|
Snake In Chinese Mythology
Snakes (also known as serpents) are an important motif in Chinese mythology. There are various myths, legends, and folk tales about snakes. Chinese mythology refers to these and other myths found in the historical geographic area(s) of China. These myths include Chinese and other languages, as transmitted by Han Chinese as well as other ethnic groups (of which fifty-six are officially recognized by the current administration of China). Snakes often appear in myth, religion, legend, or tales as fantastic beings unlike any possible real snake, often having a mix of snake with other body parts, such as having a human head, or magical abilities, such as shape-shifting. One famous snake that was able to transform back and forth between a snake and a human being was Madam White Snake in the Legend of the White Snake. Other snakes or snake-like beings sometimes include deities, such as Fuxi and Nüwa and Gong Gong. Sometimes, Fuxi and Nuwa are described as snakes with human heads an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptozoology
Cryptozoology is a pseudoscience and subculture that searches for and studies unknown, legendary, or extinct animals whose present existence is disputed or unsubstantiated, particularly those popular in folklore, such as Bigfoot, the Loch Ness Monster, Yeti, the chupacabra, the Jersey Devil, or the Mokele-mbembe. Cryptozoologists refer to these entities as '' cryptids'', a term coined by the subculture. Because it does not follow the scientific method, cryptozoology is considered a pseudoscience by mainstream science: it is neither a branch of zoology nor of folklore studies. It was originally founded in the 1950s by zoologists Bernard Heuvelmans and Ivan T. Sanderson. Scholars have noted that the subculture rejected mainstream approaches from an early date, and that adherents often express hostility to mainstream science. Scholars studying cryptozoologists and their influence (including cryptozoology's association with Young Earth creationism) noted parallels in crypto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Five Noxious Creatures
The Five Poisons (Chinese: 五毒; Pinyin: ''wǔ dú''; Jyutping: ''ng5 duk6''; Vietnamese: ''Ngũ độc''), or the ''five noxious creatures'', can refer to an ancient Chinese set of poisonous or otherwise hazardous animals or five perceived threats the Chinese Communist Party sees for its rule over mainland China. Ancient Chinese Five Poisons The fifth day of the fifth month or Duanwu in ancient Chinese folklore symbolised the beginning of the Summer, this day also known as "Double 5 day" or "Double 5th day" or more commonly ''tiān zhōng jié'' () was seen as one of the most inauspicious and dangerous days of the year. This was because all the poisonous animals and bugs would then begin to appear. "Double five" day was furthermore seen as the hottest day and it was believed that the heat would cause illness. The Ancient Chinese believed that the only way to combat poison was with poison, and one way they believed that they could protect themselves on this day was by dri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duanwu
The Dragon Boat Festival ( zh, s=端午节, t=端午節, first=t, p=Duānwǔ jié, cy=Dyūnńgh jit) is a traditional Chinese holiday that occurs on the fifth day of the fifth month of the Chinese calendar, which corresponds to late May or early June in the Gregorian calendar. The holiday commemorates Qu Yuan who was the beloved prime minister of the southern Chinese state of Chu during the Warring States period, about 600 B.C. to 200 B.C., and is celebrated by holding dragon boat races and eating sticky rice dumplings called ''zongzi'', which were southern Chinese traditions. Dragon Boat Festival integrates praying for good luck and taking respite from the summer heat. In September 2009, UNESCO officially approved the holiday's inclusion in the Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity, becoming the first Chinese holiday to be selected. Names The English language name for the holiday is "Dragon Boat Festival", used as the official English translation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
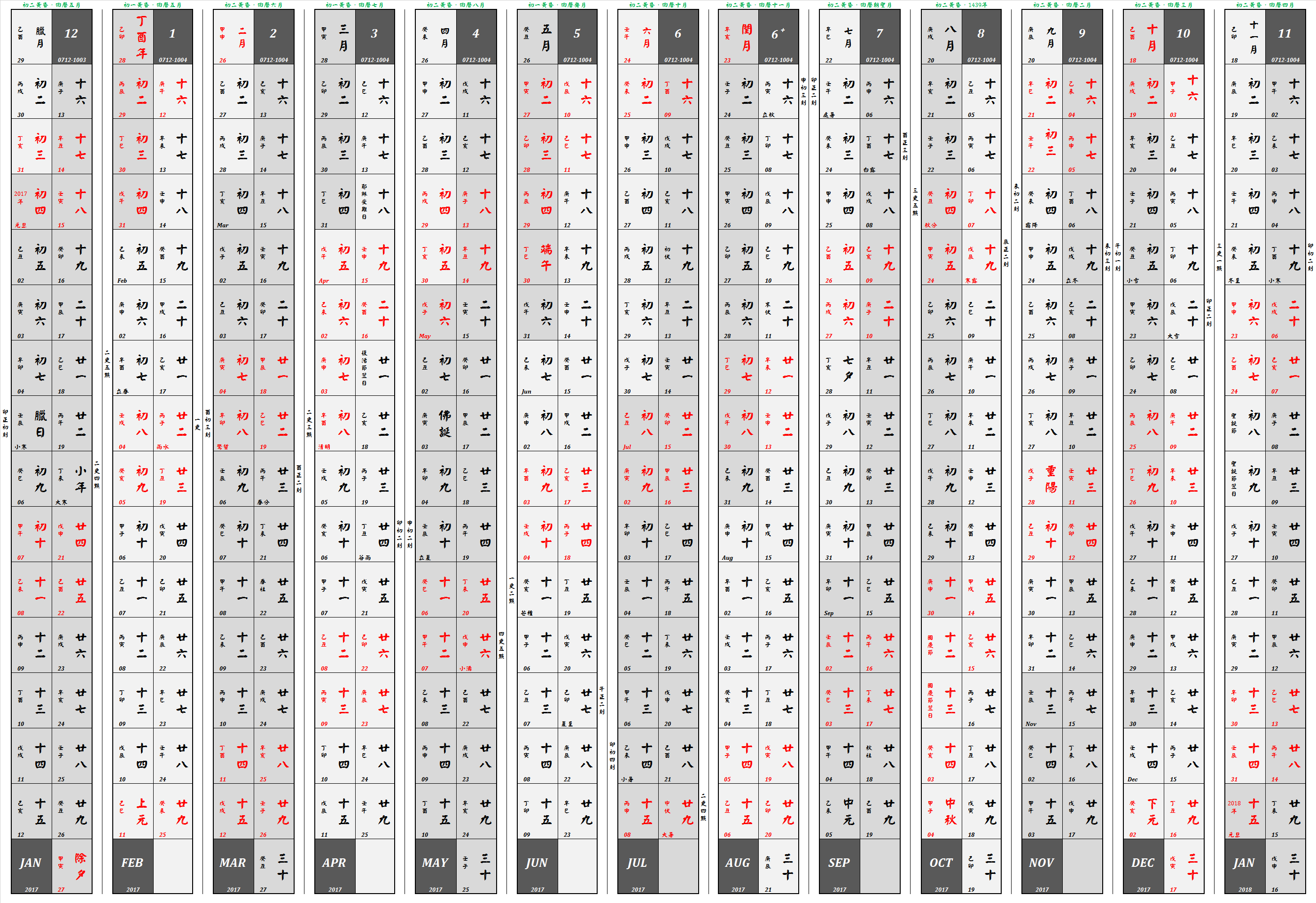
Chinese Calendar
The traditional Chinese calendar, dating back to the Han dynasty, is a lunisolar calendar that blends solar, lunar, and other cycles for social and agricultural purposes. While modern China primarily uses the Gregorian calendar for official purposes, the traditional calendar remains culturally significant. It determines the timing of Chinese New Year with traditions like the twelve animals of the Chinese zodiac, Chinese Zodiac still widely observed. The traditional Chinese calendar uses the Sexagenary cycle, sexagenary cycle, a repeating system of Heavenly Stems and Earthly Branches, to mark years, months, and days. This system, along with astronomical observations and mathematical calculations, was developed to align solar and lunar cycles, though some approximations are necessary due to the natural differences between these cycles. Over centuries, the calendar was refined through advancements in astronomy and horology, with dynasties introducing variations to improve accu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthly Branches
The Earthly Branches (also called the Terrestrial Branches or the 12-cycle) are a system of twelve ordered symbols used throughout East Asia. They are indigenous to China, and are themselves Chinese characters, corresponding to words with no concrete meaning other than the associated branch's ordinal position in the list. Cultural applications of the Branches include a dating system known as the sexagenary cycle, and their use in Chinese astrology. They are associated with the ten Heavenly Stems in Chinese calendars, and in Taoist practice. Overview The twelve Earthly Branches are: The branches each have specific names in the languages of the Sinosphere—which include Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Turkic, Vietnamese, and Mongolian. Branches are commonly used when counting in a manner similar to how letters are used according to their alphabetical ordering. In addition to the calendar months, each branch has been associated with several distinct cultural categori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse (zodiac)
The Horse ( ⾺) is the seventh of the 12-year cycle of animals which appear in the Chinese zodiac related to the Chinese calendar. There is a long tradition of the Horse in Chinese mythology. Certain characteristics of the Horse nature are supposed to be typical of or to be associated with either a year of the Horse and its events, or in regard to the personality of someone born in such a year. Horse aspects can also enter by other chronomantic factors or measures, such as hourly. The year of the horse is associated with the Earthly Branch symbol 午. History The lunar calendar paved the sequence of the Chinese zodiac animals. This calendar can be traced back to the 14th century B.C. Myths say that Emperor Huangdi, the first Chinese emperor, in 2637 B.C. invented the Chinese lunar calendar, which follows the cycles of the moon. In a folklore story that explains the origins of the cycle, the animals hold a race to determine their order. The custom of pairing an animal wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yin And Yang
Originating in Chinese philosophy, yin and yang (, ), also yinyang or yin-yang, is the concept of opposite cosmic principles or forces that interact, interconnect, and perpetuate each other. Yin and yang can be thought of as complementary and at the same time opposing forces that interact to form a dynamic system in which the whole is greater than the assembled parts and the parts are as important for the cohesion of the whole. In Chinese cosmology, the universe creates itself out of a primary chaos of primordial qi or material energy, organized into the cycles of yin and yang, force and motion leading to form and matter. "Yin" is retractive, passive and contractive in nature, while "yang" is repelling, active and expansive in principle; this dichotomy in some form, is seen in all things in nature—patterns of change and difference. For example, biological, psychological and seasonal cycles, the historical evolution of landscapes over days, weeks, years to eons. The origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Calendar Correspondence Table
This Chinese calendar correspondence table shows the stem/branch year names, correspondences to the Western ( Gregorian) calendar, and other related information for the current, 79th sexagenary cycle of the Chinese calendar based on the 2697 BC epoch or the 78th cycle if using the 2637 BC epoch. Footnotes {{DEFAULTSORT:Chinese Calendar Correspondence Table Astronomy Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest includ ... Specific calendars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragon (zodiac)
The dragon () is the fifth of the 12-year cycle of animals that appear in the Chinese zodiac related to the Chinese calendar. The Year of the Dragon is associated with the Earthly Branch symbol 辰 (pinyin: ''chén''). It has been proposed that the Earthly Branch character may have been associated with scorpions; it may have symbolized the star Antares. In the Buddhist calendar used in Thailand, Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, and Sri Lanka, the dragon is replaced by the nāga. In the Gurung zodiac, the dragon is replaced by the eagle. In the Old Turkic calendar it is replaced by a fish or crocodile. Early Persian translations of the medieval period change the dragon to a sea serpent, although in current times it is generally referred to as whale. During China's Cultural Revolution, there was an attempt to replace the dragon with the giant panda; however, the movement was short lived. Years and the five elements People born within these date ranges can be said to have been born ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snake (zodiac)
The snake ( 蛇) is the sixth of the twelve-year cycle of animals which appear in the Chinese zodiac related to the Chinese calendar. The Year of the Snake is associated with the Earthly Branch symbol 巳. Besides its use in the cycle of years, the zodiacal snake is otherwise used to also represent hours of the day. Snakes have a long and complicated place in Chinese mythology and culture. Other uses The same twelve animals are also used to symbolize the cycle of hours in the day, each being associated with a two-hour time period. The hour of the snake is 9:00 to 11:00 a.m., the time when the Sun warms up the Earth, and snakes are said to slither out of their holes. The month of the snake is the 4th month of the Chinese lunar calendar and it usually falls within the months of May through June depending on the Chinese to Gregorian calendar conversion. The reason the animal signs are referred to as zodiacal is that one's personality is said to be influenced by the animal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |