|
Silent Piano
A silent piano is an acoustic piano where there is an option to silence the strings by stopping the hammers from striking them. A silent piano is designed for private silent practice. On modern, electric keyboards, sensors can pick up the piano key movement, converting it to a MIDI signal that can be sent to an electronic sound module, allowing the person playing to use headphones. The pianos also have full MIDI capability for sending signals and can be linked to a computer for use with notation software, etc. Mechanics In all silent systems, engaging the silent function causes a bar to move into place such that it intercepts the hammer shank and stops the hammer from hitting the piano string. Older models detected key movement by using mechanical sensors that affected the touch and produced a clicking sound, whereas newer models use optical sensors that do not affect the feel or sound of the piano. In more advanced systems, usually on grand pianos, the piano's action is also al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
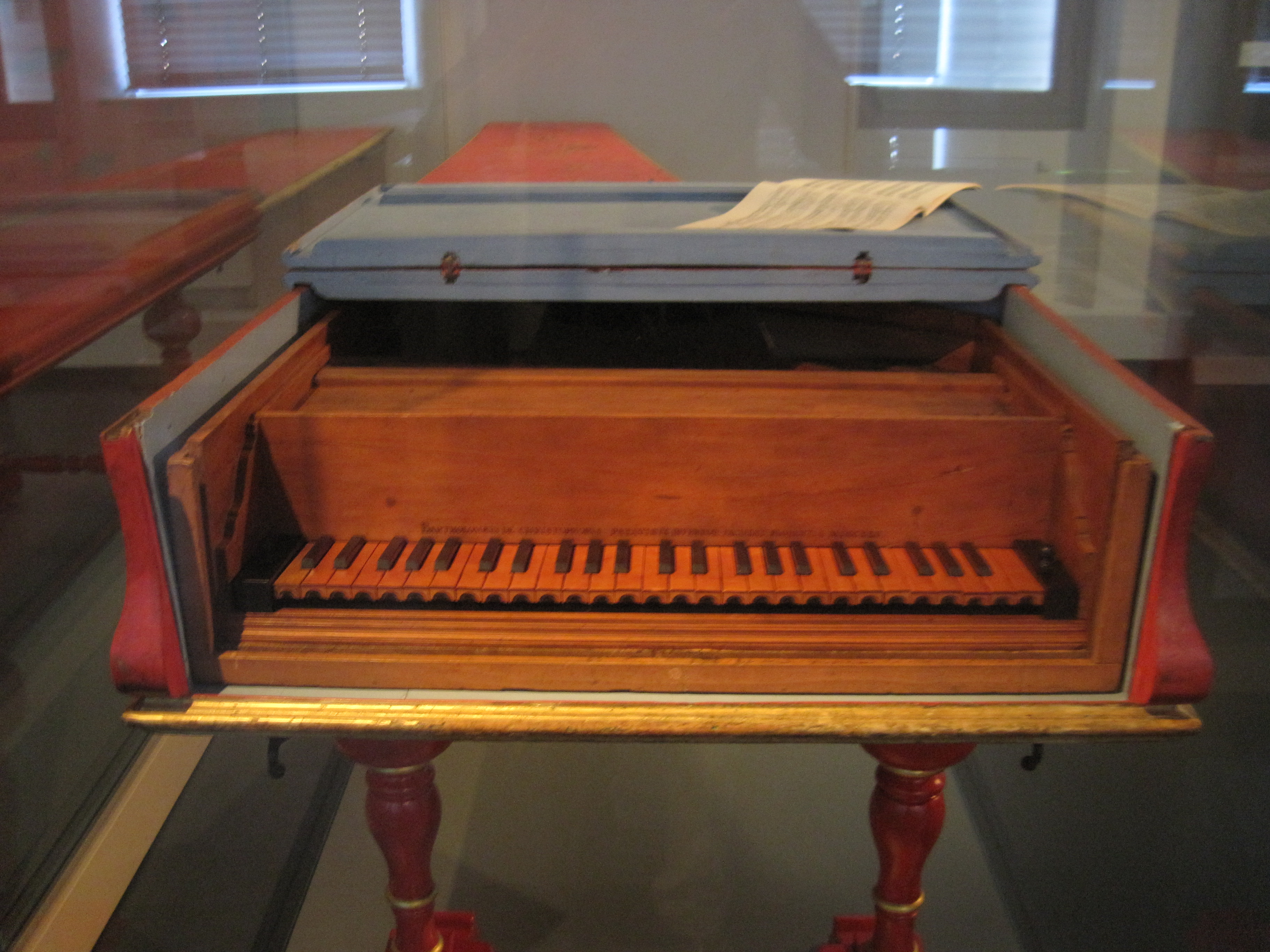
Piano
A piano is a keyboard instrument that produces sound when its keys are depressed, activating an Action (music), action mechanism where hammers strike String (music), strings. Modern pianos have a row of 88 black and white keys, tuned to a chromatic scale in equal temperament. A musician who specializes in piano is called a pianist. There are two main types of piano: the #Grand, grand piano and the #Upupright piano. The grand piano offers better sound and more precise key control, making it the preferred choice when space and budget allow. The grand piano is also considered a necessity in venues hosting skilled pianists. The upright piano is more commonly used because of its smaller size and lower cost. When a key is depressed, the strings inside are struck by felt-coated wooden hammers. The vibrations are transmitted through a Bridge (instrument), bridge to a Soundboard (music), soundboard that amplifies the sound by Coupling (physics), coupling the Sound, acoustic energy t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piano Key
A key is a component of a musical instrument, the purpose and function of which depends on the instrument. However, the term is most often used in the context of keyboard instruments, in which case it refers to the exterior part of the instrument that the player physically interacts in the process of sound production. On instruments equipped with tuning machines such as guitars or mandolins, a key is part of a tuning machine. It is a worm gear with a key shaped end used to turn a cog, which, in turn, is attached to a post which winds the string. The key is used to make pitch adjustments to a string. With other instruments, zithers and drums, for example, a key is essentially a small wrench used to turn a tuning machine or lug. On woodwind instruments such as a flute or saxophone, keys are finger operated levers used to open or close tone holes, the operation of which effectively shortens or lengthens the resonating tube of the instrument. By doing so, the player is able to ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIDI
Musical Instrument Digital Interface (; MIDI) is an American-Japanese technical standard that describes a communication protocol, digital interface, and electrical connectors that connect a wide variety of electronic musical instruments, computers, and related audio devices for playing, editing, and recording music. A single MIDI cable can carry up to sixteen channels of MIDI data, each of which can be routed to a separate device. Each interaction with a key, button, knob or slider is converted into a MIDI event, which specifies musical instructions, such as a note's pitch, timing and velocity. One common MIDI application is to play a MIDI keyboard or other controller and use it to trigger a digital sound module (which contains synthesized musical sounds) to generate sounds, which the audience hears produced by a keyboard amplifier. MIDI data can be transferred via MIDI or USB cable, or recorded to a sequencer or digital audio workstation to be edited or played back. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Music
Computer music is the application of computing technology in music composition, to help human composers create new music or to have computers independently create music, such as with algorithmic composition programs. It includes the theory and application of new and existing computer software technologies and basic aspects of music, such as sound synthesis, digital signal processing, sound design, sonic diffusion, acoustics, electrical engineering, and psychoacoustics. The field of computer music can trace its roots back to the origins of electronic music, and the first experiments and innovations with electronic instruments at the turn of the 20th century. History Much of the work on computer music has drawn on the relationship between music and mathematics, a relationship that has been noted since the Ancient Greeks described the " harmony of the spheres". Musical melodies were first generated by the computer originally named the CSIR Mark 1 (later renamed CSIRAC) in Austra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
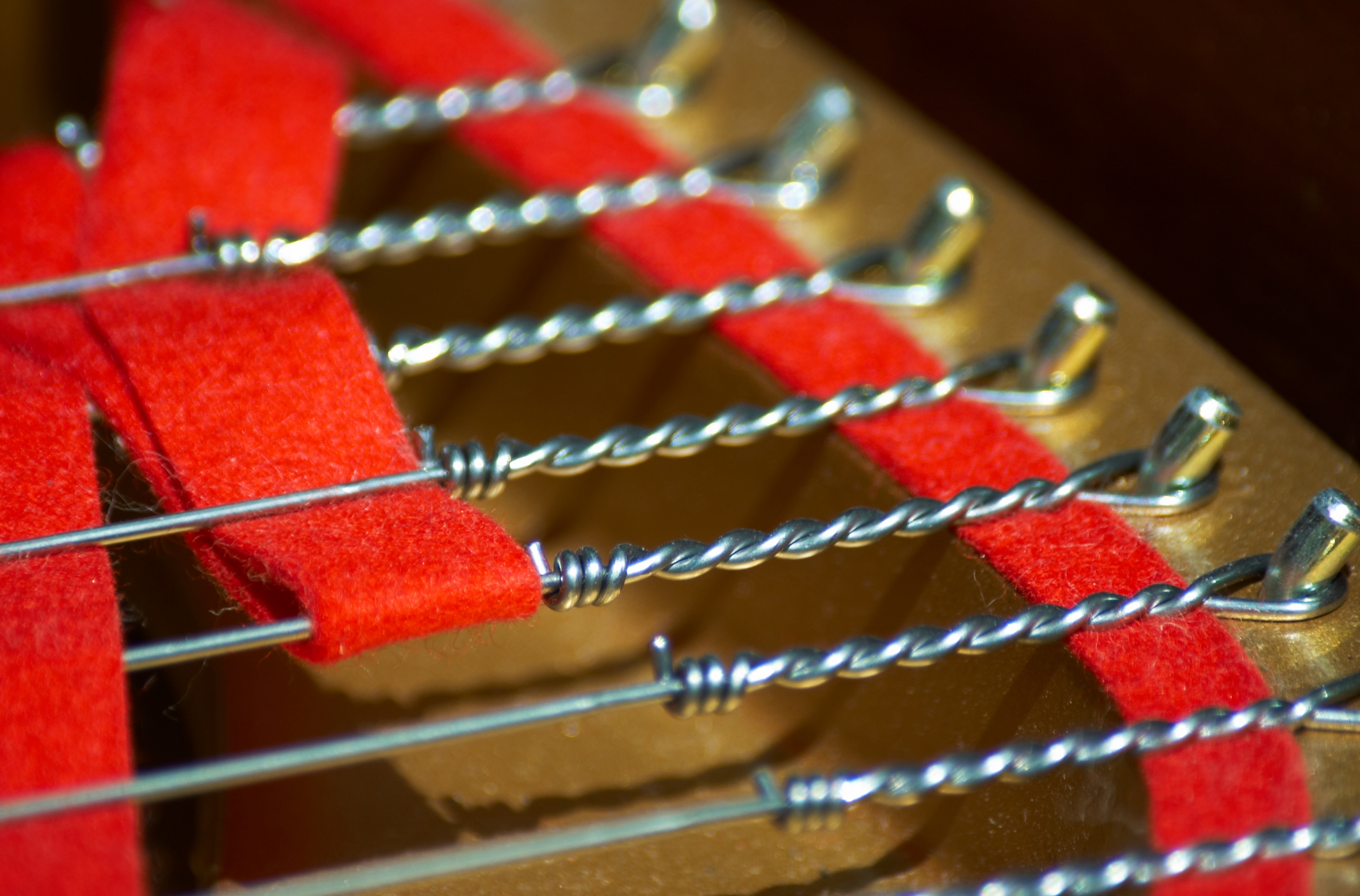
Piano String
Piano wire, or "music wire", is a specialized type of wire made for use in piano strings but also in other applications as springs. It is made from tempered high-carbon steel, also known as spring steel, which replaced iron as the material starting in 1834. Piano wire has a very high tensile strength to cope with the heavy demands placed upon piano strings; accordingly, piano wire is also used for a number of other purposes, including springs, surgical uses, and in special effects. History The oldest record of wire being made for musical instruments is from Augsburg in 1351.Dolge (1911, 124) Starting around 1800, the piano began to be built ever more ambitiously, with sturdier (eventually, iron) framing and greater string tension. This led to innovations in making tougher piano wire. In 1834, the Webster & Horsfal firm of Birmingham, United Kingdom brought out a form of piano wire made from cast steel; according to Dolge it was "so superior to the iron wire that the Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
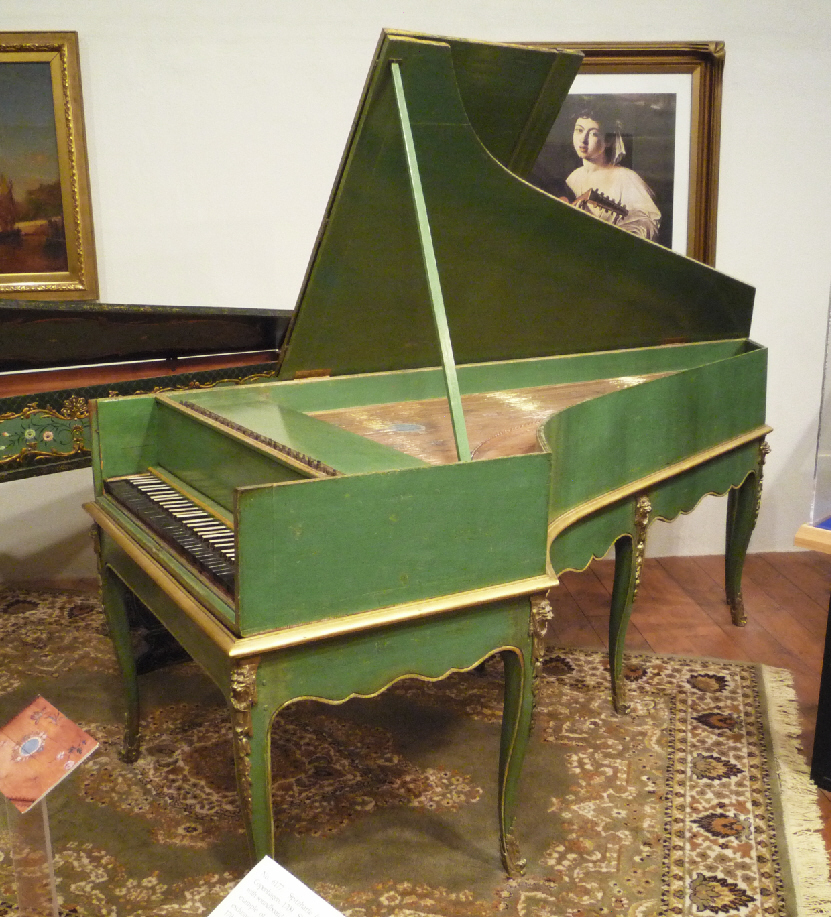
Grand Piano
A piano is a keyboard instrument that produces sound when its keys are depressed, activating an Action (music), action mechanism where hammers strike String (music), strings. Modern pianos have a row of 88 black and white keys, tuned to a chromatic scale in equal temperament. A musician who specializes in piano is called a pianist. There are two main types of piano: the #Grand, grand piano and the #Upupright piano. The grand piano offers better sound and more precise key control, making it the preferred choice when space and budget allow. The grand piano is also considered a necessity in venues hosting skilled pianists. The upright piano is more commonly used because of its smaller size and lower cost. When a key is depressed, the strings inside are struck by felt-coated wooden hammers. The vibrations are transmitted through a Bridge (instrument), bridge to a Soundboard (music), soundboard that amplifies the sound by Coupling (physics), coupling the Sound, acoustic energy t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action (piano)
The piano action mechanism (also known as the key action mechanismPressing, Jeffrey Lynn, PhD (1946–2002), (1992''Synthesizer performance and real-time techniques'' p. 124. or simply the action) of a piano or other musical keyboard is the mechanical assembly which translates the depression of the keys into rapid motion of a hammer, which creates sound by striking the strings. Action can refer to that of a piano or other musical keyboards, including the electronic or digital stage piano and synthesizer, on which some models have "weighted keys", which simulate the touch and feel of an acoustic piano. The design of the key action mechanism determines the "weight" of the keys, i.e., the force required to sound a note or striking power. "A professional pianist is likely to care most about the piano's action, because that is what controls its responsiveness and relative lightness--or heaviness--of touch. Roughly speaking, a piano's action is light when its keys fall easily under the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steinway
Steinway & Sons, also known as Steinway (), is a German-American piano company, founded in 1853 in New York City by German piano builder Henry E. Steinway, Heinrich Engelhard Steinweg (later known as Henry E. Steinway). The company's growth led to a move to a larger factory in New York, and later opening an additional factory in Hamburg, Germany. The New York factory, in the borough of Queens, supplies the Americas, and the factory in Hamburg supplies the rest of the world. Steinway is a prominent piano company, known for its high quality and for inventions within the area of piano development. Steinway has been granted 139 patents in piano making, with the first in 1857. The company's share of the high-end grand piano market consistently exceeds 80 percent. The dominant position has been criticized, with some musicians and writers arguing that it has blocked innovation and led to a homogenization of the sound favored by pianists. Steinway pianos have received numerous aw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bösendorfer
Bösendorfer (L. Bösendorfer Klavierfabrik GmbH) is an Austrian piano manufacturer and, since 2008, a wholly owned subsidiary of Yamaha Corporation. Bösendorfer is unusual in that it produces Imperial Bösendorfer, 97- and 92-Key (instrument), key models in addition to instruments with standard 88-key musical keyboard, keyboards. History Bösendorfer, one of the oldest piano manufacturers, was established in 1828 by Ignaz Bösendorfer. It has a history of producing highly respected instruments. In 1830, it was granted the status of official piano maker to the Emperor of Austria. Ignaz's son Ludwig Bösendorfer (1835–1919) assumed control in 1859, operating from new premises from 1860. Between 1872 and its closure in 1913, the associated Bösendorfer-Saal was one of the premier concert halls of Vienna. In 1909, Carl Hutterstrasser purchased the company and was succeeded by his sons Alexander and Wolfgang in 1931. In 1966, the Jasper Corporation (later renamed Kimball In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grotrian-Steinweg
Grotrian-Steinweg, known as Grotrian in the US, was a German manufacturer of prestige pianos. The company is based in Braunschweig, Germany, commonly known as Brunswick in English. Grotrian-Steinweg made premium grand pianos and upright pianos. Grotrian-Steinweg's history dates back to 1835 when the first Steinweg piano factory was built by Henry E. Steinway, Heinrich Engelhard Steinweg (later known as Henry Steinway after his emigration to the US where he founded Steinway & Sons). In 1856, Friedrich Grotrian became a partner; in 1865 his son Wilhelm Grotrian and two associates bought the factory and the right to market their pianos as successors to the Steinweg brand. Ensuing generations of Grotrian family members led the company to become one of the finest piano manufacturers in Germany. Grotrian-Steinweg pianos were preferred by some famous pianists, and they received accolades at the World's Columbian Exposition in Chicago. Grotrian-Steinweg operated an orchestra and a conce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kawai Musical Instruments
is a musical instrument manufacturing company headquartered in Hamamatsu, Shizuoka, Japan. It is best known for its grand pianos, upright pianos, digital pianos, electronic keyboards and electronic synthesizers. The company was founded in August 1927. History Koichi Kawai, the company founder, was born in Hamamatsu, Japan in 1886. His neighbor, Torakusu Yamaha, a watchmaker and reed organ builder, took him in as an apprentice. Kawai became a member of the research and development team that introduced pianos to Japan. Yamaha died in 1916, and in the 1920s the piano industry faltered in Japan. New management took over control of Yamaha's company, Nippon Gakki Co. (later renamed the Yamaha Corporation), and began to diversify its production line. This led Kawai to leave Nippon Gakki in 1927 and found the Kawai Musical Instrument Research Laboratory. After Koichi Kawai's death in 1955, his son, Shigeru Kawai became company president at 33 and expanded production facilities. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamaha Corporation
is a Japanese multinational musical instrument and audio equipment manufacturer. It is one of the constituents of Nikkei 225 and is the world's largest musical instrument manufacturing company. The former motorcycle division was established in 1955 as Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd., which started as an affiliated company but has been spun-off as its own independent company. History was established in 1887 as a reed organ manufacturer by Torakusu Yamaha () in Hamamatsu, Shizuoka Prefecture, and was incorporated on 12 October 1897. In 1900, the company manufactured the first piano to be made in Japan, and its first grand piano two years later. In 1987, 100 years after the first reed organ built by Yamaha, the company was renamed Yamaha Corporation in honor of its founder. The company's origins as a musical instrument manufacturer are still reflected today in the group's logo—a trio of interlocking tuning forks. After World War II, company president Genichi Kawakami repur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |