|
Shuttle Vector
A shuttle vector is a vector (usually a plasmid) constructed so that it can propagate in two different host species. Therefore, DNA inserted into a shuttle vector can be tested or manipulated in two different cell types. The main advantage of these vectors is they can be manipulated in ''E. coli'', then used in a system which is more difficult or slower to use (e.g. yeast). Shuttle vectors include plasmids that can propagate in eukaryotes and prokaryotes (e.g. both ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' and ''Escherichia coli'') or in different species of bacteria (e.g. both ''E. coli'' and ''Rhodococcus erythropolis''). There are also adenovirus shuttle vectors, which can propagate in ''E. coli'' and mammals. Shuttle vectors are frequently used to quickly make multiple copies of the gene in ''E. coli'' (amplification). They can also be used for ''in vitro'' experiments and modifications (e.g. mutagenesis, PCR). One of the most common types of shuttle vectors is the yeast shuttle vector. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector (molecular Biology)
In molecular cloning, a vector is any particle (e.g., plasmids, cosmids, Lambda phages) used as a vehicle to artificially carry a foreign nucleic acid sequence, nucleic sequence – usually DNA – into another Cell (biology), cell, where it can DNA replication, be replicated and/or Gene expression, expressed. A vector containing foreign DNA is termed recombinant DNA. The four major types of vectors are plasmids, viral vectors, cosmids, and Bacterial artificial chromosome, artificial chromosomes. Of these, the most commonly used vectors are plasmids. Common to all engineered vectors are an origin of replication, a multiple cloning site, multicloning site, and a selectable marker. The vector itself generally carries a DNA sequence that consists of an Insert (molecular biology), insert (in this case the transgene) and a larger sequence that serves as the "backbone" of the vector. The purpose of a vector which transfers genetic information to another cell is typically to isolate, mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom (biology), kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitute 1% of all described fungal species. Some yeast species have the ability to develop multicellular characteristics by forming strings of connected budding cells known as pseudohyphae or false hyphae, or quickly evolve into a Multicellular organism, multicellular cluster with specialised Organelle, cell organelles function. Yeast sizes vary greatly, depending on species and environment, typically measuring 3–4 micrometre, μm in diameter, although some yeasts can grow to 40 μm in size. Most yeasts reproduce asexual reproduction, asexually by mitosis, and many do so by the asymmetric division process known as budding. With their single-celled growth habit, yeasts can be contrasted with Mold (fungus), molds, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uracil
Uracil () (nucleoside#List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases, symbol U or Ura) is one of the four nucleotide bases in the nucleic acid RNA. The others are adenine (A), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). In RNA, uracil binds to adenine via two hydrogen bonds. In DNA, the uracil nucleobase is replaced by thymine (T). Uracil is a demethylated form of thymine. Uracil is a common and naturally occurring pyrimidine derivative. The name "uracil" was coined in 1885 by the German chemist Robert Behrend, who was attempting to synthesize derivatives of uric acid. Originally discovered in 1900 by Alberto Ascoli, it was isolated by hydrolysis of yeast nuclein; it was also found in bovine thymus and spleen, herring sperm, and wheat Cereal germ, germ. It is a planar, unsaturated compound that has the ability to absorb light. Uracil that was formed extraterrestrially has been detected in the Murchison meteorite, in near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, Ryugu, and possibly on the surface of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
URA3
URA3 is a gene on chromosome V in ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' (yeast). Its systematic name is YEL021W. URA3 is often used in yeast research as a "marker gene", that is, a gene to label chromosomes or plasmids. URA3 encodes Orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase (ODCase), which is an enzyme that catalyzes one reaction in the synthesis of pyrimidine ribonucleotides (a component of RNA). Use in yeast research Loss of ODCase activity leads to a lack of cell growth unless uracil or uridine is added to the media. The presence of the URA3 gene in yeast restores ODCase activity, facilitating growth on media not supplemented with uracil or uridine, thereby allowing selection for yeast carrying the gene. In contrast, if 5-FOA (5-Fluoroorotic acid) is added to the media, the active ODCase will convert 5-FOA into the toxic compound (a suicide inhibitor) 5-fluorouracil causing cell death, which allows for selection against yeast carrying the gene. Since URA3 allows for both positive and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selectable Marker
A selectable marker is a gene introduced into cell (biology), cells, especially bacteria or cells in cell culture, culture, which confers one or more traits suitable for artificial selection. They are a type of reporter gene used in laboratory microbiology, molecular biology, and genetic engineering to indicate the success of a transfection or genetic transformation, transformation or other procedure meant to introduce foreign DNA into a cell. Selectable markers are often antibiotic resistance genes: bacteria subjected to a procedure by which exogenous DNA containing an antibiotic resistance gene (usually alongside other genes of interest) has been introduced are grown on a medium containing an antibiotic, such that only those bacterial cells which have successfully taken up and gene expression, expressed the introduced genetic material, including the gene which confers antibiotic resistance, can survive and produce colony (biology), colonies. The genes encoding resistance to antibio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centromere
The centromere links a pair of sister chromatids together during cell division. This constricted region of chromosome connects the sister chromatids, creating a short arm (p) and a long arm (q) on the chromatids. During mitosis, spindle fibers attach to the centromere via the kinetochore. The physical role of the centromere is to act as the site of assembly of the kinetochores – a highly complex multiprotein structure that is responsible for the actual events of chromosome segregation – i.e. binding microtubules and signaling to the cell cycle machinery when all chromosomes have adopted correct attachments to the spindle, so that it is safe for cell division to proceed to completion and for cells to enter anaphase. There are, broadly speaking, two types of centromeres. "Point centromeres" bind to specific proteins that recognize particular DNA sequences with high efficiency. Any piece of DNA with the point centromere DNA sequence on it will typically form a centr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autonomously Replicating Sequence
An autonomously replicating sequence (ARS) contains the origin of replication in the yeast genome. The ARS of ''S. cerevisiae'' is a minimal 125 bp, and contains four regions (A, B1, B2, and B3), named in order of their effect on plasmid stability. The A-Domain is highly conserved, any mutation abolishes origin function. Mutations on B1, B2, and B3 will diminish, but not prevent functioning of the origin. Element A is highly conserved, consisting of the consensus sequence: (where ''Y'' is either pyrimidine and ''R'' is either purine). When this element is mutated, the ARS loses all activity. As seen above the ARS are considerably A-T rich which makes it easy for replicative proteins to disrupt the H-bonding in that area. ORC protein complex (origin recognition complex) is bound at the ARS throughout the cell cycle, allowing replicative proteins access to the ARS. Mutational analysis for the yeast ARS elements have shown that any mutation in the B1, B2 and B3 regions result in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Lactamase
Beta-lactamases (β-lactamases) are enzymes () produced by bacteria that provide multi-resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins, cephamycins, monobactams and carbapenems ( ertapenem), although carbapenems are relatively resistant to beta-lactamase. Beta-lactamase provides antibiotic resistance by breaking the antibiotics' structure. These antibiotics all have a common element in their molecular structure: a four-atom ring known as a beta-lactam (β-lactam) ring. Through hydrolysis, the enzyme lactamase breaks the β-lactam ring open, deactivating the molecule's antibacterial properties. Beta-lactamases produced by gram-negative bacteria are usually secreted, especially when antibiotics are present in the environment. Structure The structure of a ''Streptomyces'' serine β-lactamase (SBLs) is given by . The alpha-beta fold () resembles that of a DD-transpeptidase, from which the enzyme is thought to have evolved. β-lactam antibiotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimicrobial Resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR or AR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from antimicrobials, which are drugs used to treat infections. This resistance affects all classes of microbes, including bacteria (antibiotic resistance), viruses (antiviral resistance), Parasitic disease, parasites (antiparasitic resistance), and fungi (antifungal resistance). Together, these adaptations fall under the AMR umbrella, posing significant challenges to healthcare worldwide. Misuse and improper management of antimicrobials are primary drivers of this resistance, though it can also occur naturally through genetic mutations and the spread of resistant genes. Antibiotic resistance, a significant AMR subset, enables bacteria to survive antibiotic treatment, complicating infection management and treatment options. Resistance arises through spontaneous mutation, horizontal gene transfer, and increased selective pressure from Antibiotic misuse, antibiotic overuse, both in medicin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
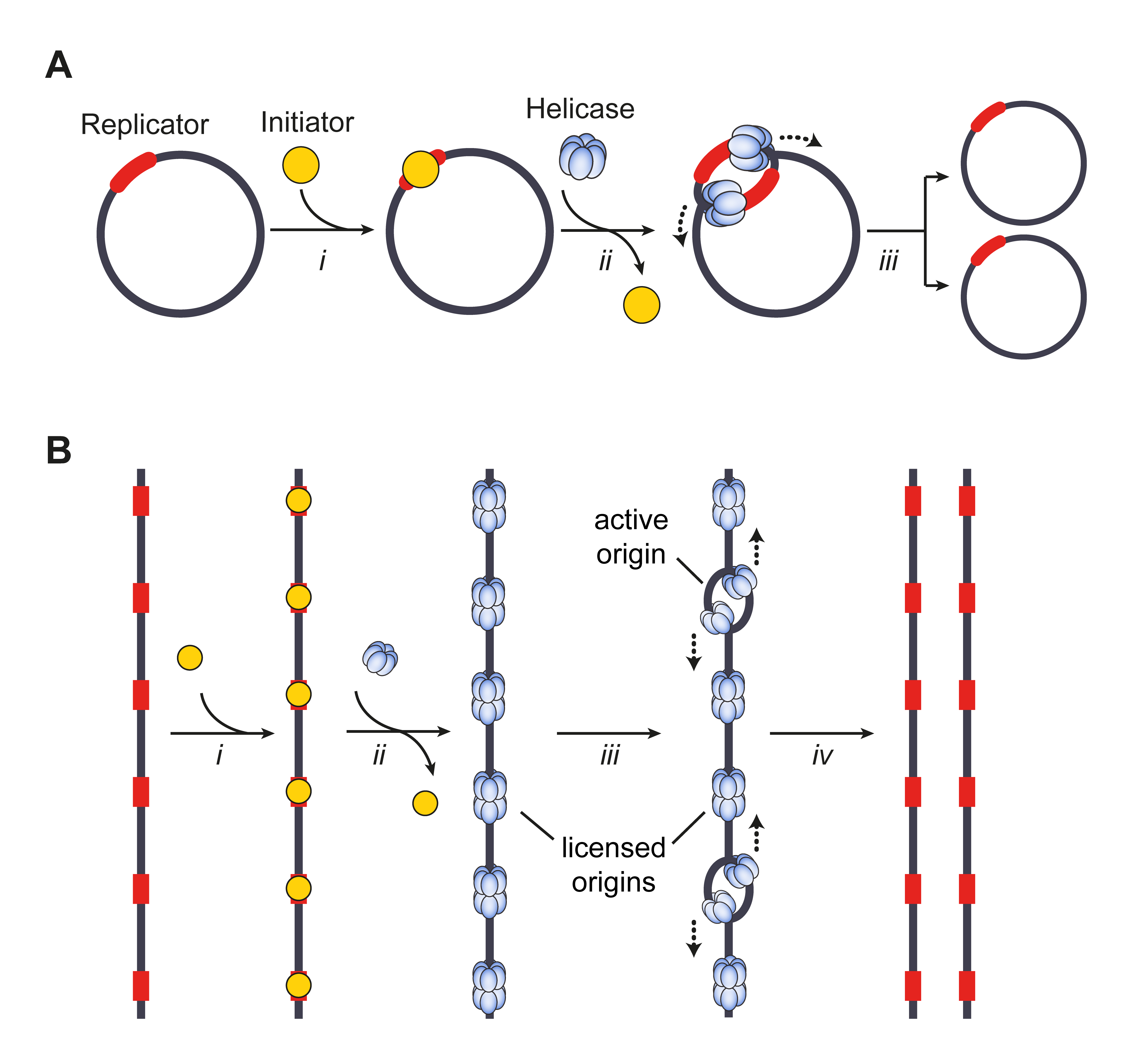
Origin Of Replication
The origin of replication (also called the replication origin) is a particular sequence in a genome at which replication is initiated. Propagation of the genetic material between generations requires timely and accurate duplication of DNA by semiconservative replication prior to cell division to ensure each daughter cell receives the full complement of chromosomes. Material was copied from this source, which is available under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License This can either involve the DNA replication, replication of DNA in living organisms such as prokaryotes and eukaryotes, or that of DNA virus, DNA or RNA virus, RNA in viruses, such as double-stranded RNA viruses. Synthesis of daughter strands starts at discrete sites, termed replication origins, and proceeds in a bidirectional manner until all genomic DNA is replicated. Despite the fundamental nature of these events, organisms have evolved surprisingly divergent strategies that control replication onset. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymerase Chain Reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to make millions to billions of copies of a specific DNA sample rapidly, allowing scientists to amplify a very small sample of DNA (or a part of it) sufficiently to enable detailed study. PCR was invented in 1983 by American biochemist Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation. Mullis and biochemist Michael Smith (chemist), Michael Smith, who had developed other essential ways of manipulating DNA, were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993. PCR is fundamental to many of the procedures used in genetic testing and research, including analysis of Ancient DNA, ancient samples of DNA and identification of infectious agents. Using PCR, copies of very small amounts of DNA sequences are exponentially amplified in a series of cycles of temperature changes. PCR is now a common and often indispensable technique used in medical laboratory research for a broad variety of applications including biomedical research and forensic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmid
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria and archaea; however plasmids are sometimes present in and eukaryotic organisms as well. Plasmids often carry useful genes, such as those involved in antibiotic resistance, virulence, secondary metabolism and bioremediation. While chromosomes are large and contain all the essential genetic information for living under normal conditions, plasmids are usually very small and contain additional genes for special circumstances. Artificial plasmids are widely used as vectors in molecular cloning, serving to drive the replication of recombinant DNA sequences within host organisms. In the laboratory, plasmids may be introduced into a cell via transformation. Synthetic plasmids are available for procurement over the internet by various vendors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |