|
Singular Optics
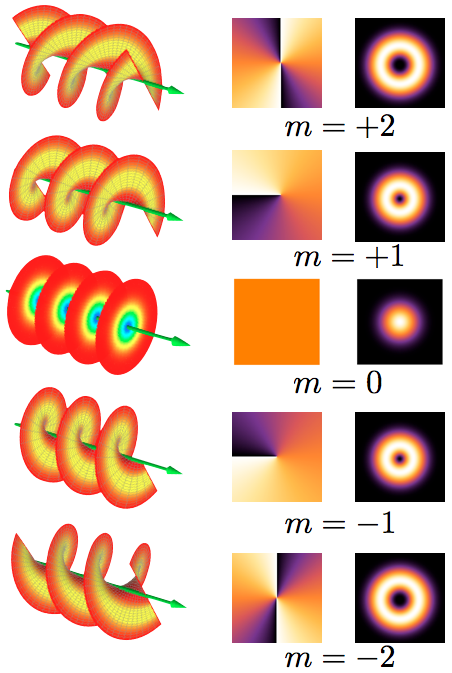
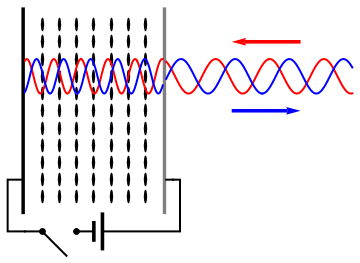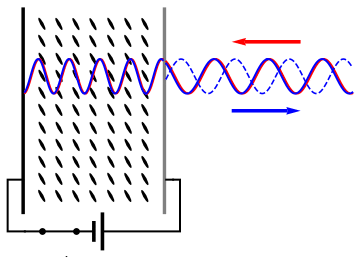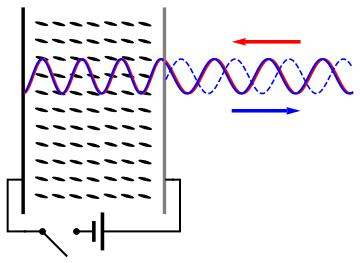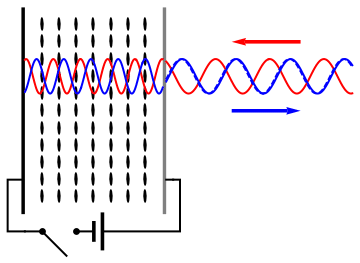
An optical vortex (also known as a photonic quantum vortex, screw dislocation or phase singularity) is a zero of an optical field; a point of zero intensity. The term is also used to describe a beam of light that has such a zero in it. The study of these phenomena is known as singular optics. The concept of "optical vortices" was first described by Coullet et al. in 1989, based on solutions of the Maxwell-Bloch equations. According to one review, studies in 1989-1999 mainly focused on fundamentals; studies in 1999-2009 developed many applications; and studies in 2009-2019 made a number of technological breakthroughs. Explanation In an optical vortex, light is twisted like a corkscrew around its axis of travel. Because of the twisting, the light waves at the axis itself cancel each other out. When projected onto a flat surface, an optical vortex looks like a ring of light, with a dark hole in the center. The vortex is given a number, called the topological charge, according to how ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helix Oam
A helix (; ) is a shape like a cylindrical coil spring or the thread of a machine screw. It is a type of smoothness (mathematics), smooth space curve with tangent lines at a constant angle to a fixed axis. Helices are important in biology, as the DNA molecule is formed as double helix, two intertwined helices, and many proteins have helical substructures, known as alpha helix, alpha helices. The word ''helix'' comes from the Greek language, Greek word , "twisted, curved". A "filled-in" helix – for example, a "spiral" (helical) ramp – is a surface called a ''helicoid''. Properties and types The pitch of a helix is the height of one complete helix turn (angle), turn, measured parallel to the axis of the helix. A double helix consists of two (typically congruence (geometry), congruent) helices with the same axis, differing by a translation along the axis. A circular helix (i.e. one with constant radius) has constant band curvature and constant Torsion of curves, torsion. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Static Spiral Phase Plate(s) Or Mirror(s)
Static may refer to: Places *Static Nunatak, in Antarctica * Static, Kentucky and Tennessee, U.S. *Static Peak, a mountain in Wyoming, U.S. ** Static Peak Divide, a mountain pass near the peak Science and technology Physics *Static electricity, a net charge of an object **Triboelectric effect, due to frictional contact between different materials *Static spacetime, a spacetime having a global, non-vanishing, timelike Killing vector field which is irrotational *Statics, a branch of physics concerned with physical systems in equilibrium **Hydrostatics, the branch of fluid mechanics that studies fluids at rest Engineering *Static pressure, in aircraft instrumentation and fluid dynamics ** Static port, a proprietary sensor used on aircraft to measure static pressure *White noise or static noise, a random signal with a flat power spectral density **Radio noise, in radio reception **Noise (video), the random black-and-white image produced by televisions attempting to display a weak or i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
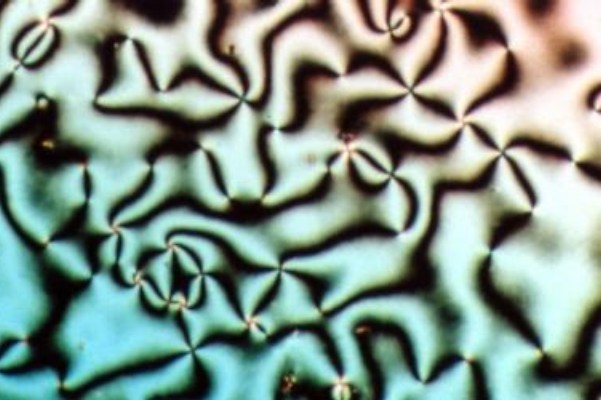
Liquid Crystal
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal can flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a common direction as in a solid. There are many types of LC Phase (matter), phases, which can be distinguished by their Optics, optical properties (such as Texture (crystalline), textures). The contrasting textures arise due to molecules within one area of material ("domain") being oriented in the same direction but different areas having different orientations. An LC material may not always be in an LC state of matter (just as water may be ice or water vapour). Liquid crystals can be divided into three main types: thermotropic, lyotropic, and #Metallotropic liquid crystals, metallotropic. Thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals consist mostly of organic molecules, although a few minerals are also known. Thermotropic LCs exhibit a phase transition into the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birefringent
Birefringence, also called double refraction, is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are described as birefringent or birefractive. The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with non-cubic crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress. Birefringence is responsible for the phenomenon of double refraction whereby a ray of light, when incident upon a birefringent material, is split by polarization into two rays taking slightly different paths. This effect was first described by Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who observed it in Iceland spar (calcite) crystals which have one of the strongest birefringences. In the 19th century Augustin-Jean Fresnel described the phenomenon in terms of polarization, understanding li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Q-plate
A q-plate is an optical device that can form a light beam with orbital angular momentum (OAM) from a beam with well-defined spin angular momentum (SAM). Q-plates are based on the SAM-OAM coupling that may occur in media that are both anisotropic and inhomogeneous, such as an inhomogeneous anisotropic birefringent waveplate. Q-plates are also currently realized using total internal reflection devices, liquid crystals, metasurfaces based on polymers, and sub-wavelength gratings. The sign of the OAM is controlled by the input beam's polarization Polarization or polarisation may refer to: Mathematics *Polarization of an Abelian variety, in the mathematics of complex manifolds *Polarization of an algebraic form, a technique for expressing a homogeneous polynomial in a simpler fashion by .... References Optical components Nonlinear optics {{optics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deformable Mirror
Deformable mirrors (DM) are mirrors whose surface can be deformed, in order to achieve wavefront control and correction of optical Optical aberration, aberrations. Deformable mirrors are used in combination with wavefront sensors and real-time control systems in adaptive optics. In 2006 they found a new use in femtosecond pulse shaping. The shape of a DM can be controlled with a speed that is appropriate for compensation of dynamic aberrations present in the optical system. In practice the DM shape should be changed much faster than the process to be corrected, as the correction process, even for a static aberration, may take several iterations. A DM usually has many degrees of freedom. Typically, these degrees of freedom are associated with the mechanical actuators and it can be roughly taken that one actuator corresponds to one Degrees of freedom (mechanics), degree of freedom. Deformable mirror parameters Number of actuators determines the number of degrees of freedom (wave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Light Modulator
A spatial light modulator (SLM) is a device that can control the intensity, phase, or polarization of light in a spatially varying manner. A simple example is an overhead projector transparency. Usually when the term SLM is used, it means that the transparency can be controlled by a computer. SLMs are primarily marketed for image projection, displays devices, and maskless lithography. SLMs are also used in optical computing and holographic optical tweezers. Usually, an SLM modulates the intensity of the light beam. However, it is also possible to produce devices that modulate the phase of the beam or both the intensity and the phase simultaneously. It is also possible to produce devices that modulate the polarization of the beam, and modulate the polarization, phase, and intensity simultaneously. SLMs are used extensively in holographic data storage setups to encode information into a laser beam similarly to the way a transparency does for an overhead projector. They can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermite-Gaussian Mode
In optics, a Gaussian beam is an idealized beam of electromagnetic radiation whose amplitude envelope in the transverse plane is given by a Gaussian function; this also implies a Gaussian intensity (irradiance) profile. This fundamental (or TEM00) transverse Gaussian mode describes the intended output of many lasers, as such a beam diverges less and can be focused better than any other. When a Gaussian beam is refocused by an ideal lens, a new Gaussian beam is produced. The electric and magnetic field amplitude profiles along a circular Gaussian beam of a given wavelength and polarization are determined by two parameters: the waist , which is a measure of the width of the beam at its narrowest point, and the position relative to the waist.Svelto, pp. 153–5. Since the Gaussian function is infinite in extent, perfect Gaussian beams do not exist in nature, and the edges of any such beam would be cut off by any finite lens or mirror. However, the Gaussian is a useful approxima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mode Conversion
Mode conversion is the transformation of a wave at an interface into other wave types (Normal mode, modes). Principle Mode conversion occurs when a wave encounters an interface between materials of different Wave impedance, impedances and the incident angle is not normal to the interface. Thus, for example, if a longitudinal wave from a fluid (e.g., water or air) strikes a solid (e.g., steel plate), it is usually refracted and reflected as a function of the angle of incidence, but if some of the energy causes particle movement in the transverse direction, a second transverse wave is generated, which can also be refracted and reflected. Snellius' law of refraction can be formulated as: \frac = \frac = \frac = \frac This means that the incident wave is split into two different wave types at the interface. If we consider a wave incident on an interface of two different solids (e.g. aluminum and steel), the wave type of the reflected wave also splits. Besides these simple mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blazed Grating
A blazed grating – also called echelette grating (from French ''échelle'' = ladder) – is a special type of diffraction grating. It is optimized to achieve maximum light efficiency in a given diffraction order. For this purpose, maximum optical power is concentrated in the desired diffraction order while the residual power in the other orders (particularly the zeroth) is minimized. Since this condition can only exactly be achieved for one wavelength, it is specified for which ''blaze wavelength'' the grating is optimized (or ''blazed''). The direction in which maximum efficiency is achieved is called the ''blaze angle'' and is the third crucial characteristic of a blazed grating directly depending on blaze wavelength and diffraction order. Blaze angle Like every optical grating, a blazed grating has a constant line spacing d, determining the magnitude of the wavelength splitting caused by the grating. The grating lines possess a triangular, sawtooth-shaped cross sect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ronchi Linear Diffraction Grating
A Ronchi ruling, Ronchi grating, or Ronchi mask, named after the Italian physicist Vasco Ronchi, is a constant-interval bar and space square-wave optical target or mask. The design produces a precisely patterned light source by reflection or illumination, or a stop pattern by transmission, with precise uniformity, spatial frequency, sharp edge definition, and high contrast ratio. Manufacturing Ronchi rulings are typically manufactured through photolithographic deposition of metallic chromium on a substrate, which yields a precise, nearly 100% contrast pattern. For a reflective or illuminated type, dark stripes are printed on a diffusely reflecting or translucent substrate, such as a square of white ceramic material or opal glass. For a transmissive type, opaque stripes are printed on a transparent glass substrate. A transmissive type may be readily modified to act as an illuminated type by stacking a reflective object behind it. Applications A test target in the Ronchi patter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |