|
Sigma Non-innocence
Sigma non-innocence is a special form of non-innocence, an oxidation characteristic in metal complexes. It is mainly discussed in coordination complexes of late transition metals in their high formal oxidation states. Complexes exhibiting sigma non-innocence differ from classical Werner coordination complexes in that their bonding and antibonding orbitals have an inverted distribution of metal and ligand character (cf. inverted ligand field). The oxidation of the ligand and a lowered charge at the metal center renders the assignment of the oxidation state non-trivial. Sigma non-innocence in copper complexes Sigma non-innocence has been extensively discussed for the prototypical example of a copper complex u(CF3)4sup>− in conjunction with the concept of an inverted ligand field. In 1995, Snyder suggested, based on his quantum chemical calculations, that this formal Cu(III) (d8) complex would be more appropriately represented as a Cu(I) (d10) complex. Snyder pointed out that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-innocent Ligand
In chemistry, a (redox) non-innocent ligand is a ligand in a metal complex where the oxidation state is not clear. Typically, complexes containing non-innocent ligands are redox active at mild potentials. The concept assumes that redox reactions in metal complexes are either metal or ligand localized, which is a simplification, albeit a useful one. C.K. Jørgensen first described ligands as "innocent" and "suspect": "Ligands are innocent when they allow oxidation states of the central atoms to be defined. The simplest case of a suspect ligand is NO..." Redox reactions of complexes of innocent vs. non-innocent ligands Conventionally, redox reactions of coordination complexes are assumed to be metal-centered. The reduction of MnO4− to MnO42− is described by the change in oxidation state of manganese from +7 to +6. The oxide ligands do not change in oxidation state, remaining −2. Oxide is an innocent ligand. Another example of conventional metal-centered redox couple i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal Complex
A coordination complex is a chemical compound consisting of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the periodic table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom through several of the ligand's atoms; ligands with 2, 3, 4 or even 6 bonds to the central a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination Complex
A coordination complex is a chemical compound consisting of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of chemical bond, bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing chemical compound, compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the periodic table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A Ligand#Polydentate and polyhapto ligand motifs and nomenclature, polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverted Ligand Field Theory
Inverted ligand field theory (ILFT) describes a phenomenon in the bonding of coordination complexes where the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital is primarily of ligand character. This is contrary to the traditional ligand field theory or crystal field theory picture and arises from the breaking down of the assumption that in Organometallic chemistry, organometallic complexes, ligands are more electronegative and have frontier orbitals below those of the d orbitals of electropositive metals. Towards the right of the d-block, when approaching the transition-metalmain group boundary, the d orbitals become more core-like, making their cations more electronegative. This decreases their energies and eventually arrives at a point where they are lower in energy than the ligand frontier orbitals. Here the ligand field inverts so that the bonding orbitals are more metal-based, and antibonding orbitals more ligand-based. The relative arrangement of the d orbitals are also inverted in complex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
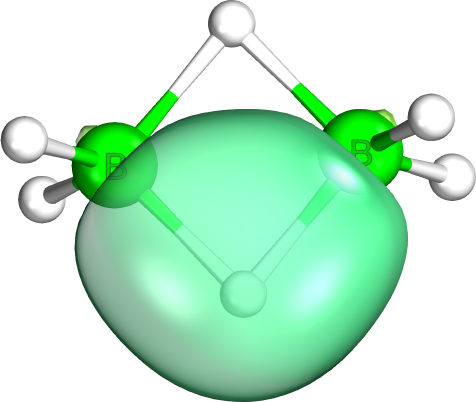
Sigma Non Innocence 3
Sigma ( ; uppercase Σ, lowercase σ, lowercase in word-final position ς; ) is the eighteenth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 200. In general mathematics, uppercase Σ is used as an operator for summation. When used at the end of a letter-case word (one that does not use all caps), the final form (ς) is used. In ' (Odysseus), for example, the two lowercase sigmas (σ) in the center of the name are distinct from the word-final sigma (ς) at the end. The Latin letter S derives from sigma while the Cyrillic letter Es derives from a lunate form of this letter. History The shape (Σς) and alphabetic position of sigma is derived from the Phoenician letter ( ''shin''). Sigma's original name may have been ''san'', but due to the complicated early history of the Greek epichoric alphabets, ''san'' came to be identified as a separate letter in the Greek alphabet, represented as Ϻ. Herodotus reports that "san" was the name giv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy
X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) is a set of advanced techniques used for probing the local environment of matter at atomic level and its electronic structure. The experiments require access to synchrotron radiation facilities for their intense and tunable X-ray beams. Samples can be in the gas phase, solutions, or solids. Background XAS data are obtained by tuning the photon energy, using a crystalline monochromator, to a range where core electrons can be excited (0.1-100 keV). The edges are, in part, named by which core electron is excited: the principal quantum numbers n = 1, 2, and 3, correspond to the K-, L-, and M-edges, respectively. For instance, excitation of a 1s electron occurs at the metal K-edge, K-edge, while excitation of a 2s or 2p electron occurs at an metal L-edge, L-edge (Figure 1). There are three main regions found on a spectrum generated by XAS data, which are then thought of as separate spectroscopic techniques (Figure 2): # The ''absorption thresho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigma Non Innocence
Sigma ( ; uppercase Σ, lowercase σ, lowercase in word-final position ς; ) is the eighteenth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 200. In general mathematics, uppercase Σ is used as an operator for summation. When used at the end of a letter-case word (one that does not use all caps), the final form (ς) is used. In ' (Odysseus), for example, the two lowercase sigmas (σ) in the center of the name are distinct from the word-final sigma (ς) at the end. The Latin letter S derives from sigma while the Cyrillic letter Es derives from a lunate form of this letter. History The shape (Σς) and alphabetic position of sigma is derived from the Phoenician letter ( ''shin''). Sigma's original name may have been ''san'', but due to the complicated early history of the Greek epichoric alphabets, ''san'' came to be identified as a separate letter in the Greek alphabet, represented as Ϻ. Herodotus reports that "san" was the name giv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrinsic Bond Orbitals
Intrinsic bond orbitals (IBO) are localized molecular orbitals giving exact and non-empirical representations of Wave function, wave functions. They are obtained by unitary transformation and form an orthogonal set of orbitals localized on a minimal number of atoms. IBOs present an intuitive and unbiased interpretation of chemical bonding with naturally arising Lewis structure, Lewis structures. For this reason IBOs have been successfully employed for the elucidation of molecular structures and electron flow along the intrinsic reaction coordinate (IRC). IBOs have also found application as Wannier function, Wannier functions in the study of solids. Theory The IBO method entails molecular wave-functions calculated using self-consistent field (SCF) methods such as Kohn-Sham density functional theory (DFT) which are expressed as linear combinations of localized molecular orbitals. In order to arrive at IBOs, intrinsic atomic orbitals (IAOs) are first calculated as representations of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wikipedia Student Program
Wikipedia is a free online encyclopedia that is written and maintained by a community of volunteers, known as Wikipedians, through open collaboration and the wiki software MediaWiki. Founded by Jimmy Wales and Larry Sanger in 2001, Wikipedia has been hosted since 2003 by the Wikimedia Foundation, an American nonprofit organization funded mainly by donations from readers. Wikipedia is the largest and most-read reference work in history. Initially available only in English, Wikipedia exists in over 340 languages. The English Wikipedia, with over million articles, remains the largest of the editions, which together comprise more than articles and attract more than 1.5 billion unique device visits and 13 million edits per month (about 5edits per second on average) . , over 25% of Wikipedia's traffic comes from the United States, while Japan, the United Kingdom, Germany and Russia each account for around 5%. Wikipedia has been praised for enabling the democra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |