especially a drug, into a person's body using a needle (usually a hypodermic needle) and a syringe. An injection is considered a form of parenteral drug administration; it does not involve absorption in the digestive tract. This allows the medication to be absorbed more rapidly and avoid the first pass effect. There are many types of injection, which are generally named after the body tissue the injection is administered into. This includes common injections such as subcutaneous, intramuscular, and intravenous injections, as well as less common injections such as epidural, intraperitoneal, intraosseous, intracardiac, intraarticular, and intracavernous injections. Injections are among the most common health care procedures, with at least 16 billion administered in developing and transitional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaginal Administration
Intravaginal administration is a route of administration where the substance is applied inside the vagina. Pharmacologically, it has the potential advantage to result in effects primarily in the vagina or nearby structures (such as the vaginal portion of cervix) with limited systemic adverse effects compared to other routes of administration. Formulation methods include vaginal tablets, vaginal cream, vaginal gel, vaginal suppository and vaginal ring. It is used as an administration method for issues related to women's health, such as contraception. Medicines primarily delivered by intravaginal administration include vaginally administered estrogens and progestogens (a group of hormones including progesterone), and antibacterials and antifungals to treat bacterial vaginosis and yeast infections respectively. Medicines may also be administered intravaginally as an alternative to oral route in the case of nausea or other digestive problems. It is a potential means of artificial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transdermal Administration
Transdermal is a route of administration wherein active ingredients are delivered across the skin for systemic distribution. Examples include transdermal patches used for medicine delivery. The drug is administered in the form of a patch or ointment that delivers the drug into the circulation for systemic effect. Techniques Obstacles Although the skin is a large and logical target for drug delivery, its basic functions limit its utility for this purpose. The skin functions mainly to protect the body from external penetration (by e.g. harmful substances and microorganisms) and to contain all body fluids. There are two important layers to the human skin: (1) the epidermis and (2) the dermis. For transdermal delivery, drugs must pass through the two sublayers of the epidermis to reach the microcirculation of the dermis. The stratum corneum is the top layer of the skin and varies in thickness from approximately ten to several hundred micrometres, depending on the region of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |