|
Sitosterolemia
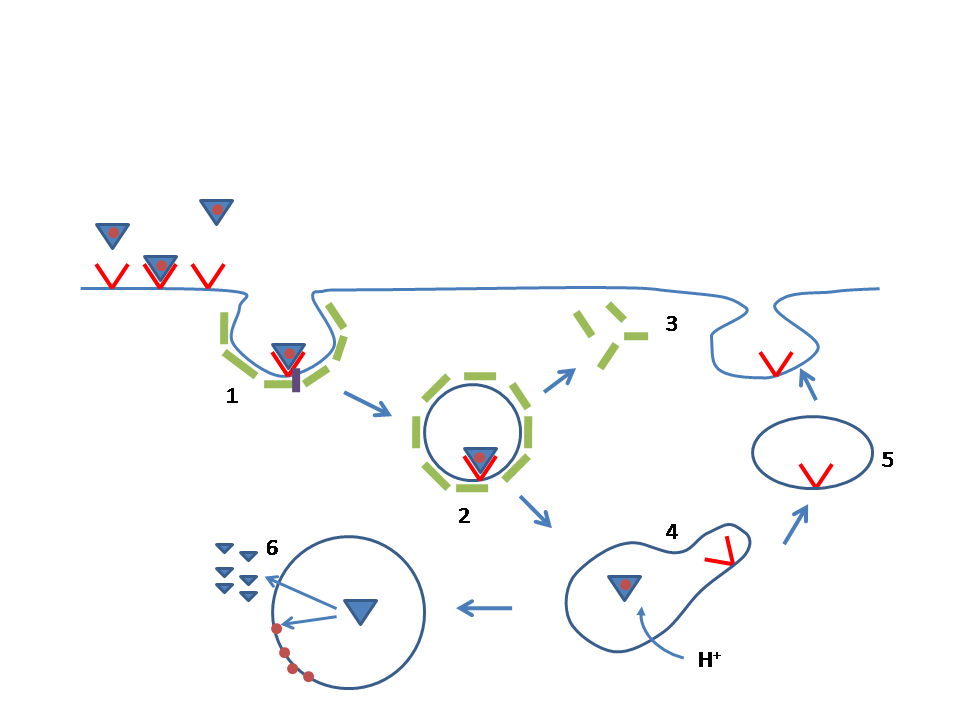
Sitosterolemia, also known as phytosterolemia, is a rare autosomal recessively inherited lipid metabolic disorder. It is characterized by hyperabsorption and decreased biliary excretion of dietary sterols (including the phytosterol beta-sitosterol). Healthy persons absorb only about 5% of dietary plant sterols, but sitosterolemia patients absorb 15% to 60% of ingested sitosterol without excreting much into the bile. It's named after the most abundant phytosterol in the diet, sitosterol, though other phytosterols are also involved. The phytosterol campesterol is more readily absorbed than sitosterol. Sitosterolemia patients develop hypercholesterolemia, tendon and tuberous xanthomas, premature development of atherosclerosis, and abnormal hematologic and liver function test results. Signs and symptoms Sitosterolemia may share several clinical characteristics with the well-characterized familial hypercholesterolemia (FH), such as the development of tendon xanthomas in the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ABCG5
ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ABCG5'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intra-cellular membranes. ABC genes are divided into seven distinct subfamilies (ABC1, MDR/TAP, MRP, ALD, OABP, GCN20, White). This protein is a member of the White subfamily. The protein encoded by this gene functions as a half-transporter to limit intestinal absorption and promote biliary excretion of sterols. It is expressed in a tissue-specific manner in the liver, colon, and intestine. This gene is tandemly arrayed on chromosome 2, in a head-to-head orientation with family member ABCG8. Mutations in this gene may contribute to sterol accumulation and atherosclerosis, and have been observed in patients with sitosterolemia Sitosterolemia, also known as phytosterolemia, is a rare autosomal recessi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ABCG8
ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ABCG8'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intra-cellular membranes. ABC genes are divided into seven distinct subfamilies (ABC1, MDR/TAP, MRP, ALD, OABP, GCN20, White). This protein is a member of the White subfamily. The protein encoded by this gene functions as a half-transporter to limit intestinal absorption and promote biliary excretion of sterols. It is expressed in a tissue-specific manner in the liver, colon, and intestine. This gene is tandemly arrayed on chromosome 2, in a head-to-head orientation with family member ABCG5. Mutations in this gene may contribute to sterol accumulation and atherosclerosis, and have been observed in patients with sitosterolemia. A loss-of-function mutation in ABCG8 impairs the removal of sterols from cells and, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Familial Hypercholesterolemia
Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a genetic disorder characterized by high cholesterol levels, specifically very high levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL cholesterol), in the blood and early cardiovascular diseases. The most common mutations diminish the number of functional LDL receptors in the liver or produce abnormal LDL receptors that never go to the cell surface to function properly (abnormal trafficking). Since the underlying body biochemistry is slightly different in individuals with FH, their high cholesterol levels are less responsive to the kinds of cholesterol control methods which are usually more effective in people without FH (such as dietary modification and statin tablets). Nevertheless, treatment (including higher statin doses and PCSK9 inhibitors) is usually effective. FH is classified as a type 2 familial dyslipidemia. There are five types of familial dyslipidemia (not including subtypes), and each are classified from both the altered l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMG-CoA Reductase
HMG-CoA reductase (3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase, official symbol HMGCR) is the rate-limiting enzyme (NADH-dependent, ; NADPH-dependent, ) of the mevalonate pathway, the metabolic pathway that produces cholesterol and other isoprenoids. HMGCR catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonic acid, a necessary step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol. Normally in mammalian cells this enzyme is competitively suppressed so that its effect is controlled. This enzyme is the target of the widely available cholesterol-lowering drugs known collectively as the statins, which help treat dyslipidemia. HMG-CoA reductase is anchored in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum, and was long regarded as having seven transmembrane domains, with the active site located in a long carboxyl terminal domain in the cytosol. More recent evidence shows it to contain eight transmembrane domains. In humans, the gene for HMG-CoA reductase (NADPH) is located on the long arm of the fif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytosterol
Phytosterols are phytosteroids, similar to cholesterol, that serve as structural components of biological membranes of plants. They encompass plant sterols and stanol ester, stanols. More than 250 sterols and related compounds have been identified. Free phytosterols extracted from oils are insoluble in water, relatively insoluble in oil, and soluble in alcohols. Phytosterol-enriched foods and dietary supplements have been marketed for decades. Despite well-documented LDL cholesterol-lowering effects from long-term consumption of phytosterols, there is insufficient evidence for an effect on cardiovascular diseases, fasting blood sugar, glycated hemoglobin, or overall mortality rate. Structure They have a fused polycyclic structure and vary in carbon side chains and / or presence or absence of a double bond (saturation). They are divided into 4,4-dimethyl phytosterols, 4-monomethyl phytosterols, and 4-desmethyl phytosterols based on the location of methyl groups at the carbon-4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campesterol
Campesterol is a phytosterol whose chemical structure is similar to that of cholesterol, and is one of the ingredients for E number E499. Natural occurrences Many vegetables, fruits, nuts, and seeds contain campesterol, but in low concentrations. Banana, pomegranate, pepper, coffee, grapefruit, cucumber, onion, oat, potato, and lemon grass (citronella) are few examples of common sources containing campesterol at roughly 1–7 mg/100 g of the edible portion. In contrast, canola and corn oils contain as much as 16–100 mg/100 g. Levels are variable and are influenced by geography and growing environment. In addition, different strains have different levels of plant sterols. A number of new genetic strains are currently being engineered with the goal of producing varieties high in campesterol and other plant sterols. It is also found in dandelion coffee. It is so named because it was first isolated from the rapeseed (''Brassica campestris''). Precursor o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xanthomas
A xanthoma (pl. xanthomas or xanthomata) (condition: xanthomatosis) is a deposition of yellowish cholesterol-rich material that can appear anywhere in the body in various disease states. They are cutaneous manifestations of lipidosis in which lipids accumulate in large foam cells within the skin. They are associated with hyperlipidemias, both primary and secondary types. Tendon xanthomas are associated with type II hyperlipidemia, chronic biliary tract obstruction, primary biliary cirrhosis, sitosterolemia and the rare metabolic disease cerebrotendineous xanthomatosis. Palmar xanthomata and tuberoeruptive xanthomata (over knees and elbows) occur in type III hyperlipidemia. Etymology The term xanthoma stems from Greek ξανθός (xanthós) 'yellow', and -ωμα -oma, a suffix forming nouns indicating a mass or tumor. Types Xanthelasma A xanthelasma is a sharply demarcated yellowish collection of cholesterol underneath the skin, usually on or around the eyelids. Strictly, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosomes is collectively known as atDNA or auDNA. For example, humans have a diploid genome that usually contains 22 pairs of autosomes and one allosome pair (46 chromosomes total). The autosome pairs are labeled with numbers (1–22 in humans) roughly in order of their sizes in base pairs, while allosomes are labelled with their letters. By contrast, the allosome pair consists of two X chromosomes in females or one X and one Y chromosome in males. Unusual combinations XYY, XXY, XXX, XXXX, XXXXX or XXYY, among other irregular combinations, are known to occur and usually cause developmental abnormalities. Autosomes still contain sexual determination genes even though they are not sex chromosomes. For example, the SRY gene on the Y chrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splenomegaly
Splenomegaly is an enlargement of the spleen. The spleen usually lies in the left upper quadrant (LUQ) of the human abdomen. Splenomegaly is one of the four cardinal signs of ''hypersplenism'' which include: some reduction in number of circulating blood cells affecting granulocytes, erythrocytes or platelets in any combination; a compensatory proliferative response in the bone marrow; and the potential for correction of these abnormalities by splenectomy. Splenomegaly is usually associated with increased workload (such as in hemolytic anemias), which suggests that it is a response to hyperfunction. It is therefore not surprising that splenomegaly is associated with any disease process that involves abnormal red blood cells being destroyed in the spleen. Other common causes include congestion due to portal hypertension and infiltration by leukemias and lymphomas. Thus, the finding of an enlarged spleen, along with caput medusae, is an important sign of portal hypertension ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronary Heart Disease
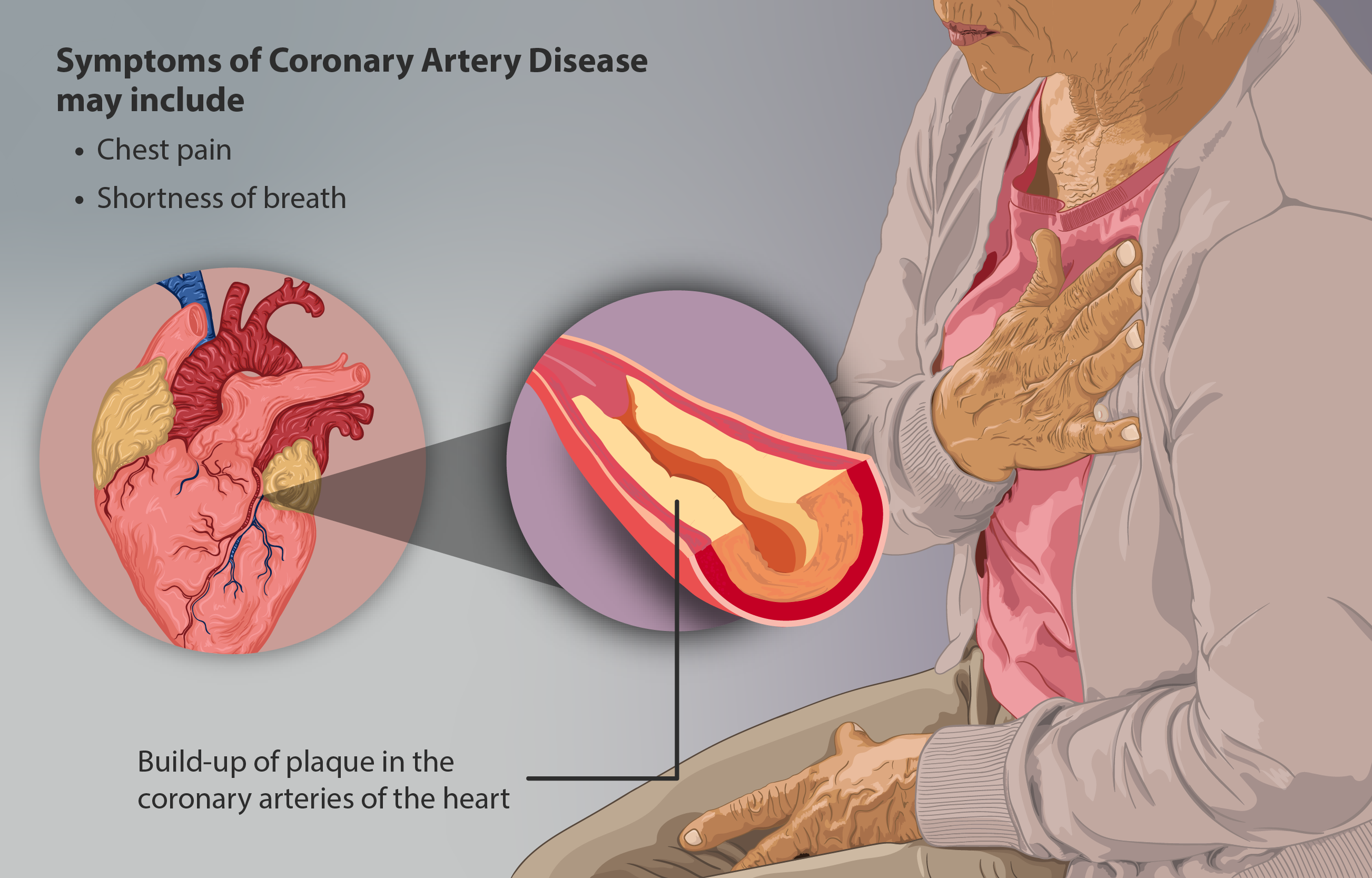
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), or ischemic heart disease (IHD), is a type of cardiovascular disease, heart disease involving Ischemia, the reduction of blood flow to the cardiac muscle due to a build-up of atheromatous plaque in the Coronary arteries, arteries of the heart. It is the most common of the cardiovascular diseases. CAD can cause stable angina, unstable angina, myocardial ischemia, and myocardial infarction. A common symptom is angina, which is chest pain or discomfort that may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Occasionally it may feel like heartburn. In stable angina, symptoms occur with exercise or emotional Psychological stress, stress, last less than a few minutes, and improve with rest. Shortness of breath may also occur and sometimes no symptoms are present. In many cases, the first sign is a Myocardial infarction, heart attack. Other complications include heart failure or an Heart arrhythmia, abnormal h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NPC1L1
Niemann-Pick C1-Like 1 (NPC1L1) is a protein found on the gastrointestinal tract's epithelial cells as well as in hepatocytes. Specifically, it appears to bind to a critical mediator of cholesterol absorption. The drug ezetimibe inhibits NPC1L1 causing a reduction in cholesterol absorption, resulting in a blood cholesterol reduction of 15-20%. Polymorphic variations in the NPC1L1 gene could be associated with non-response to ezetimibe treatment. One study found that people with inactivating mutations in the NPC1L1 gene had a lower LDL cholesterol level, as well as an around 50% reduction in the risk of coronary heart disease. NPC1L1 has been shown to be an accessory receptor for hepatitis C virus entry into cells, and thus ezetimibe might be used as a therapeutic strategy. As cancer appeared more frequently in patients treated with simvastatin-ezetimibe combination therapy in one clinical trial, it had been hypothesized that NPC1L1 inhibition by ezetimibe might be associate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |