|
Shetland Pony
The Shetland pony or Sheltie is a Scottish breed of pony originating in the Shetland Islands in the north of Scotland. It may stand up to at the withers. It has a heavy coat and short legs, is strong for its size, and is used for riding, driving, and pack purposes. History Shetland ponies originated in the Shetland Islands, located northeast of mainland Scotland. Small horses have been kept in the Shetland Islands since the Bronze Age. People who lived on the islands probably later crossed the native stock with ponies imported by Norse settlers. Shetland ponies were probably also influenced by the Celtic pony, brought to the islands by settlers between 2000 and 1000 BC. The harsh climate and scarce food developed the ponies into extremely hardy animals. Shetland ponies were first used for pulling carts and for carrying peat, seaweed, and ploughing land. Then, as the Industrial Revolution increased the need for coal in the mid-nineteenth century, thousands of Shetland p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shetland Islands
Shetland (until 1975 spelled Zetland), also called the Shetland Islands, is an archipelago in Scotland Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ... lying between Orkney, the Faroe Islands, and Norway, marking the northernmost region of the United Kingdom. The islands lie about to the northeast of Orkney, from mainland Scotland and west of Norway. They form part of the border between the Atlantic Ocean to the west and the North Sea to the east. The island's area is and the population totalled in . The islands comprise the Shetland (Scottish Parliament constituency), Shetland constituency of the Scottish Parliament. The islands' administrative centre, largest settlement and only burgh is Lerwick, which has been the capital of Shetland since 1708, before which time the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Shetland Pony
The American Shetland Pony is an American breed of pony. It derives from the traditional Shetland Pony from the Shetland Isles of Scotland, but as a result of cross-breeding with other horse and pony breeds, is taller and more elegant. It does not have the thick coat of the traditional Shetland, and in conformation is more similar to the Hackney Pony, with some Arab influence. It is the most numerous pony breed in the United States; numbers in 1994 were estimated at over 50,000. It is one of two American pony breeds derived from the traditional Shetland, the other being the Pony of the Americas. History The first documented importation of Shetland Ponies to the United States was in 1885, when Eli Elliot imported seventy-five of them. A breed association, the American Shetland Pony Club, was formed in 1888. The original stock was crossbred with various other breeds, principally the Hackney Pony. Arabian, Harness Show Pony and Welsh breeds were also used. The result was a tal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Therapeutic Horseback Riding
Equine-assisted therapy (EAT) encompasses a range of treatments that involve activities with horses and other equines to promote human physical and mental health. Modern use of horses for mental health treatment dates to the 1990s. Systematic review of studies of EAT as applied to physical health date only to about 2007, and a lack of common terminology and standardization has caused problems with meta-analysis. Due to a lack of high-quality studies assessing the efficacy of equine-assisted therapies for mental health treatment, concerns have been raised that these therapies should not replace or divert resources from other evidence-based mental health therapies. The existing body of evidence does not justify the promotion and use of equine-related treatments for mental disorders. Terminology An overall term that encompasses all forms of equine therapy is ''equine-assisted activities and therapy'' (EAAT). Various therapies that involve interactions with horses and other equines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traveling Carnival
A traveling carnival (American English), usually simply called a carnival, travelling funfair or travelling show (British English), is an amusement show that may be made up of List of amusement rides, amusement rides, food vendors, merchandise vendors, games of chance and skill, thrill acts, and animal acts. A traveling carnival is not set up at a permanent location, like an amusement park or funfair, but is moved from place to place. Its roots are similar to the 19th century circus with both being Fit-up, fitted-up in open fields near or in town and moving to a new location after a period of time. In fact, many carnivals have circuses while others have a clown aesthetic in their decor. Unlike traditional Carnival celebrations, the North American traveling carnival is not tied to a religious observance. History In 1893, the Chicago's World's Columbian Exposition (also called the Chicago World's Fair) was the economic catalyst, catalyst for the development of the modern travel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fair
A fair (archaic: faire or fayre) is a gathering of people for a variety of entertainment or commercial activities. Fairs are typically temporary with scheduled times lasting from an afternoon to several weeks. Fairs showcase a wide range of goods, products, and services, and often include competitions, exhibitions, and educational activities. Fairs can be thematic, focusing on specific industries or interests. Types Variations of fairs include: * Art fairs, including art exhibitions and arts festivals * Book Fairs in communities and schools provide an opportunity for readers, writers, publishers to come together and celebrate literature. * County fair (US) or county show (UK), a public agricultural show exhibiting the equipment, animals, sports and recreation associated with agriculture and animal husbandry. * Festival, an event ordinarily coordinated with a theme e.g. music, art, season, tradition, history, ethnicity, religion, or a national holiday. * Health fair, an event d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Driving (horse)
Driving means guiding a horse in Horse harness, harness to pull a load such as a horse-drawn vehicle, a farm implement, or other load. Horses, pony, ponies, donkeys, mules, and Working animal#Draft animals, other animals can be driven. Typical horse-drawn vehicles are wagons, carriages, carts, and sleighs. Driving activities include pleasure driving, racing, farm work, Horse show, showing horses, and other competitions. Styles For horse training purposes, "driving" may also include the practice of ''long-lining'' (''long reining''), wherein a horse is driven without a cart by a handler walking behind or behind and to the side of the animal. This technique is used in the early stages of training horses for riding as well as for driving. Horses, mules and donkeys are driven in horse harness, harness in many different ways. For working purposes, they can pull a plow or other farm equipment designed to be pulled by animals. In many parts of the world they still pull carts, wagons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse Show
A horse show is a judged exhibition of horses and pony, ponies. Many different horse breeds and equestrianism, equestrian disciplines hold competitions worldwide, from local to the international levels. Most horse shows run from one to three days, sometimes longer for major, all-breed events or national and international championships. Most shows consist of a series of different performances, called ''classes'', wherein a group of horses with similar training or characteristics compete against one another for awards and, often, prize money. International organizations and competitions There are several international disciplines run under rules established by the ''International Federation for Equestrian Sports, Fédération équestre internationale'' (FEI): *Combined driving *Dressage *Endurance riding *Eventing *Para-equestrian *Reining *Show jumping *Horse showmanship, Showmanship *Tent pegging *equestrian vaulting, Vaulting *Western Pleasure The rules of the FEI govern com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shetland Pony Grand National, Somerley Park - Geograph
Shetland (until 1975 spelled Zetland), also called the Shetland Islands, is an archipelago in Scotland lying between Orkney, the Faroe Islands, and Norway, marking the northernmost region of the United Kingdom. The islands lie about to the northeast of Orkney, from mainland Scotland and west of Norway. They form part of the border between the Atlantic Ocean to the west and the North Sea to the east. The island's area is and the population totalled in . The islands comprise the Shetland constituency of the Scottish Parliament. The islands' administrative centre, largest settlement and only burgh is Lerwick, which has been the capital of Shetland since 1708, before which time the capital was Scalloway. Due to its location it is accessible only by ferry or flight with an airport located in Sumburgh as well as a port and emergency airstrip in Lerwick. The archipelago has an oceanic climate, complex geology, rugged coastline, and many low, rolling hills. The largest island, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
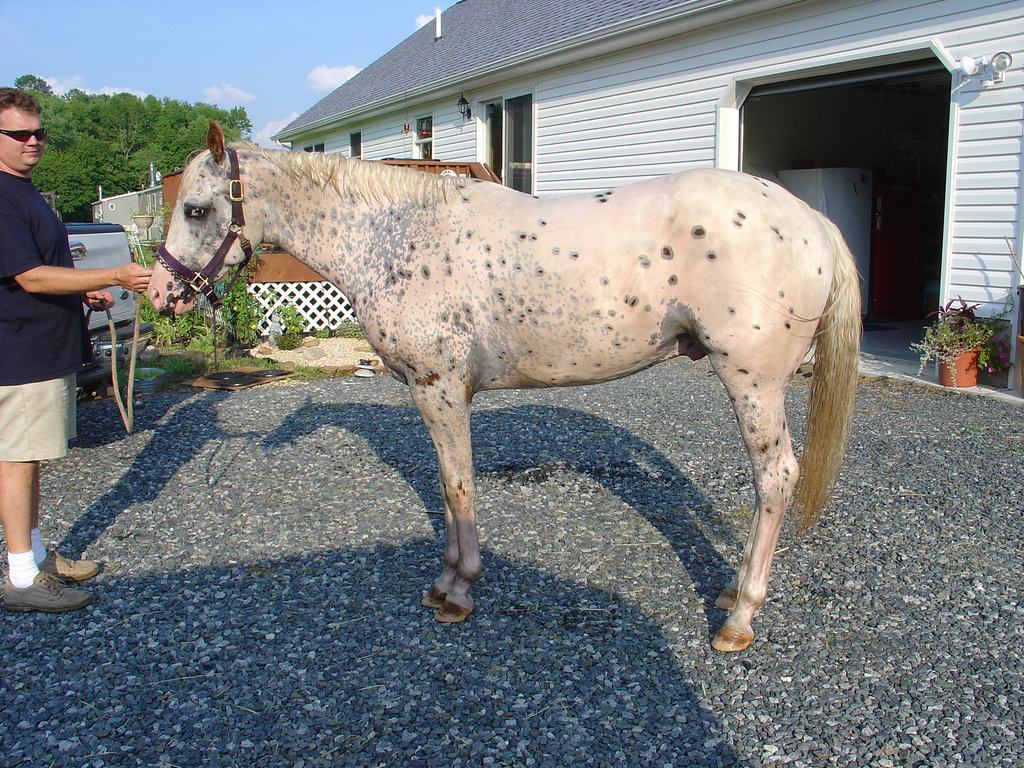
Leopard Complex
The leopard complex is a group of genetically related Equine coat color, coat patterns in horses. These patterns range from progressive increases in interspersed white hair similar to Gray (horse), graying or Roan (horse), roan to distinctive, Dalmatian (dog), Dalmatian-like leopard (pattern), leopard spots on a white coat. Secondary characteristics associated with the leopard complex include a white sclera around the eye, striped horse hoof, hooves and mottling, mottled skin. The leopard complex gene is also linked to abnormalities in the eyes and vision. These patterns are most closely identified with the Appaloosa and Knabstrupper breeds, though its presence in breeds from Asia to western Europe has indicated that it is due to a very ancient mutation. Leopard complex patterns Coat patterns in the leopard complex range from being hardly distinguishable from an unaffected coat, to nearly pure white. Unlike most other Pinto horse, spotting patterns, the spotting and especially th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equine Coat Color
Horses exhibit a diverse array of coat colors and distinctive horse markings, markings. A specialized vocabulary has evolved to describe them. While most horses remain the same coat color throughout life, some undergo gradual color changes as they age. Most horse markings, white markings are present at birth, and the underlying skin color of a healthy horse does not change. Certain coat colors are also associated with specific breeds, such as the Friesian, which is almost exclusively black. The basic outline of equine coat color genetics has largely been resolved, and DNA tests to determine the likelihood that a horse will have offspring of a given color have been developed for some colors. Discussion, research, and even controversy continue about some of the details, particularly those surrounding spotting patterns, color sub-shades such as "sooty (gene), sooty" or "flaxen gene, flaxen", and horse markings, markings. Basic coat colors The two basic pigment colors of horse hair ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannon-bone
The limbs of the horse are structures made of dozens of bones, joints, muscles, tendons, and ligaments that support the weight of the equine body. They include three apparatuses: the suspensory apparatus, which carries much of the weight, prevents overextension of the joint and absorbs shock, the stay apparatus, which locks major joints in the limbs, allowing horses to remain standing while relaxed or asleep, and the reciprocal apparatus, which causes the hock to follow the motions of the stifle. The limbs play a major part in the movement of the horse, with the legs performing the functions of absorbing impact, bearing weight, and providing thrust. In general, the majority of the weight is borne by the front legs, while the rear legs provide propulsion. The hooves are also important structures, providing support, traction and shock absorption, and containing structures that provide blood flow through the lower leg. As the horse developed as a cursorial animal, with a primary def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |