|
Shunting Inhibition
Shunting inhibition, also known as divisive inhibition, is a form of postsynaptic potential inhibition that can be represented mathematically as reducing the excitatory potential by division, rather than linear subtraction. The term "shunting" is used because of the synaptic conductance short-circuit currents that are generated at adjacent excitatory synapses. If a shunting inhibitory synapse is activated, the input resistance is reduced locally. The amplitude of subsequent excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) is reduced by this, in accordance with Ohm's Law. This simple scenario arises if the inhibitory synaptic reversal potential is identical to or even more negative than the resting potential. Discovery Shunting inhibition was discovered by Fatt and Katz in 1953. Mechanism Shunting inhibition is theorized to be a type of gain control mechanism, regulating the responses of neurons. Simple inhibition such as hyperpolarization has a subtractive effect on the depolar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential
An inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) is a kind of synaptic potential that makes a postsynaptic neuron less likely to generate an action potential.Purves et al. Neuroscience. 4th ed. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates, Incorporated; 2008. The opposite of an inhibitory postsynaptic potential is an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP), which is a synaptic potential that makes a postsynaptic neuron ''more'' likely to generate an action potential. IPSPs can take place at all chemical synapses, which use the secretion of neurotransmitters to create cell-to-cell signalling. EPSPs and IPSPs compete with each other at numerous synapses of a neuron. This determines whether an action potential occurring at the presynaptic terminal produces an action potential at the postsynaptic membrane. Some common neurotransmitters involved in IPSPs are GABA and glycine. Inhibitory presynaptic neurons release neurotransmitters that then bind to the postsynaptic receptors; this induces a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential
In neuroscience, an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) is a postsynaptic potential that makes the postsynaptic neuron more likely to fire an action potential. This temporary depolarization of postsynaptic membrane potential, caused by the flow of positively charged ions into the postsynaptic cell, is a result of opening ligand-gated ion channels. These are the opposite of inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs), which usually result from the flow of ''negative'' ions into the cell or positive ions ''out'' of the cell. EPSPs can also result from a decrease in outgoing positive charges, while IPSPs are sometimes caused by an increase in positive charge outflow. The flow of ions that causes an EPSP is an excitatory postsynaptic current (EPSC). EPSPs, like IPSPs, are graded (i.e. they have an additive effect). When multiple EPSPs occur on a single patch of postsynaptic membrane, their combined effect is the sum of the individual EPSPs. Larger EPSPs result in greater membra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synapse
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that allows a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or a target effector cell. Synapses can be classified as either chemical or electrical, depending on the mechanism of signal transmission between neurons. In the case of electrical synapses, neurons are coupled bidirectionally with each other through gap junctions and have a connected cytoplasmic milieu. These types of synapses are known to produce synchronous network activity in the brain, but can also result in complicated, chaotic network level dynamics. Therefore, signal directionality cannot always be defined across electrical synapses. Chemical synapses, on the other hand, communicate through neurotransmitters released from the presynaptic neuron into the synaptic cleft. Upon release, these neurotransmitters bind to specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, inducing an electrical or chemical response in the target neuron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Conductance
The electrical resistance of an object is a measure of its opposition to the flow of electric current. Its reciprocal quantity is , measuring the ease with which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with mechanical friction. The SI unit of electrical resistance is the ohm (), while electrical conductance is measured in siemens (S) (formerly called the 'mho' and then represented by ). The resistance of an object depends in large part on the material it is made of. Objects made of electrical insulators like rubber tend to have very high resistance and low conductance, while objects made of electrical conductors like metals tend to have very low resistance and high conductance. This relationship is quantified by resistivity or conductivity. The nature of a material is not the only factor in resistance and conductance, however; it also depends on the size and shape of an object because these properties are extensive rather tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short Circuit
A short circuit (sometimes abbreviated to short or s/c) is an electrical circuit that allows a current to travel along an unintended path with no or very low electrical impedance. This results in an excessive current flowing through the circuit. The opposite of a short circuit is an open circuit, which is an infinite resistance (or very high impedance) between two nodes. Definition A short circuit is an abnormal connection between two nodes of an electric circuit intended to be at different voltages. This results in an electric current limited only by the Thévenin equivalent resistance of the rest of the network which can cause circuit damage, overheating, fire or explosion. Although usually the result of a fault, there are cases where short circuits are caused intentionally, for example, for the purpose of voltage-sensing crowbar circuit protectors. In circuit analysis, a ''short circuit'' is defined as a connection between two nodes that forces them to be at the sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excitatory Synapse
An excitatory synapse is a synapse in which an action potential in a presynaptic neuron increases the probability of an action potential occurring in a postsynaptic cell. Neurons form networks through which nerve impulses travels, each neuron often making numerous connections with other cells of neurons. These electrical signals may be excitatory or inhibitory, and, if the total of excitatory influences exceeds that of the inhibitory influences, the neuron will generate a new action potential at its axon hillock, thus transmitting the information to yet another cell. This phenomenon is known as an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP). It may occur via direct contact between cells (i.e., via gap junctions), as in an electrical synapse, but most commonly occurs via the vesicular release of neurotransmitters from the presynaptic axon terminal into the synaptic cleft, as in a chemical synapse. The excitatory neurotransmitters, the most common of which is glutamate, then migra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Input Resistance
In electrical engineering Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems that use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the l ..., the input impedance of an electrical network is the measure of the opposition to Electric current, current (Electrical_impedance, impedance), both static (Electrical resistance and conductance, resistance) and dynamic (Electrical reactance, reactance), into a Electrical load, load network or circuit that is ''external'' to the electrical source network. The input admittance (the Multiplicative inverse, reciprocal of impedance) is a measure of the load network's propensity to draw current. The source network is the portion of the network that transmits Electric power, power, and the load network is the portion of the network that consumes power. For an electrical property measurement instrument like an osci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohm's Law
Ohm's law states that the electric current through a Electrical conductor, conductor between two Node (circuits), points is directly Proportionality (mathematics), proportional to the voltage across the two points. Introducing the constant of proportionality, the Electrical resistance, resistance, one arrives at the three mathematical equations used to describe this relationship: V = IR \quad \text\quad I = \frac \quad \text\quad R = \frac where is the current through the conductor, ''V'' is the voltage measured across the conductor and ''R'' is the electrical resistance, resistance of the conductor. More specifically, Ohm's law states that the ''R'' in this relation is constant, independent of the current. If the resistance is not constant, the previous equation cannot be called ''Ohm's law'', but it can still be used as a definition of Electrical resistance and conductance#Static and differential resistance, static/DC resistance. Ohm's law is an empirical law, empirical rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
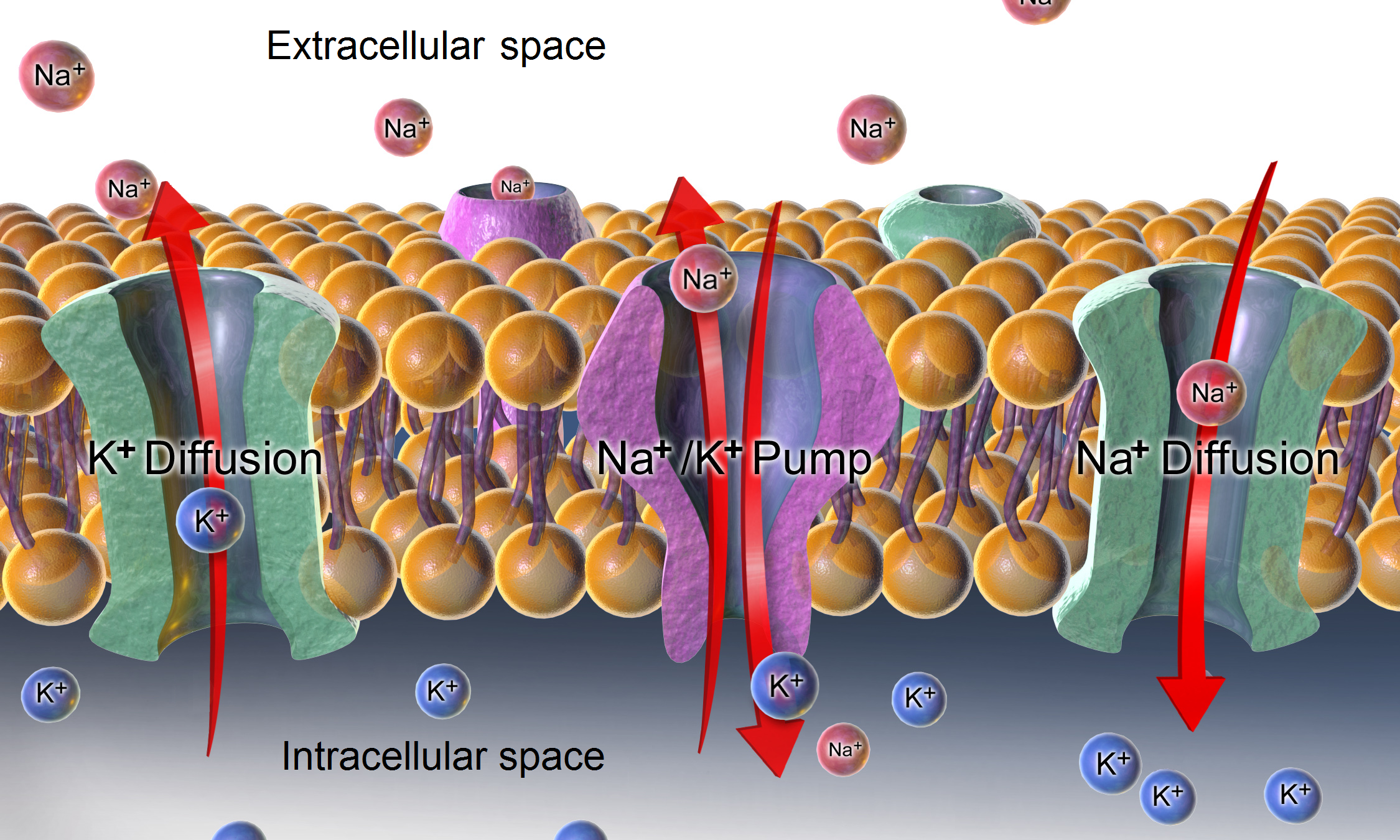
Resting Potential
The relatively static membrane potential of quiescent cells is called the resting membrane potential (or resting voltage), as opposed to the specific dynamic electrochemical phenomena called action potential and graded membrane potential. The resting membrane potential has a value of approximately −70 mV or −0.07 V. Apart from the latter two, which occur in excitable cells (neurons, muscles, and some secretory cells in glands), membrane voltage in the majority of non-excitable cells can also undergo changes in response to environmental or intracellular stimuli. The resting potential exists due to the differences in membrane permeabilities for potassium, sodium, calcium, and chloride ions, which in turn result from functional activity of various ion channels, ion transporters, and exchangers. Conventionally, resting membrane potential can be defined as a relatively stable, ground value of transmembrane voltage in animal and plant cells. Because the membrane pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Theory
Control theory is a field of control engineering and applied mathematics that deals with the control system, control of dynamical systems in engineered processes and machines. The objective is to develop a model or algorithm governing the application of system inputs to drive the system to a desired state, while minimizing any ''delay'', ''overshoot'', or ''steady-state error'' and ensuring a level of control Stability theory, stability; often with the aim to achieve a degree of Optimal control, optimality. To do this, a controller with the requisite corrective behavior is required. This controller monitors the controlled process variable (PV), and compares it with the reference or Setpoint (control system), set point (SP). The difference between actual and desired value of the process variable, called the ''error'' signal, or SP-PV error, is applied as feedback to generate a control action to bring the controlled process variable to the same value as the set point. Other aspects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural network in the nervous system. They are located in the nervous system and help to receive and conduct impulses. Neurons communicate with other cells via synapses, which are specialized connections that commonly use minute amounts of chemical neurotransmitters to pass the electric signal from the presynaptic neuron to the target cell through the synaptic gap. Neurons are the main components of nervous tissue in all Animalia, animals except sponges and placozoans. Plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Molecular evidence suggests that the ability to generate electric signals first appeared in evolution some 700 to 800 million years ago, during the Tonian period. Predecessors of neurons were the peptidergic secretory cells. They eventually ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperpolarization (biology)
Hyperpolarization is a change in a cell's membrane potential that makes it more negative. Cells typically have a negative resting potential, with neuronal action potentials depolarizing the membrane. When the resting membrane potential is made more negative, it increases the minimum stimulus needed to surpass the needed threshold. Neurons naturally become hyperpolarized at the end of an action potential, which is often referred to as the relative refractory period. Relative refractory periods typically last 2 milliseconds, during which a stronger stimulus is needed to trigger another action potential. Cells can also become hyperpolarized depending on channels and receptors present on the membrane, which can have an inhibitory effect. Hyperpolarization is often caused by efflux of K+ (a cation) through K+ channels, or influx of Cl– (an anion) through Cl– channels. On the other hand, influx of cations, e.g. Na+ through Na+ channels or Ca2+ through Ca2+ cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |