|
Single-molecule
A single-molecule experiment is an experiment that investigates the properties of individual molecules. Single-molecule studies may be contrasted with measurements on an ensemble or bulk collection of molecules, where the individual behavior of molecules cannot be distinguished, and only average characteristics can be measured. Since many measurement techniques in biology, chemistry, and physics are not sensitive enough to observe single molecules, single-molecule fluorescence techniques (that have emerged since the 1990s for probing various processes on the level of individual molecules) caused a lot of excitement, since these supplied many new details on the measured processes that were not accessible in the past. Indeed, since the 1990s, many techniques for probing individual molecules have been developed. The first single-molecule experiments were patch clamp experiments performed in the 1970s, but these were limited to studying ion channels. Today, systems investigated using s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-molecule Magnet
A single-molecule magnet (SMM) is a metal-organic compound that has superparamagnetic behavior below a certain blocking temperature at the molecular scale. In this temperature range, a SMM exhibits magnetic hysteresis of purely molecular origin.Introduction to Molecular Magnetism by Dr. Joris van Slageren. In contrast to conventional bulk s and s, collective long-range magnetic ordering of |
SmFRET
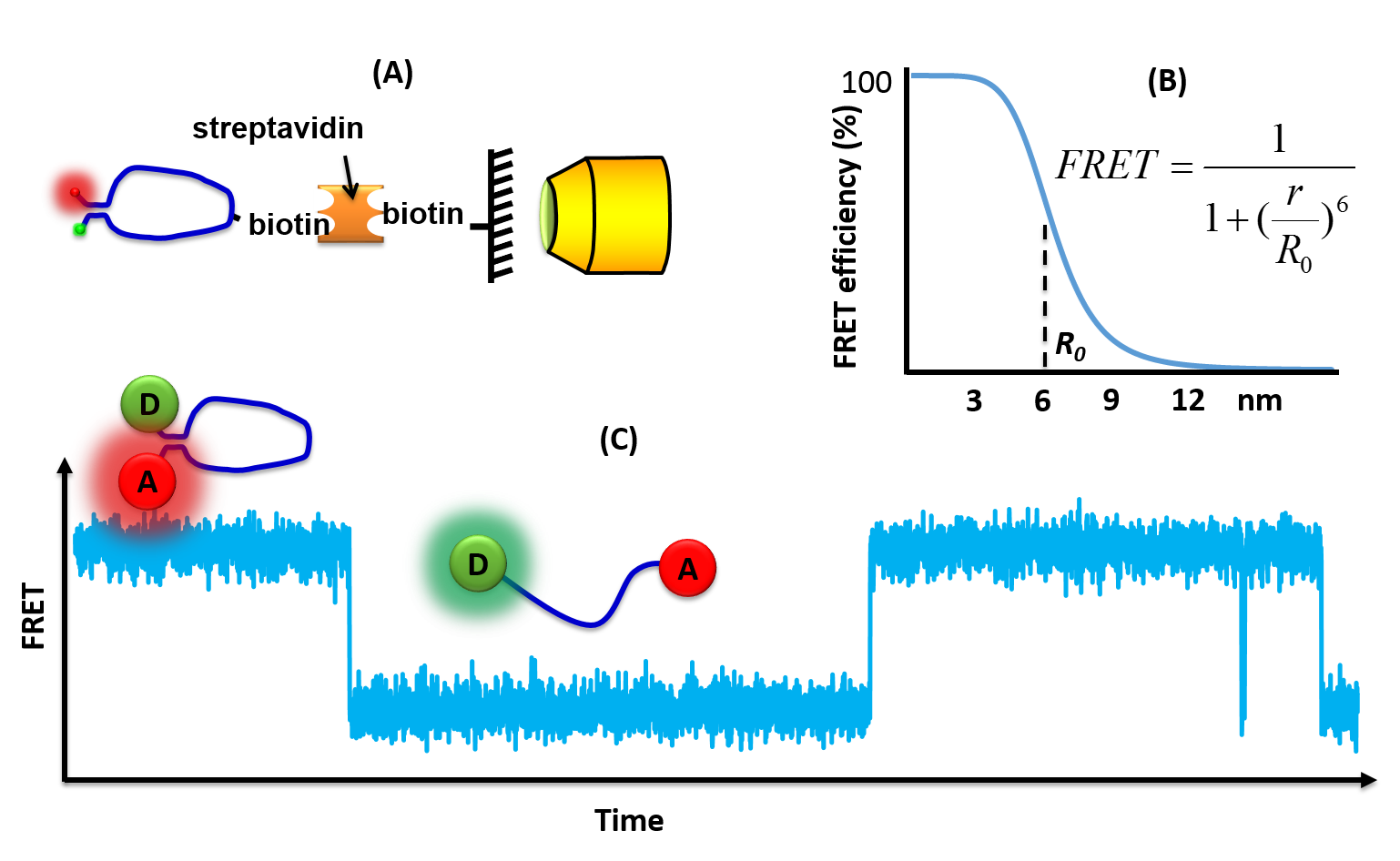
Single molecule fluorescence (or Förster) resonance energy transfer (or smFRET) is a biophysical technique used to measure distances at the 1-10 nanometer scale in single molecules, typically biomolecules. It is an application of FRET wherein a pair of donor and acceptor fluorophores are excited and detected on a single molecule level. In contrast to "ensemble FRET" which provides the FRET signal of a high number of molecules, single-molecule FRET is able to resolve the FRET signal of each individual molecule. The variation of the smFRET signal is useful to reveal kinetic information that an ensemble measurement cannot provide, especially when the system is under equilibrium. Heterogeneity among different molecules can also be observed. This method has been applied in many measurements of biomolecular dynamics such as DNA/RNA/protein folding/unfolding and other conformational changes, and intermolecular dynamics such as reaction, binding, adsorption, and desorption that are partic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Force Spectroscopy
Force spectroscopy is a set of techniques for the study of the interactions and the binding forces between individual molecules. These methods can be used to measure the mechanical properties of single polymer molecules or proteins, or individual chemical bonds. The name "force spectroscopy", although widely used in the scientific community, is somewhat misleading, because there is no true matter-radiation interaction. Techniques that can be used to perform force spectroscopy include atomic force microscopy, optical tweezers, magnetic tweezers, acoustic force spectroscopy, microneedles, and biomembranes. Force spectroscopy measures the behavior of a molecule under stretching or torsional mechanical force. In this way a great deal has been learned in recent years about the mechanochemical coupling in the enzymes responsible for muscle contraction, transport in the cell, energy generation (F1-ATPase), DNA replication and transcription (polymerases), DNA unknotting and unwinding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reduced Dimensions Form
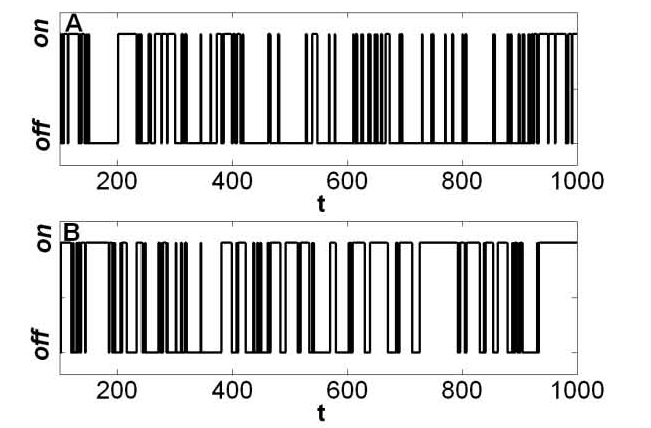
In biophysics and related fields, reduced dimension forms (RDFs) are unique on-off mechanisms for random walks that generate two-state trajectories (see Fig. 1 for an example of a RDF and Fig. 2 for an example of a two-state trajectory). It has been shown that RDFs solve two-state trajectories, since only one RDF can be constructed from the data, where this property does not hold for on-off kinetic schemes, where many kinetic schemes can be constructed from a particular two-state trajectory (even from an ideal on-off trajectory). Two-state time trajectories are very common in measurements in chemistry, physics, and the biophysics of individual molecules (e.g. measurements of protein dynamics and DNA and RNA dynamics, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Force Spectroscopy
Force spectroscopy is a set of techniques for the study of the interactions and the binding forces between individual molecules. These methods can be used to measure the mechanical properties of single polymer molecules or proteins, or individual chemical bonds. The name "force spectroscopy", although widely used in the scientific community, is somewhat misleading, because there is no true matter-radiation interaction. Techniques that can be used to perform force spectroscopy include atomic force microscopy, optical tweezers, magnetic tweezers, acoustic force spectroscopy, microneedles, and biomembranes. Force spectroscopy measures the behavior of a molecule under stretching or torsional mechanical force. In this way a great deal has been learned in recent years about the mechanochemical coupling in the enzymes responsible for muscle contraction, transport in the cell, energy generation (F1-ATPase), DNA replication and transcription (polymerases), DNA unknotting and unwinding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raman Spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy () (named after Indian physicist C. V. Raman) is a spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules, although rotational and other low-frequency modes of systems may also be observed. Raman spectroscopy is commonly used in chemistry to provide a structural fingerprint by which molecules can be identified. Raman spectroscopy relies upon inelastic scattering of photons, known as Raman scattering. A source of monochromatic light, usually from a laser in the visible, near infrared, or near ultraviolet range is used, although X-rays can also be used. The laser light interacts with molecular vibrations, phonons or other excitations in the system, resulting in the energy of the laser photons being shifted up or down. The shift in energy gives information about the vibrational modes in the system. Infrared spectroscopy typically yields similar yet complementary information. Typically, a sample is illuminated with a laser beam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Tweezers
Optical tweezers (originally called single-beam gradient force trap) are scientific instruments that use a highly focused laser beam to hold and move microscopic and sub-microscopic objects like atoms, nanoparticles and droplets, in a manner similar to tweezers. If the object is held in air or vacuum without additional support, it can be called optical levitation. The laser light provides an attractive or repulsive force (typically on the order of piconewtons), depending on the relative refractive index between particle and surrounding medium. Levitation is possible if the force of the light counters the force of gravity. The trapped particles are usually micron-sized, or even smaller. Dielectric and absorbing particles can be trapped, too. Optical tweezers are used in biology and medicine (for example to grab and hold a single bacterium, a cell like a sperm cell or a blood cell, or a molecule like DNA), nanoengineering and nanochemistry (to study and build materials fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-particle Tracking
Single-particle tracking (SPT) is the observation of the motion of individual particles within a medium. The coordinates time series, which can be either in two dimensions (''x'', ''y'') or in three dimensions (''x'', ''y'', ''z''), is referred to as a ''trajectory''. The trajectory is typically analyzed using statistical methods to extract information about the underlying dynamics of the particle. These dynamics can reveal information about the type of transport being observed (e.g., thermal or active), the medium where the particle is moving, and interactions with other particles. In the case of random motion, trajectory analysis can be used to measure the diffusion coefficient. Applications In life sciences, single-particle tracking is broadly used to quantify the dynamics of molecules/proteins in live cells (of bacteria, yeast, mammalian cells and live ''Drosophila'' embryos). It has been extensively used to study the transcription factor dynamics in live cells. This method h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinesin
A kinesin is a protein belonging to a class of motor proteins found in eukaryotic cells. Kinesins move along microtubule (MT) filaments and are powered by the hydrolysis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) (thus kinesins are ATPases, a type of enzyme). The active movement of kinesins supports several cellular functions including mitosis, meiosis and transport of cellular cargo, such as in axonal transport, and intraflagellar transport. Most kinesins walk towards the plus end of a microtubule, which, in most cells, entails transporting cargo such as protein and membrane components from the center of the cell towards the periphery. This form of transport is known as anterograde transport. In contrast, dyneins are motor proteins that move toward the minus end of a microtubule in retrograde transport. Discovery Kinesins were discovered in 1985, based on their motility in cytoplasm extruded from the giant axon of the squid. They turned out as MT-based anterograde intracellular tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorophores
A fluorophore (or fluorochrome, similarly to a chromophore) is a fluorescence, fluorescent chemical compound that can re-emit light upon light excitation. Fluorophores typically contain several combined aromaticity, aromatic groups, or planar or cyclic molecules with several pi bond, π bonds. Fluorophores are sometimes used alone, as a dye tracing, tracer in fluids, as a dye for staining of certain structures, as a substrate of enzymes, or as a probe or indicator (when its fluorescence is affected by environmental aspects such as polarity or ions). More generally they are covalent bond, covalently bonded to a macromolecule, serving as a marker (or dye, or tag, or reporter) for affine or bioactive reagents (antibodies, peptides, nucleic acids). Fluorophores are notably used to stain tissues, cells, or materials in a variety of analytical methods, i.e., Fluorescence microscope, fluorescent imaging and fluorescence spectroscopy, spectroscopy. Fluorescein, via its amine-reactive i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-state Trajectory
A two-state trajectory (also termed two-state time trajectory or a trajectory with two states) is a dynamical signal that fluctuates between two distinct values: ON and OFF, open and closed, +/-, etc. Mathematically, the signal X(t) has, for every t, either the value X(t)=c_\mathrm or X(t)=c_\mathrm. In most applications, the signal is stochastic; nevertheless, it can have deterministic ON-OFF components. A completely deterministic two-state trajectory is a square wave. There are many ways one can create a two-state signal, e.g. flipping a coin repeatedly. A stochastic two-state trajectory is among the simplest stochastic processes. Extensions include: three-state trajectories, higher discrete state trajectories, and continuous trajectories in any dimension. Two state trajectories in biophysics, and related fields Two state trajectories are very common. Here, we focus on relevant trajectories in scientific experiments: these are seen in measurements in chemistry, physics, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and ''molecule'' is often used when referring to polyatomic ions. A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element, e.g. two atoms in the oxygen molecule (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, e.g. water (molecule), water (two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom; H2O). In the kinetic theory of gases, the term ''molecule'' is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. This relaxes the requirement that a molecule contains two or more atoms, since the noble gases are individual atoms. Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or ionic bonds, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |