|
Slack Tide
Slack tide or slack water is the short period in a body of tidal water when the water is completely unstressed, and there is no movement either way in the tidal stream. It occurs before the direction of the tidal stream reverses. Slack water can be estimated using a tidal atlas or the tidal diamond information on a nautical chart. The time of slack water, particularly in constricted waters, does not occur at high and low water, and in certain areas, such as Primera Angostura, the ebb may run for up to three hours after the water level has started to rise. Similarly, the flood may run for up to three hours after the water has started to fall. In 1884, Thornton Lecky illustrated the phenomenon with an inland basin of infinite size, connected to the sea by a narrow mouth. Since the level of the basin is always at mean sea level, the flood in the mouth starts at half tide, and its velocity is at its greatest at the time of high water, with the strongest ebb occurring conversely at l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another. Tide tables can be used for any given locale to find the predicted times and amplitude (or " tidal range"). The predictions are influenced by many factors including the alignment of the Sun and Moon, the phase and amplitude of the tide (pattern of tides in the deep ocean), the amphidromic systems of the oceans, and the shape of the coastline and near-shore bathymetry (see '' Timing''). They are however only predictions, the actual time and height of the tide is affected by wind and atmospheric pressure. Many shorelines experience semi-diurnal tides—two nearly equal high and low tides each day. Other locations have a diurnal tide—one high and low tide each day. A "mixed tide"—two uneven magnitude tides a day—is a third regular category. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tidal Atlas
A tidal atlas or a tidal stream atlas is used to predict the direction and speed of tidal currents. A tidal atlas usually consists of a set of 12 or 13 diagrams, one for each hour of the tidal cycle, for a coastal region. Each diagram uses arrows to indicate the direction of the flow at that time. The speed of the flow is shown by the length and thickness of the arrows. For all except the smallest arrows numbers give more precise information. Areas of slack water may be indicated by no arrows or the words "slack water". UK Admiralty Tidal Atlases show speed in units of tenth of a knot. Two figures are given separated by a comma, the first is the mean neap rate and the second the mean spring rate. The dot of the comma indicates where the observations were made. It is important to realise that the tidal hour lasts from half an hour before the nominal time to half an hour after. For instance the chart for 3 hours after high water is valid from HW+2½ to HW+3½, not from HW+3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tidal Diamond
Tidal diamonds are symbols on British admiralty charts and others that indicate the direction and speed of tidal streams. The symbols consist of a letter of the ISO basic Latin alphabet in a rhombus, printed in purple ink. On any particular chart each tidal diamond will have a unique letter starting from "A" and continuing alphabetically. Either somewhere on the chart (generally on land) or else on a separate sheet, will be a ''Tidal Diamond table''. This contains a grid of thirteen rows and three columns for each Diamond. The rows are the hours of the tidal cycle showing the 6 hours before high water, high water itself and the 6 hours after high water. It is important to realise that the tidal hour lasts from half an hour before the nominal time to half an hour after. For instance the row for 3 hours after high water is valid from HW+2½ to HW+3½, not from HW+3 to HW+4. The columns show the bearing of the tidal stream and its speed, in knots, at both spring tide and neap tid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nautical Chart
A nautical chart or hydrographic chart is a graphic representation of a sea region or water body and adjacent coasts or river bank, banks. Depending on the scale (map), scale of the chart, it may show depths of water (bathymetry) and heights of land (topography), natural features of the seabed, details of the coastline, navigational hazards, locations of natural and human-made aids to navigation, information on tides and Ocean current, currents, local details of the Earth's magnetic field, and human-made structures such as harbor, harbours, buildings, and bridges. Nautical charts are essential tools for marine navigation; many countries require vessels, especially commercial ships, to carry them. Nautical charting may take the form of charts printed on paper (raster navigational charts) or computerized electronic navigational charts. Recent technologies have made available paper charts which are printed "on demand" with cartographic data that has been downloaded to the commercial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primera Angostura
Primera Angostura is a sound of the Strait of Magellan in the Chilean region of Magallanes. It is located near Punta Delgada. It lies between the commune of San Gregorio, in Magallanes Province, to the north, and the commune of Primavera, in Tierra del Fuego Province, to the south. It is the narrowest part of the Strait between the continent and the island of Tierra del Fuego. The sound was named ''Primera Angostura'' (Spanish for ''First Narrows'') as it was the first narrows of the strait that ships met when sailing through the strait from east to west. The ferry company Transbordadora Austral Broom S.A. operates across the narrows. During the White Earthquake in August 1995 the ferry service across Primera Angostura was suspended. The international road to Río Gallegos was also closed in the events. See also * Bahía Posesión * Segunda Angostura * Spanish colonization attempt of the Strait of Magellan In the late 16th century, the Spanish Empire attempted t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another. Tide tables can be used for any given locale to find the predicted times and amplitude (or " tidal range"). The predictions are influenced by many factors including the alignment of the Sun and Moon, the phase and amplitude of the tide (pattern of tides in the deep ocean), the amphidromic systems of the oceans, and the shape of the coastline and near-shore bathymetry (see '' Timing''). They are however only predictions, the actual time and height of the tide is affected by wind and atmospheric pressure. Many shorelines experience semi-diurnal tides—two nearly equal high and low tides each day. Other locations have a diurnal tide—one high and low tide each day. A "mixed tide"—two uneven magnitude tides a day—is a third regular category. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scuba Diving
Scuba diving is a Diving mode, mode of underwater diving whereby divers use Scuba set, breathing equipment that is completely independent of a surface breathing gas supply, and therefore has a limited but variable endurance. The word ''scuba'' is an Acronym#Normal case and acronyms, acronym for "Self-Contained Underwater Breathing Apparatus" and was coined by Christian J. Lambertsen in a patent submitted in 1952. Scuba divers carry their own source of breathing gas, affording them greater independence and movement than surface-supplied divers, and more time underwater than freedivers. Although the use of compressed air is common, other gas blends are also used. Open-circuit scuba systems discharge the breathing gas into the environment as it is exhaled and consist of one or more diving cylinders containing breathing gas at high pressure which is supplied to the diver at ambient pressure through a diving regulator. They may include additional cylinders for range extension, de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visibility
In meteorology, visibility is the measure of the distance at which an object or light can be clearly discerned. It depends on the Transparency and translucency, transparency of the surrounding air and as such, it is unchanging no matter the ambient light level or time of day. It is reported within surface weather observations and METAR code either in Metre, meters or statute miles, depending upon the country. Visibility affects all forms of traffic: road traffic, roads, railways, sailing and aviation. The geometric range of vision is limited by the curvature of the Earth and depends on the eye level and the height of the object being viewed. In geodesy, the atmospheric refraction must be taken into account when calculating geodetic visibility. Meteorological visibility Definition ICAO Annex 3 ''Meteorological Service for International Air Navigation'' contains the following definitions and note: :a) the greatest distance at which a black object of suitable dimensions, situa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf St Vincent
Gulf St Vincent, sometimes referred to as St Vincent Gulf, St Vincent's Gulf or Gulf of St Vincent, is the eastern of two large inlets of water on the southern coast of Australia, in the state of South Australia, the other being the larger Spencer Gulf, from which it is separated by Yorke Peninsula. On its eastern side the gulf is bordered by the Adelaide Plains and the Fleurieu Peninsula. Description The St Vincent basin is formed from Cenozoic sediments deposited over, and surrounded by, Proterozoic and Paleozoic rock. Around 55 million years ago Gondwanaland broke up and Australia separated from Antarctica, causing a number of basins to form along the southern Australian coastline. Around 40 million years ago a number of blocks formed with the Mount Lofty Ranges rising to the east of the St Vincent basin. At the end of the Last Glacial Maximum around 10,000-15,000 years ago, the sea levels rose and covered the St. Vincent basin. Location To the south it is defined b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neap Tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another. Tide tables can be used for any given locale to find the predicted times and amplitude (or "tidal range"). The predictions are influenced by many factors including the alignment of the Sun and Moon, the phase and amplitude of the tide (pattern of tides in the deep ocean), the amphidromic systems of the oceans, and the shape of the coastline and near-shore bathymetry (see ''Timing''). They are however only predictions, the actual time and height of the tide is affected by wind and atmospheric pressure. Many shorelines experience semi-diurnal tides—two nearly equal high and low tides each day. Other locations have a diurnal tide—one high and low tide each day. A "mixed tide"—two uneven magnitude tides a day—is a third regular category. Tides v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Rowland Twidale
Charles Rowland Twidale is an Australian geomorphologist active at the University of Adelaide. Twidale's research has covered varied subjects including structural geomorphology, weathering, ancient landscapes in shield regions, granite landforms in deserts, paleosurfaces and the history of geomorphology. Twidale has been most active investigating the geomorphology of Australia, Spain and southwestern United States. In 1976 C. R. Twidale was president of the Royal Society of South Australia The Royal Society of South Australia (RSSA) is a learned society whose interest is in science, particularly, but not only, of South Australia. The major aim of the society is the promotion and diffusion of scientific knowledge, particularly in re .... In 1993 he was awarded the Mueller Medal by the Australian and New Zealand Association for the Advancement of Science.ANZAAS > Mueller Medal Recipientsarchive.is Retrieved 9 July 2017, References External links * Australian geomorp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
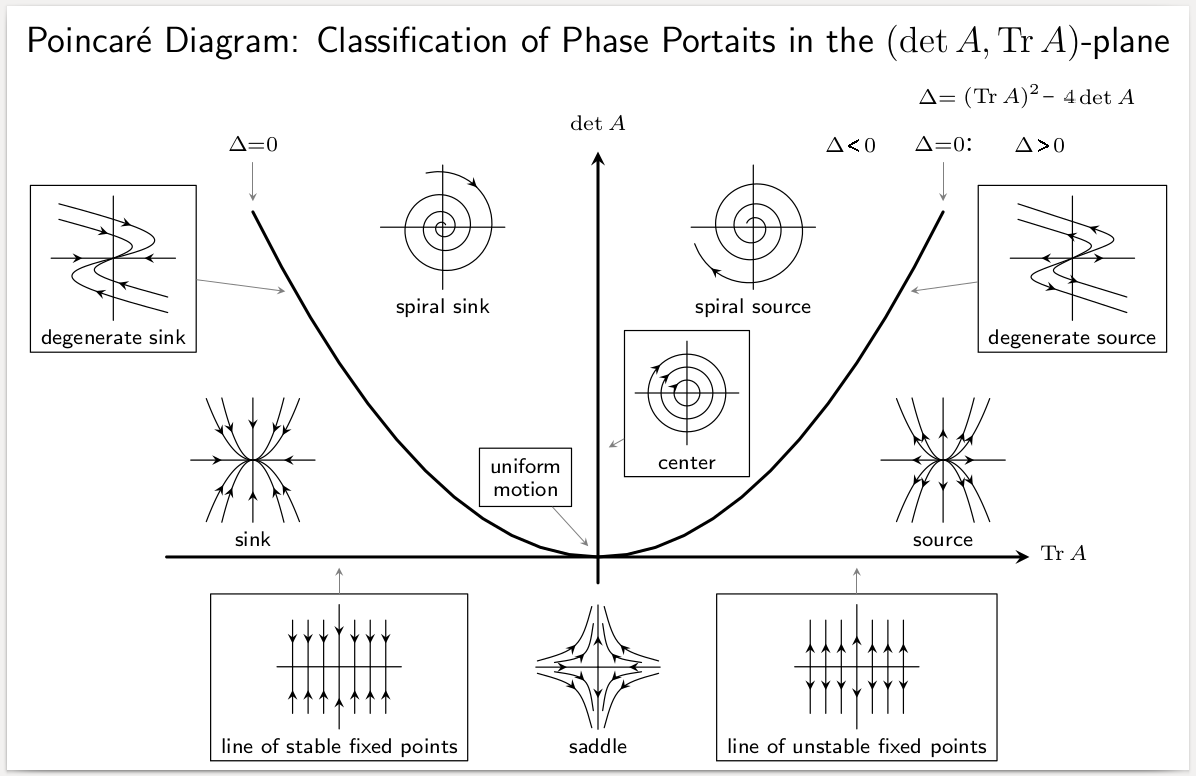
Stability Theory
In mathematics, stability theory addresses the stability of solutions of differential equations and of trajectories of dynamical systems under small perturbations of initial conditions. The heat equation, for example, is a stable partial differential equation because small perturbations of initial data lead to small variations in temperature at a later time as a result of the maximum principle. In partial differential equations one may measure the distances between functions using Lp space, Lp norms or the sup norm, while in differential geometry one may measure the distance between spaces using the Gromov–Hausdorff convergence, Gromov–Hausdorff distance. In dynamical systems, an orbit (dynamics), orbit is called ''Lyapunov stability, Lyapunov stable'' if the forward orbit of any point is in a small enough neighborhood or it stays in a small (but perhaps, larger) neighborhood. Various criteria have been developed to prove stability or instability of an orbit. Under favorable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |