|
Shatkarma
The shatkarmas (Sanskrit: षटकर्म ''ṣaṭkarma'', literally ''six actions''), also known as shatkriyas,Shatkarmas - Cleansing Techniques in Yoga Magazine, a publication of are a set of purifications of the body, to prepare for the main work of yoga towards (liberation). These practices, outlined by |
Hatha Ratnavali
Hatha yoga (; Sanskrit हठयोग, IAST: ''haṭhayoga'') is a branch of yoga that uses physical techniques to try to preserve and channel vital force or energy. The Sanskrit word हठ ''haṭha'' literally means "force", alluding to a system of physical techniques. Some hatha yoga style techniques can be traced back at least to the 1st-century CE, in texts such as the Hindu Sanskrit epics and Buddhism's Pali canon. The oldest dated text so far found to describe hatha yoga, the 11th-century ''Amṛtasiddhi'', comes from a tantric Buddhist milieu. The oldest texts to use the terminology of ''hatha'' are also Vajrayana Buddhist. Hindu hatha yoga texts appear from the 11th century onward. Some of the early hatha yoga texts (11th-13th c.) describe methods to raise and conserve bindu (vital force, that is, semen, and in women ''rajas –'' menstrual fluid). This was seen as the physical essence of life that was constantly dripping down from the head and being lost. Two ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatha Yoga
Hatha yoga (; Sanskrit हठयोग, International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: ''haṭhayoga'') is a branch of yoga that uses physical techniques to try to preserve and channel vital force or energy. The Sanskrit word हठ ''haṭha'' literally means "force", alluding to a system of physical techniques. Some hatha yoga style techniques can be traced back at least to the 1st-century CE, in texts such as the Hindu Itihasa, Sanskrit epics and Buddhism's Pali canon. The oldest dated text so far found to describe hatha yoga, the 11th-century ''Amritasiddhi, Amṛtasiddhi'', comes from a Tantra, tantric Buddhist milieu. The oldest texts to use the terminology of ''hatha'' are also Vajrayana Buddhist. Hindu hatha yoga texts appear from the 11th century onward. Some of the early hatha yoga texts (11th-13th c.) describe methods to raise and conserve bindu (vital force, that is, semen, and in women ''rajas –'' menstrual fluid). This was seen as the physical esse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gheranda Samhita
''Gheranda Samhita'' (IAST: gheraṇḍasaṁhitā, घेरंडसंहिता, meaning “Gheranda's collection”) is a Sanskrit text of Yoga in Hinduism. It is one of the three classic texts of hatha yoga (the other two being the '' Hatha Yoga Pradipika'' and the '' Shiva Samhita''), and one of the most encyclopedic treatises in yoga.B. Heimann (1937)Review: The Ǧheraṇda Saṁhitā. A Treatise on Haṭha Yoga by Śrīś Chandra Vasu The Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland, Cambridge University Press, No. 2 (Apr., 1937), pp. 355-357 Fourteen manuscripts of the text are known, which were discovered in a region stretching from Bengal to Rajasthan. The first critical edition was published in 1933 by Adyar Library, and the second critical edition was published in 1978 by Digambarji and Ghote. Some of the Sanskrit manuscripts contain ungrammatical and incoherent verses, and some cite older Sanskrit texts. It is likely a late 17th-century te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
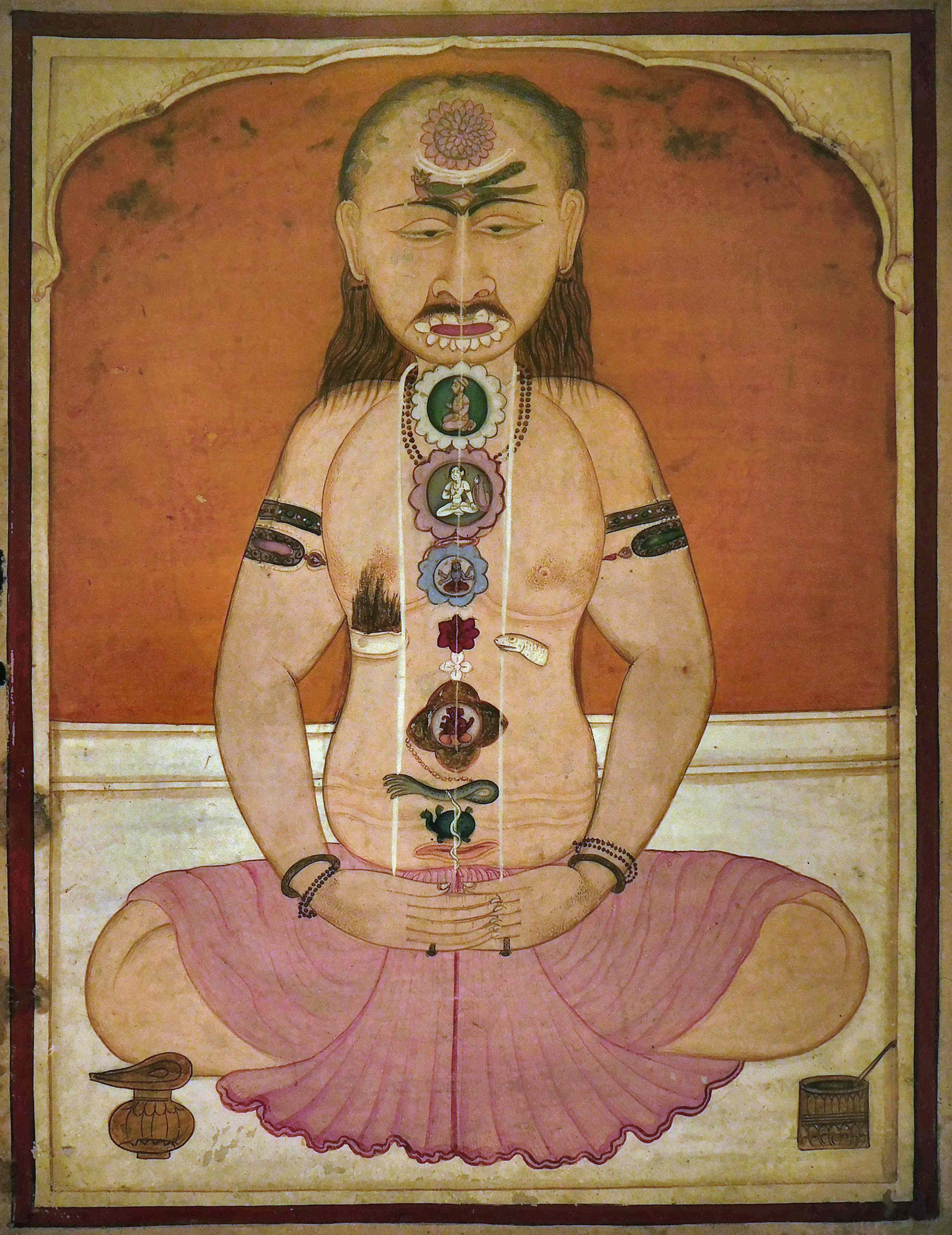
Sushumna
() is a term for the channels through which, in traditional Indian medicine and spiritual theory, the energies such as prana of the physical body, the subtle body and the causal body are said to flow. Within this philosophical framework, the nadis are said to connect at special points of intensity, the chakras. All nadis are said to originate from one of two centres; the heart and the ''kanda'', the latter being an egg-shaped bulb in the pelvic area, just below the navel. The three principal nadis run from the base of the spine to the head, and are the ida on the left, the sushumna in the centre, and the pingala on the right. Ultimately the goal is to unblock these nadis to bring liberation. Overview Nadi is an important concept in Hindu philosophy, mentioned and described in the sources, some as much as 3,000 years old. The number of nadis of the human body is claimed to be up to hundreds-of-thousands and even millions. The '' Shiva Samhita'' treatise on yoga states, for e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trāṭaka
Trāṭaka (Sanskrit: त्राटक "look, gaze") is a yogic purification (a shatkarma) and a tantric method of meditation that involves staring at a single point such as a small object, black dot or candle flame. Description The practitioner may fix attention on a symbol or yantra, such as the Om symbol, a black dot, the image of some deity or guru, a flame, a mirror or any point, and stare at it. A candle should be three to four feet (1 metre plus) away, the flame level with the eyes. The practitioner relaxes but keeps the spine erect and remains wakeful and vigilant. References Further reading * The Bihar School of Yoga, in India has published several books on meditation that discuss trataka. ''Dharana Darshan'' by Swami Niranjanananda Saraswati Swami Niranjanananda Saraswati (born 14 February 1960) is the successor of Satyananda Saraswati, founder of Satyananda Yoga, who passed on the worldwide coordination of Satyananda Yoga to Niranjanananda in 1988. He is Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kapalabhati
Kapalabhati (, "Skull-polishing") is an important shatkarma, a purification in hatha yoga. The word kapalabhati is made up of two Sanskrit words: ''kapāla'' meaning "skull", and ''bhāti'' meaning "shining, illuminating". It is intended mainly for cleaning the sinuses but according to the ''Gheranda Samhita'' has magical curative effects. In the Jivamukti Yoga of David Life and Sharon Gannon, three forms of Kapalabhati are practised, derived from the ''Gheranda Samhita'' 1:54: * ''Vatakrama'', a practice similar to the pranayama technique of Bhastrika Bhastrikā is an important breath exercise in yoga and pranayama. It is sometimes treated as a kriya or 'cleansing action' along with kapalabhati to clear the airways in preparation for other pranayama techniques. Bhastrika involves a rapid and f ... or "Breath of Fire", except that exhalation is active while inhalation is passive, the opposite of normal breathing. * ''Vyutkrama'', a practice similar to Jala neti, it involves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svatmarama
The ''Haṭha Yoga Pradīpikā'' ( or Light on Hatha Yoga) is a classic fifteenth-century Sanskrit manual on haṭha yoga, written by Svātmārāma, who connects the teaching's lineage to Matsyendranath of the Nathas. It is among the most influential surviving texts on haṭha yoga, being one of the three classic texts alongside the ''Gheranda Samhita'' and the '' Shiva Samhita''. More recently, eight works of early hatha yoga that may have contributed to the ''Hatha Yoga Pradipika'' have been identified. Title and composition Different manuscripts offer different titles for the text, including ''Haṭhayogapradīpikā'', ''Haṭhapradīpikā'', ''Haṭhapradī'', and ''Hath-Pradipika''. It was composed by Svātmārāma in the 15th century as a compilation of the earlier haṭha yoga texts. Svātmārāma incorporates older Sanskrit concepts into his synthesis. He introduces his system as a preparatory stage for physical purification before higher meditation or Raja Yoga. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kapalabhati - International Day Of Yoga Celebration - NCSM - Kolkata 2017-06-21 2472
Kapalabhati (, "Skull-polishing") is an important shatkarma, a purification in hatha yoga. The word kapalabhati is made up of two Sanskrit words: ''kapāla'' meaning "skull", and ''bhāti'' meaning "shining, illuminating". It is intended mainly for cleaning the sinuses but according to the ''Gheranda Samhita'' has magical curative effects. In the Jivamukti Yoga of David Life and Sharon Gannon, three forms of Kapalabhati are practised, derived from the ''Gheranda Samhita'' 1:54: * ''Vatakrama'', a practice similar to the pranayama technique of Bhastrika or "Breath of Fire", except that exhalation is active while inhalation is passive, the opposite of normal breathing. * ''Vyutkrama'', a practice similar to Jala neti, it involves sniffing water through the nostrils and letting it flow down into the mouth, and then spitting it out. * ''Shītkrama'', essentially the reverse of ''Vyutkrama'', in which water is taken through the mouth and expelled through the nose. See also * Kundali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
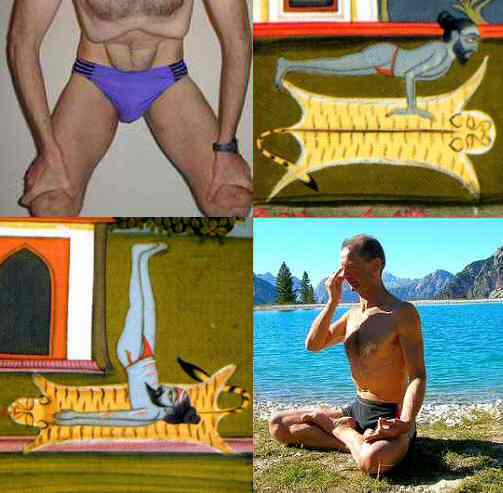
Nauli
__notoc__ Nauli is one of the '' kriyas'' or ''shatkarmas'', preliminary purifications, used in yoga. The exercise is claimed to serve the cleaning of the abdominal region (digestive organs, small intestine) and is based on a massage of the internal belly organs by a circular movement of the abdominal muscles. It is performed standing with the feet apart and the knees bent. The 15th century ''Hatha Yoga Pradipika'' claims that Nauli (magically) removes all diseases. ''Nauli'' is an exercise of classical hatha yoga; it is not often taught in yoga as exercise. There are four steps, which are learned one after another: # the abdominal lock, uddiyana bandha A bandha () is a kriyā in Hatha Yoga, being a kind of internal mudra described as a "body lock," to lock the vital energy into the body. ''Bandha'' literally means bond, fetter, or "catching hold of".Iyengar, 1976: pp.435–437Iyengar, 1976: p.52 ...: the lungs are emptied, and the abdomen is pulled inwards and upwards under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kapalabhati (Hatha Yoga)
Kapalabhati (, "Skull-polishing") is an important shatkarma, a purification in hatha yoga. The word kapalabhati is made up of two Sanskrit words: ''kapāla'' meaning "skull", and ''bhāti'' meaning "shining, illuminating". It is intended mainly for cleaning the sinuses but according to the ''Gheranda Samhita'' has magical curative effects. In the Jivamukti Yoga of David Life and Sharon Gannon, three forms of Kapalabhati are practised, derived from the ''Gheranda Samhita'' 1:54: * ''Vatakrama'', a practice similar to the pranayama technique of Bhastrika or "Breath of Fire", except that exhalation is active while inhalation is passive, the opposite of normal breathing. * ''Vyutkrama'', a practice similar to Jala neti, it involves sniffing water through the nostrils and letting it flow down into the mouth, and then spitting it out. * ''Shītkrama'', essentially the reverse of ''Vyutkrama'', in which water is taken through the mouth and expelled through the nose. See also * Kundali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |