|
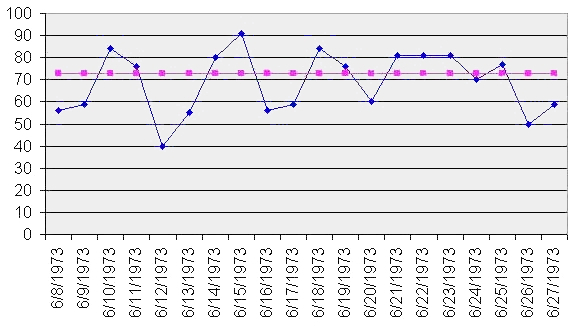
Sinusoidal Model
In statistics, signal processing, and time series analysis, a sinusoidal model is used to approximate a sequence ''Yi'' to a sine function: :Y_i = C + \alpha\sin(\omega T_i + \phi) + E_i where ''C'' is constant defining a mean level, α is an amplitude for the sine, ω is the angular frequency, ''Ti'' is a time variable, φ is the phase-shift, and ''Ei'' is the error sequence. This sinusoidal model can be fit using nonlinear least squares; to obtain a good fit, routines may require good starting values for the unknown parameters. Fitting a model with a single sinusoid is a special case of spectral density estimation and least-squares spectral analysis. Good starting values Good starting value for the mean A good starting value for ''C'' can be obtained by calculating the mean of the data. If the data show a trend, i.e., the assumption of constant location is violated, one can replace ''C'' with a linear or quadratic least squares fit. That is, the model becomes :Y_i = (B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of statistical survey, surveys and experimental design, experiments. When census data (comprising every member of the target population) cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey sample (statistics), samples. Representative sampling assures that inferences and conclusions can reasonably extend from the sample ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Demodulation
Complex commonly refers to: * Complexity, the behaviour of a system whose components interact in multiple ways so possible interactions are difficult to describe ** Complex system, a system composed of many components which may interact with each other * Complex (psychology), a core pattern of emotions etc. in the personal unconscious organized around a common theme such as power or status Complex may also refer to: Arts, entertainment and media * Complex (English band), formed in 1968, and their 1971 album ''Complex'' * Complex (band), a Japanese rock band * ''Complex'' (album), by Montaigne, 2019, and its title track * ''Complex'' (EP), by Rifle Sport, 1985 * "Complex" (song), by Gary Numan, 1979 * "Complex", a song by Katie Gregson-MacLeod, 2022 * "Complex" a song by Be'O and Zico, 2022 * Complex Networks, publisher of the now-only-online magazine ''Complex'' Biology * Protein–ligand complex, a complex of a protein bound with a ligand * Exosome complex, a multi-protei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitch Detection Algorithm
A pitch detection algorithm (PDA) is an algorithm designed to estimate the pitch or fundamental frequency of a quasiperiodic or oscillating signal, usually a digital recording of speech or a musical note or tone. This can be done in the time domain, the frequency domain, or both. PDAs are used in various contexts (e.g. phonetics, music information retrieval, speech coding, musical performance systems) and so there may be different demands placed upon the algorithm. There is as yet no single ideal PDA, so a variety of algorithms exist, most falling broadly into the classes given below. A PDA typically estimates the period of a quasiperiodic signal, then inverts that value to give the frequency. General approaches One simple approach would be to measure the distance between zero crossing points of the signal (i.e. the zero-crossing rate). However, this does not work well with complicated waveforms which are composed of multiple sine waves with differing periods or noisy data. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is f(x) = \frac e^\,. The parameter is the mean or expectation of the distribution (and also its median and mode), while the parameter \sigma^2 is the variance. The standard deviation of the distribution is (sigma). A random variable with a Gaussian distribution is said to be normally distributed, and is called a normal deviate. Normal distributions are important in statistics and are often used in the natural and social sciences to represent real-valued random variables whose distributions are not known. Their importance is partly due to the central limit theorem. It states that, under some conditions, the average of many samples (observations) of a random variable with finite mean and variance is itself a random variable—whose distribution c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Probability Plot
The normal probability plot is a graphical technique to identify substantive departures from normality. This includes identifying outliers, skewness, kurtosis, a need for transformations, and mixtures. Normal probability plots are made of raw data, residuals from model fits, and estimated parameters. In a normal probability plot (also called a "normal plot"), the sorted data are plotted vs. values selected to make the resulting image look close to a straight line if the data are approximately normally distributed. Deviations from a straight line suggest departures from normality. The plotting can be manually performed by using a special graph paper, called ''normal probability paper''. With modern computers normal plots are commonly made with software. The normal probability plot is a special case of the Q–Q probability plot for a normal distribution. The theoretical quantiles are generally chosen to approximate either the mean or the median of the corresponding order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histogram
A histogram is a visual representation of the frequency distribution, distribution of quantitative data. To construct a histogram, the first step is to Data binning, "bin" (or "bucket") the range of values— divide the entire range of values into a series of intervals—and then count how many values fall into each interval. The bins are usually specified as consecutive, non-overlapping interval (mathematics), intervals of a variable. The bins (intervals) are adjacent and are typically (but not required to be) of equal size. Histograms give a rough sense of the density of the underlying distribution of the data, and often for density estimation: estimating the probability density function of the underlying variable. The total area of a histogram used for probability density is always normalized to 1. If the length of the intervals on the ''x''-axis are all 1, then a histogram is identical to a relative frequency plot. Histograms are sometimes confused with bar charts. In a his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Errors And Residuals In Statistics
In statistics and optimization, errors and residuals are two closely related and easily confused measures of the deviation of an observed value of an element of a statistical sample from its "true value" (not necessarily observable). The error of an observation is the deviation of the observed value from the true value of a quantity of interest (for example, a population mean). The residual is the difference between the observed value and the '' estimated'' value of the quantity of interest (for example, a sample mean). The distinction is most important in regression analysis, where the concepts are sometimes called the regression errors and regression residuals and where they lead to the concept of studentized residuals. In econometrics, "errors" are also called disturbances. Introduction Suppose there is a series of observations from a univariate distribution and we want to estimate the mean of that distribution (the so-called location model). In this case, the errors a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lag Plot
In the analysis of data, a correlogram is a chart of correlation statistics. For example, in time series analysis, a plot of the sample autocorrelations r_h\, versus h\, (the time lags) is an autocorrelogram. If cross-correlation is plotted, the result is called a cross-correlogram. The correlogram is a commonly used tool for checking randomness in a data set. If random, autocorrelations should be near zero for any and all time-lag separations. If non-random, then one or more of the autocorrelations will be significantly non-zero. In addition, correlograms are used in the model identification stage for Box–Jenkins autoregressive moving average time series models. Autocorrelations should be near-zero for randomness; if the analyst does not check for randomness, then the validity of many of the statistical conclusions becomes suspect. The correlogram is an excellent way of checking for such randomness. In multivariate analysis, correlation matrices shown as color-mappe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outliers
In statistics, an outlier is a data point that differs significantly from other observations. An outlier may be due to a variability in the measurement, an indication of novel data, or it may be the result of experimental error; the latter are sometimes excluded from the data set. An outlier can be an indication of exciting possibility, but can also cause serious problems in statistical analyses. Outliers can occur by chance in any distribution, but they can indicate novel behaviour or structures in the data-set, measurement error, or that the population has a heavy-tailed distribution. In the case of measurement error, one wishes to discard them or use statistics that are robust to outliers, while in the case of heavy-tailed distributions, they indicate that the distribution has high skewness and that one should be very cautious in using tools or intuitions that assume a normal distribution. A frequent cause of outliers is a mixture of two distributions, which may be two d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Run Sequence Plot
A run chart, also known as a run-sequence plot is a graph that displays observed data in a time sequence. Often, the data displayed represent some aspect of the output or performance of a manufacturing or other business process. It is therefore a form of line chart. Overview Run sequence plots are an easy way to graphically summarize a univariate data set. A common assumption of univariate data sets is that they behave like:NIST/SEMATECH (2003)"Run-Sequence Plot"In: ''e-Handbook of Statistical Methods'' 6/01/2003 (Date created). * random drawings; * from a fixed distribution; * with a common location; and * with a common scale. With run sequence plots, shifts in location and scale are typically quite evident. Also, outliers can easily be detected. Examples could include measurements of the fill level of bottles filled at a bottling plant or the water temperature of a dishwashing machine each time it is run. Time is generally represented on the horizontal (x) axis and the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model Validation
In statistics, model validation is the task of evaluating whether a chosen statistical model is appropriate or not. Oftentimes in statistical inference, inferences from models that appear to fit their data may be flukes, resulting in a misunderstanding by researchers of the actual relevance of their model. To combat this, model validation is used to test whether a statistical model can hold up to permutations in the data. Model validation is also called model criticism or model evaluation. This topic is not to be confused with the closely related task of model selection, the process of discriminating between multiple candidate models: model validation does not concern so much the conceptual design of models as it tests only the consistency between a chosen model and its stated outputs. There are many ways to validate a model. Residual plots plot the difference between the actual data and the model's predictions: correlations in the residual plots may indicate a flaw in the model. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Model
A statistical model is a mathematical model that embodies a set of statistical assumptions concerning the generation of Sample (statistics), sample data (and similar data from a larger Statistical population, population). A statistical model represents, often in considerably idealized form, the Data generating process, data-generating process. When referring specifically to probability, probabilities, the corresponding term is probabilistic model. All Statistical hypothesis testing, statistical hypothesis tests and all Estimator, statistical estimators are derived via statistical models. More generally, statistical models are part of the foundation of statistical inference. A statistical model is usually specified as a mathematical relationship between one or more random variables and other non-random variables. As such, a statistical model is "a formal representation of a theory" (Herman J. Adèr, Herman Adèr quoting Kenneth A. Bollen, Kenneth Bollen). Introduction Informally, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |