|
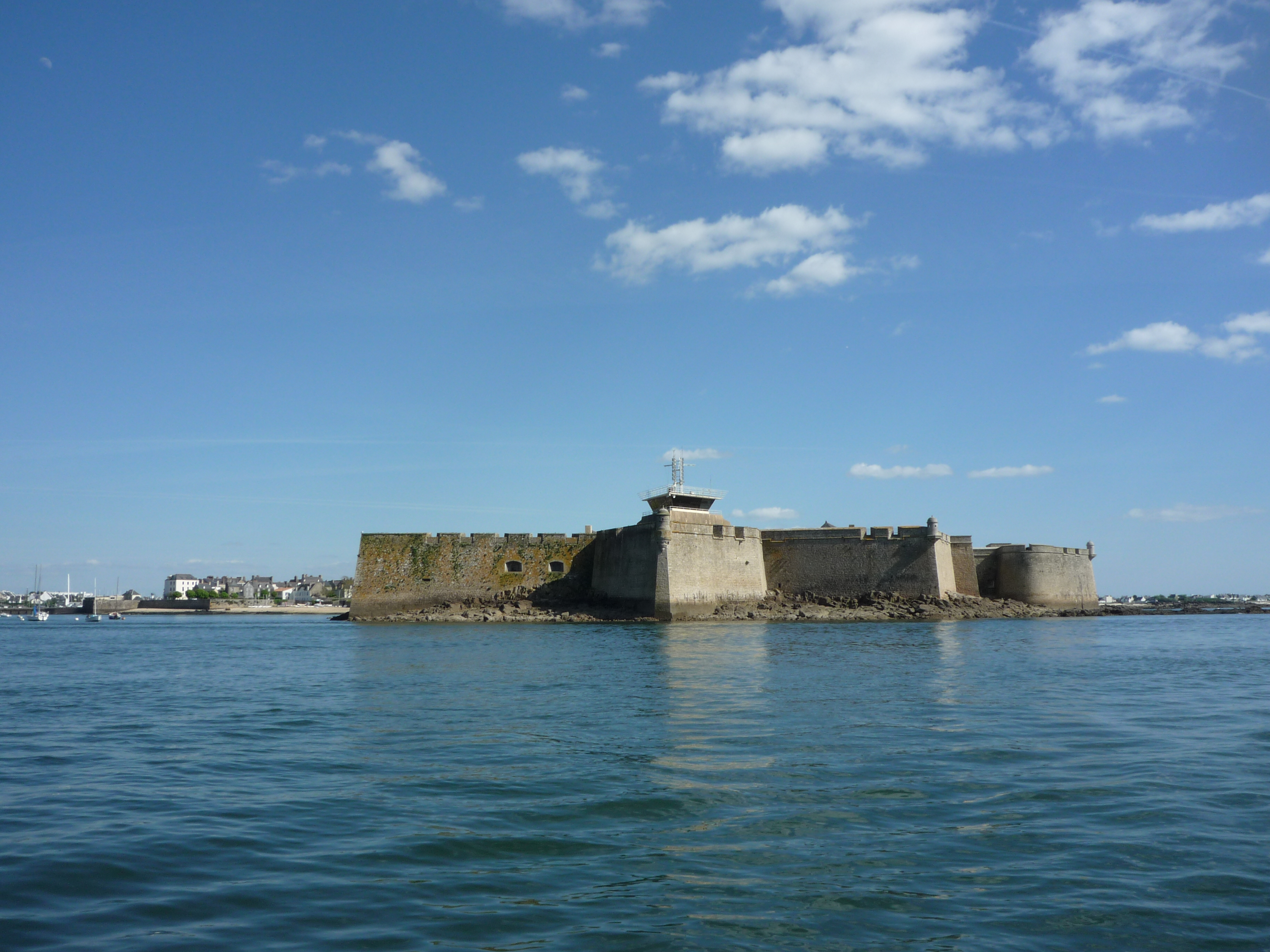
Siege Of Fort Crozon
The siege of Fort Crozon or the siege of El Leon was a land and sea engagement that took place as part of Spain's Brittany campaign late in the French wars of religion and the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604).Fissel pp 229-30 The siege was fought between 1 October and 19 November 1594 and was conducted by English and French troops against a Spanish fort constructed on the Crozon Peninsula near Brest.Nolan pp 215-17 After a number of assaults were repelled, a Spanish relief force under Juan del Águila attempted to relieve the garrison, but it was delayed by French cavalry and could not reach the garrison in time. An assault by the English using a deceitful ruse ended the siege when the defenders were all but put to the sword. The victory proved decisive in two ways. First, it denied the Spanish an important large independent base and port from which to operate in Brittany against the English and Dutch.MacCaffrey p.193 Second, the Spanish had lost most of their support from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo–Spanish War (1585)
Anglo-Spanish War may refer to: * Hundred Years' War, Hundred Years' War (1337–1453), includes the War of the Breton Succession, the Castilian Civil War, the War of the Two Peters, and the 1383–1385 Portuguese interregnum * Third Fernandine War (1381–1382) * War of the League of Cognac (1526–1530), part of the Italian Wars * Second Desmond Rebellion (1579-1583), part of the Desmond rebellions * Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604), including the Spanish Armada, the English Armada and the Nine Years' War (Ireland), part of the Eighty Years' War * Dutch–Portuguese War (1601–1661), part of the Eighty Years' War * Palatinate campaign (1620–1623), part of the Thirty Years' War * Anglo-Spanish War (1625–1630), part of the Thirty Years' War (Eighty Years' War, 1621–1648) * Anglo-Spanish War (1654–1660), part of the Franco-Spanish War (1635–1659), Franco-Spanish War * Anglo-Spanish War (1654–1660)#Caribbean war, Caribbean War (1660–71), follow on from previous war, based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brest, France
Brest (; ) is a port, port city in the Finistère department, Brittany (administrative region), Brittany. Located in a sheltered bay not far from the western tip of a peninsula and the western extremity of metropolitan France, Brest is an important harbour and the second largest French military port after Toulon. The city is located on the western edge of continental France. With 139,456 inhabitants (2020), Brest forms Lower Brittany, Western Brittany's largest functional area (France), metropolitan area (with a population of 370,000 in total), ranking third behind only Nantes and Rennes in the whole of historic Brittany, and the List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, 25th most populous city in France (2019); moreover, Brest provides services to the one million inhabitants of Western Brittany. Although Brest is by far the largest city in Finistère, the ''Prefectures in France, préfecture'' (administrative seat) of the department is in the much smaller town of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plymouth
Plymouth ( ) is a port city status in the United Kingdom, city and unitary authority in Devon, South West England. It is located on Devon's south coast between the rivers River Plym, Plym and River Tamar, Tamar, about southwest of Exeter and southwest of London. It is the most populous city in Devon. Plymouth's history extends back to the Bronze Age, evolving from a trading post at Mount Batten into the thriving market town of Sutton, which was formally re-named as Plymouth in 1439 when it was made a borough status in the United Kingdom, borough. The settlement has played a significant role in English history, notably in 1588 when an English fleet based here defeated the Spanish Armada, and in 1620 as the departure point for the Pilgrim Fathers to the New World. During the English Civil War, the town was held by the Roundhead, Parliamentarians and was besieged between 1642 and 1646. In 1690 a dockyard was established on the River Tamar for the Royal Navy and Plymouth grew as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paimpol
Paimpol (; ) is a commune in the Côtes-d'Armor department in Brittany in northwest France. It is a tourist destination, especially during the summer months when people are attracted by its port and beaches. Geography The town is located in the north of Brittany, at the western end of the bay of Saint-Brieuc, at the bottom of the bay of Paimpol. The town is on the old national road D 786, 72 mi west of Saint-Malo, 23 mi north-west of Saint-Brieuc, 21 mi east of Lannion (sub-prefecture) and 44 mi to the north-east of Morlaix . Guingamp (sub-prefecture) is 18 mi to the south, and Rennes is 88 mi to the south-east. Population Inhabitants of Paimpol are called ''paimpolais'' in French. In 1960 Paimpol absorbed the former communes Kerity and Plounez. The population data given in the table below for 1954 and earlier refer to Paimpol proper, without Kerity and Plounez. Breton language The municipality launched a linguistic plan through Ya d'ar brezhoneg on 29 September 2008. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Baskerville (general)
Sir Thomas Baskerville (died 1597), was an English general and MP. Baskerville was the son of Henry Baskerville, Esq., of the city of Hereford, and is described as of Good Rest, Warwickshire. He obtained a high reputation as a military commander. In the Harleian MSS. there is an account of his voyage after the great treasure at Puerto Rico, when he was general of Queen Elizabeth's Indian armada. He was sent with Lord Willoughby to France to assist Henry IV in 1589. He was Member of Parliament for Carmarthen borough in 1592. Subsequently, he commanded the troops despatched to Brittany (1594). He then took part in an expedition to the Spanish Main in 1595 under the command of Francis Drake. After defeat at San Juan in December, Baskerville became second in command after the death of John Hawkins. In January 1596 an attempt to cross the isthmus of Panama from Nombre de Dios in order to seize the silver rich port of Portobelo, Colón also ended in failure. Ravaged with dyse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culverin
A culverin was initially an ancestor of the hand-held arquebus, but the term was later used to describe a type of medieval and Renaissance cannon. The word is derived from the antiquated "culuering" and the French (from " grass snake", following ). From its origin as a hand-held weapon it was adapted for use as artillery by the French in the 15th century and for naval use by the English in the 16th century. The culverin as an artillery piece had a long smoothbore gun barrel with a relatively long range and flat trajectory, using solid round shot projectiles with high muzzle velocity. Hand culverins The hand culverin consisted of a simple smoothbore metal tube, closed at one end except for a small touch hole designed to allow ignition of the gunpowder. The tube was attached to a wood or metal extension which could be held under the arm. It was loaded with gunpowder and lead bullets and fired by inserting a burning slow match into the touch hole. James IV of Scotland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacis
A glacis (, ) in military engineering is an artificial slope as part of a medieval castle or in early modern fortresses. They may be constructed of earth as a temporary structure or of stone in more permanent structure. More generally, a glacis is any slope, natural or artificial, which fulfils the above requirements. The etymology of this French word suggests a slope made dangerous with ice, hence the relationship with ''glacier''. A ''glacis plate'' is the sloped front-most section of the hull of a tank or other armoured fighting vehicle. Ancient fortifications A glacis could also appear in ancient fortresses, such as the one the ancient Egyptians built at Semna in Nubia. Here it was used by them to prevent enemy siege engines from weakening defensive walls. Hillforts in Britain started to incorporate glacis around 350 BC. Those at Maiden Castle, Dorset were high. Medieval fortifications Glacises, also called taluses, were incorporated into medieval fortifications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bastion
A bastion is a structure projecting outward from the curtain wall of a fortification, most commonly angular in shape and positioned at the corners of the fort. The fully developed bastion consists of two faces and two flanks, with fire from the flanks being able to protect the curtain wall and the adjacent bastions. Compared with the medieval fortified towers they replaced, bastion fortifications offered a greater degree of passive resistance and more scope for ranged defence in the age of gunpowder artillery. As military architecture, the bastion is one element in the style of fortification dominant from the mid 16th to mid 19th centuries. Evolution By the middle of the 15th century, artillery pieces had become powerful enough to make the traditional medieval round tower and curtain wall obsolete. This was exemplified by the campaigns of Charles VII of France who reduced the towns and castles held by the English during the latter stages of the Hundred Years War, and by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedro De Zubiaur
Pedro de Zubiaur, Zubiaurre or Çubiaurre (1540 – 3 August 1605) was a Spanish naval officer and engineer, general of the Spanish Navy, distinguished for his achievements in the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604). Biography Born into a seafaring family from Biscay, Zubiaur started his naval career in 1568 plying between the ports of Bilbao and Flanders, where he worked under the command of the Grand Duke of Alba. After getting promoted to General for his naval achievements in the Low Countries, during the Brittany campaign he won several battles against the English for Philip II of Spain, the most famous of them during the relief of Blaye. He captured six English ships from Raleigh's fleet near cape Finisterre in 1597. During the 4th Spanish Armada, this time sent to Ireland, Zubiaur made landfall at Castlehaven in December after being driven back by contrary winds. His small fleet was neutralised by an English fleet led by Richard Leveson. On his return to Spain, Zubia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cristóbal De Rojas
Cristóbal or Cristobal, the Spanish version of Christopher, is a masculine given name and a surname which may refer to: Given name * Cristóbal Balenciaga (1895–1972), Spanish fashion designer * Cristóbal Cobo (born 1976), Chilean academic * Cristóbal Colón Ruiz (born 1954), Puerto Rican politician * Cristóbal de Morales (1500–1553), Spanish composer *Cristóbal de Olid Cristóbal de Olid (; 1487–1524) was a Spanish adventurer, conquistador and rebel who played a part in the conquest of the Aztec Empire and present-day Honduras. Born in Baeza, Olid grew up in the household of the governor of Cuba, Diego V ... (1487–1524), Spanish conquistador * Cristóbal Halffter (1930–2021), Spanish composer * Cristóbal Lander (born 1978), Venezuelan actor and model * Cristóbal López (other), multiple people * Cristobal Lorente, (born 1996), Spanish boxer * Cristóbal Magallanes Jara (1869–1927), Mexican martyr and Catholic saint * Cristóbal Márquez Crespo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roadstead Of Brest
The roadstead of Brest (, ; ) is a roadstead or bay located in the Finistère Departments of France, department in Brittany (administrative region), Brittany in northwestern France. The surface area is about 180 km² (70 sq mi). The port of Brest (France), Brest and one of the two French naval bases, Brest Arsenal, are located on its northern edge. It is linked to the Atlantic Ocean (called the Iroise Sea at this point) by the ''Goulet de Brest'', a strait about 1.8 km wide. Three main rivers drain into the roadstead: the Penfeld (the town of Brest and the first buildings of the naval base were built on its banks), the Élorn (or river of Landerneau) and the Aulne (or river of Châteaulin). Strategic importance For a number of centuries, Brest has been an important military port. The easily defensible roadstead of Brest therefore has a number of military installations, for example: *Fort du Mengant, and Brest Arsenal, on the north of the bay; *the submarine base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port-Louis, Morbihan
Port-Louis (; ) is a commune in the Morbihan department of Brittany in northwestern France. History At the beginning of the 17th century, merchants who were trading with India established warehouses in Port-Louis. They later built additional warehouses across the bay in 1628, at the location which became known as "L'Orient" (''the Orient'' in French). In 1664, during the reign of King Louis XIV, the French East India Company was established at Port-Louis. The company established a shipyard at Lorient. The Company was not able to maintain itself financially, and it was abolished in 1769. In 1770, King Louis XVI issued an edict that required the Company to transfer to the state all its properties, in return for which the King agreed to pay all of the Company’s debts and obligations. The French government then took over the shipyards as a naval port and arsenal. Citadel The Spanish engineer Cristóbal de Rojas built the Fuerte de Águila at the start of the Brittany C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |