|
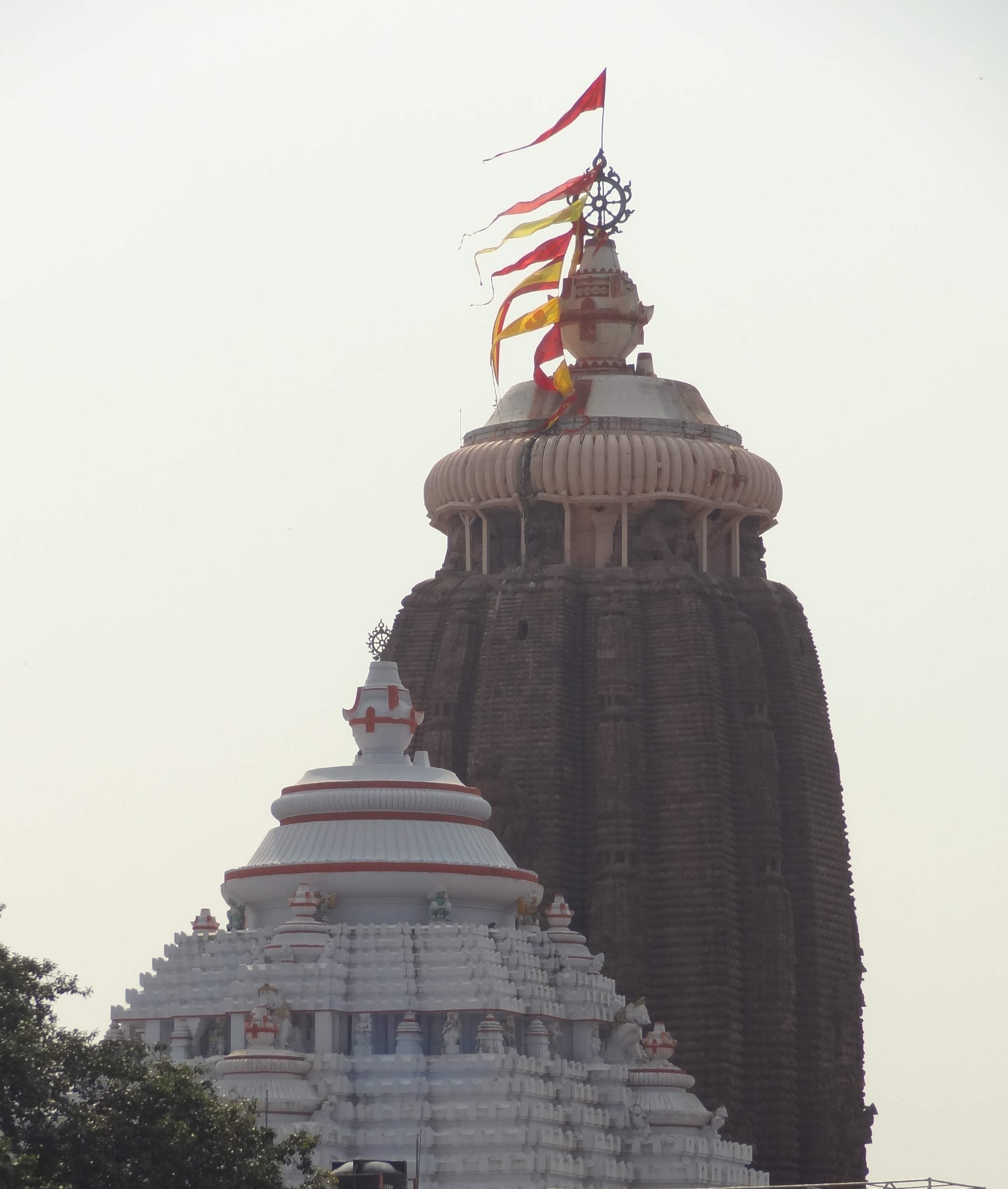
Sikhara
''Shikhara'' (IAST: '), a Sanskrit word translating literally to "mountain peak", refers to the rising tower in the Hindu temple architecture of North India, and also often used in Jain temples. A ''shikhara'' over the ''garbhagriha'' chamber where the presiding deity is enshrined is the most prominent and visible part of a Hindu temple of North India. In South India, the equivalent term is ''vimana''; unlike the ''shikhara'', this refers to the whole building, including the sanctum beneath. In the south, ''shikhara'' is a term for the top stage of the vimana only, which is usually a dome capped with a finial; this article is concerned with the northern form. The southern ''vimana'' is not to be confused with the elaborate gateway-towers of south Indian temples, called ''gopuram'', which are often taller and more prominent features in large temples. Forms ''Shikhara'' can be classified into three main forms: *''Latina''. The ''shikhara'' has four faces, which may include proj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Temple Architecture
Hindu temple architecture as the main form of Hindu architecture has many varieties of style, though the basic nature of the Hindu temple remains the same, with the essential feature an inner sanctum, the '' garbha griha'' or womb-chamber, where the primary ''Murti'' or the image of a deity is housed in a simple bare cell. This chamber often has an open area designed for movement in clockwise rotation for rituals and prayers. Around this chamber there are often other structures and buildings, in the largest cases covering several acres. On the exterior, the garbhagriha is crowned by a tower-like ''shikhara'', also called the '' vimana'' in the south. The shrine building often includes an circumambulatory passage for parikrama, a mandapa congregation hall, and sometimes an antarala antechamber and porch between garbhagriha and mandapa. There may be other mandapas or other buildings, connected or detached, in large temples, together with other small temples in the compound. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vimana (architectural Feature)
''Vimana'' is the structure over the ''garbhagriha'' or inner sanctum in the Hindu temples of South India and Odisha in East India. In typical temples of Odisha using the Kalinga style of architecture, the ''vimana'' is the tallest structure of the temple, as it is in the ''shikhara'' towers of temples in West and North India. By contrast, in large South Indian temples, it is typically smaller than the great gatehouses or '' gopuram'', which are the most immediately striking architectural elements in a temple complex. A ''vimana'' is usually shaped as a pyramid, consisting of several stories or ''tala''. ''Vimana'' are divided in two groups: ''jati vimanas'' that have up to four ''tala'' and ''mukhya vimana'' that have five ''tala'' and more. In North Indian temple architecture texts, the superstructure over the ''garbhagriha'' is called a ''shikhara''. However, in South Indian Hindu architecture texts, the term ''shikhara'' means a dome-shaped crowning cap above the ''vimana''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhumija
Bhumija is a variety of north Indian temple architecture marked by how the rotating square-circle principle is applied to construct the '' shikhara'' (superstructure or spire) on top of the sanctum. Invented about the 10th-century in the Malwa region of central India (west Madhya Pradesh and southeast Rajasthan) during the Paramara dynasty rule, it is found in Hindu and Jain temples. Most early and elegant examples are found in and around the Malwa region, but this design is also found in Gujarat, Rajasthan, Deccan and some major Hindu temple complexes of southern and eastern India.Encyclopedia Britannica (2018)Bhumija in South Asian Arts Description The hallmark of Bhumija style is a square plan that is not divided, but instead rotated around its center ''and'' this rotation is stopped at regular intervals as the superstructure rises vertically. By adjusting the pace of rotation and the interval at which the rotation stops, many creative variations can be implemented. Each tie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stupa
A stupa ( sa, स्तूप, lit=heap, ) is a mound-like or hemispherical structure containing relics (such as '' śarīra'' – typically the remains of Buddhist monks or nuns) that is used as a place of meditation. In Buddhism, circumambulation or '' pradakhshina'' has been an important ritual and devotional practice since the earliest times, and stupas always have a ''pradakhshina'' path around them. The original South Asian form is a large solid dome above a tholobate or drum with vertical sides, which usually sits on a square base. There is no access to the inside of the structure. In large stupas there may be walkways for circumambulation on top of the base as well as on the ground below it. Large stupas have or had ''vedikā'' railings outside the path around the base, often highly decorated with sculpture, especially at the torana gateways, of which there are usually four. At the top of the dome is a thin vertical element, with one of more horizontal discs spre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia occupies modern Iraq. In the broader sense, the historical region included present-day Iraq and Kuwait and parts of present-day Iran, Syria and Turkey. The Sumerians and Akkadians (including Assyrian people, Assyrians and Babylonians) originating from different areas in present-day Iraq, dominated Mesopotamia from the beginning of recorded history, written history () to the fall of Babylon in 539 BC, when it was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire. It fell to Alexander the Great in 332 BC, and after his death, it became part of the Greek Seleucid Empire. Later the Arameans dominated major parts of Mesopotamia (). Mesopotamia is the site of the earliest developments of the Neolithic Revolution from aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amalaka
An amalaka ( sa, आमलक), is a segmented or notched stone disk, usually with ridges on the rim, that sits on the top of a Hindu temple's shikhara or main tower. According to one interpretation, the amalaka represents a lotus, and thus the symbolic seat for the deity below. Another interpretation is that it symbolizes the sun, and is thus the gateway to the heavenly world. The name and, according to some sources the shape, of the amalaka comes from the fruit of Phyllanthus emblica (or Mirobalanus embilica), the Indian gooseberry, or myrobolan fig tree. This is called ''āmalaki'' in Sanskrit, and the fruit has a slightly segmented shape, though this is much less marked than in the architectural shape. The amalaka itself is crowned with a kalasam or finial, from which a temple banner is often hung. History The shape first appears (or survives) as an element in the capitals of columns around the time of Ashoka in the 3rd century BCE, recurring in some capitals of the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed from the early 4th century CE to late 6th century CE. At its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, it covered much of the Indian subcontinent. This period is considered as the Golden Age of India by historians. The ruling dynasty of the empire was founded by the king Sri Gupta; the most notable rulers of the dynasty were Chandragupta I, Samudragupta, Chandragupta II and Skandagupta. The 5th-century CE Sanskrit poet Kalidasa credits the Guptas with having conquered about twenty-one kingdoms, both in and outside India, including the kingdoms of Parasikas, the Hunas, the Kambojas, tribes located in the west and east Oxus valleys, the Kinnaras, Kiratas, and others.Raghu Vamsa v 4.60–75 The high points of this period are the great cultural developments which took place primarily during the reigns of Samudragupta, Chandragupta II and Kumaragupta I. Many Hindu epics and literary sources, such as Mahabharata and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Temple
A Hindu temple, or ''mandir'' or ''koil'' in Indian languages, is a house, seat and body of divinity for Hindus. It is a structure designed to bring human beings and gods together through worship, sacrifice, and devotion.; Quote: "The Hindu temple is designed to bring about contact between man and the gods" (...) "The architecture of the Hindu temple symbolically represents this quest by setting out to dissolve the boundaries between man and the divine". The symbolism and structure of a Hindu temple are rooted in Vedic traditions, deploying circles and squares. It also represents recursion and the representation of the equivalence of the macrocosm and the microcosm by astronomical numbers, and by "specific alignments related to the geography of the place and the presumed linkages of the deity and the patron". A temple incorporates all elements of the Hindu cosmos — presenting the good, the evil and the human, as well as the elements of the Hindu sense of cyclic time and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernest Binfield Havell
Ernest Binfield Havell (16 September 1861 – 31 December 1934), who published under the name E.B. Havell, was an influential English arts administrator, art historian and author of numerous books about Indian art and architecture. He was a member of the Havell family of artists and art educators. He was the principal of the Government School of Art, Calcutta from 1896 to 1905, where, along with Abanindranath Tagore, he developed a style of art and art education based on Indian rather than Western models, which led to the foundation of the Bengal school of art. Early life Ernest was born at Jesse Terrace, Reading in the English county of Berkshire in 1861, the son of an artist Charles Richard Havell and his wife, Charlotte Amelia Lord. The family had several artists and publishers. He went to Reading School and learned art at the Royal College of Art and in Paris and Italy. Art history In India, Havell initially served the Madras School of Art as Superintendent for a decad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
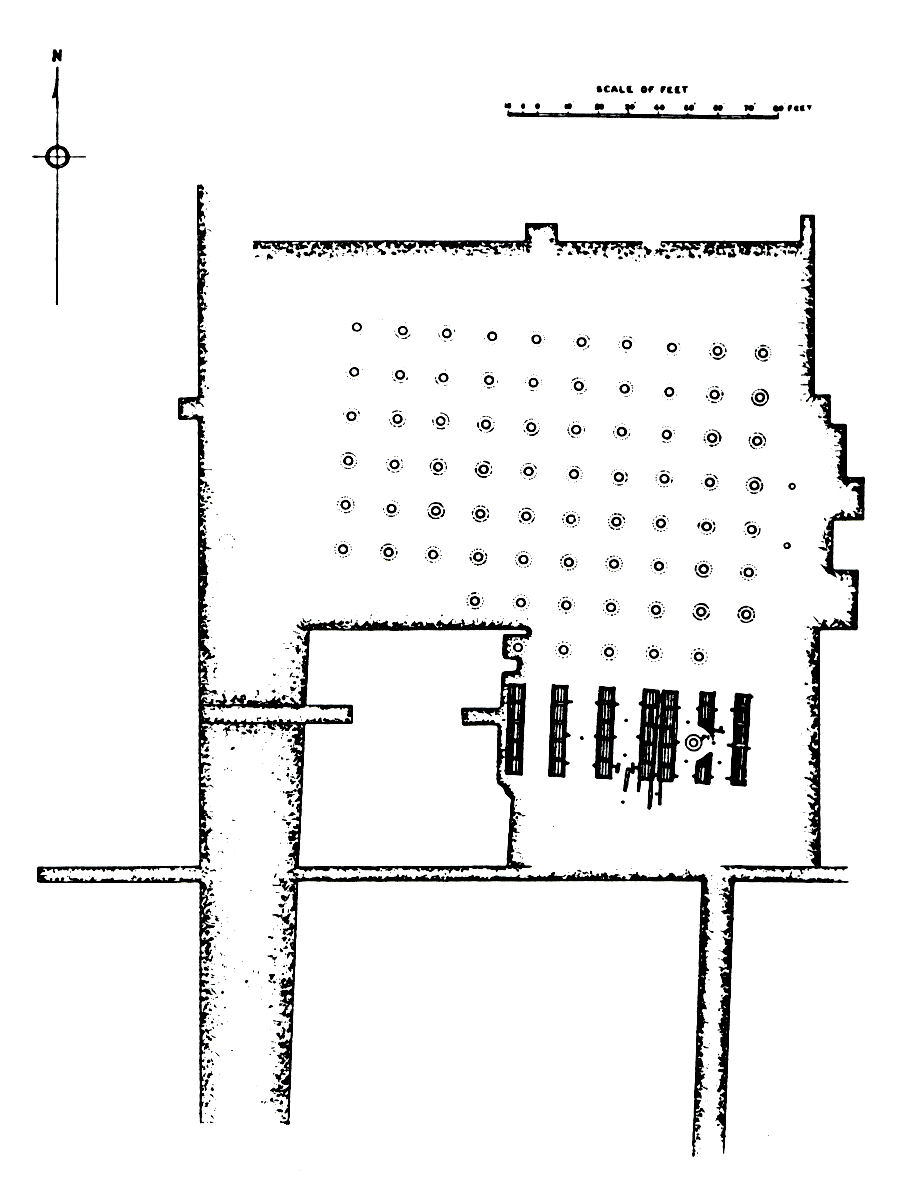
Kumrahar
Kumhrar or Kumrahar is the area of Patna where remains of the ancient city of Pataliputra were excavated by the Archaeological Survey of India starting from 1913. It is located 5 km east of Patna Railway Station. Archaeological remains of the Mauryan period (322–185 BCE) have been discovered here, this include the ruins of a hypostyle 80-pillared hallDevise plan to save Kumhrar site:HC The Times of India, 1 February 2002.Experts' meet to preserve K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind with observance of Buddhist ethics and meditation. Other widely observed practices include: monasticism; "taking refuge" in the Buddha, the , and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)