|
Sharovarshchyna
''Sharovarshchyna'' ( ; also ''sharovarstvo'' [] or ''sharovarnytstvo'' []; from ''sharovary'', stereotypical Cossack pants) is a Culturology, culturological and journalistic term, usually negative, for the ethnic stereotype of Ukrainian culture through pseudo-folk, kitsch elements of costume and life. ''Sharovarshchyna'' identifies Ukrainian culture with the culture of the peasants and Cossacks, relying on their folklore and theatrical image popularized in the late 19th century. The heyday of ''sharovarshchyna'' and the popularization of this term, however, took place in the second half of the twentieth century. Characteristics Sharovarshchyna is usually understood as an imitation of folk peasant culture that substitutes for authentic culture. Sharovarshchyna creates the impression that Ukrainian culture is entirely peasant in origin and cannot go beyond folk peasant culture; that modern phenomena and art trends are impossible in it, but exist only as layers of other cultures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2010
The year saw a multitude of natural and environmental disasters such as the 2010 Haiti earthquake, the Deepwater Horizon oil spill, and the 2010 Chile earthquake. The 2009 swine flu pandemic, swine flu pandemic which began the previous year dissipated in this year. In addition, the OECD, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) gained four new members; Chile, Slovenia, Israel, and Estonia. 2010 also saw advancements in technology such as the release of the iPad, the public launch of Instagram, and the first successful trapping of antimatter. 2010 was designated as: *International Year of Biodiversity *International Year of Youth *2010 European Year for Combating Poverty and Social Exclusion *International Year for the Rapprochement of Cultures Pronunciation There is a debate among experts and the general public on how to pronounce specific years of the 21st century in English. The year 2010 is pronounced either "twenty-ten" or "two thousand (and) ten" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borsch
Borscht () is a sour soup, made with meat Stock (food), stock, vegetables and seasonings, common in Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. In English, the word ''borscht'' is most often associated with the soup's variant of Ukraine, Ukrainian origin, made with red beetroots as one of the main ingredients, which give the dish its distinctive red color. The same name, however, is also used for a wide selection of sour-tasting soups without beetroots, such as sorrel-based Sorrel soup, green borscht, rye-based Sour rye soup, white borscht, and cabbage borscht. Borscht derives from an ancient soup originally cooked from pickled stems, leaves and umbels of Heracleum sphondylium, common hogweed (''Heracleum sphondylium''), an herbaceous plant growing in damp meadows, which lent the dish its Slavic languages, Slavic name. With time, it evolved into a diverse array of tart soups, among which the Ukrainian beet-based red borscht has become the most popular. It is typically made by combining ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
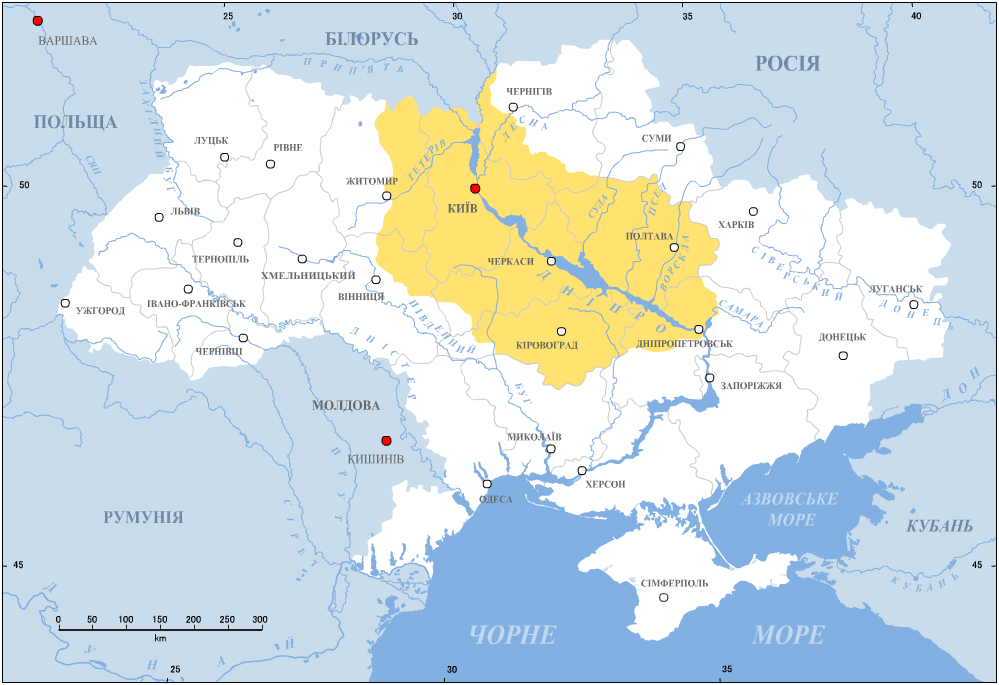
Naddniprianshchyna
The term Dnieper Ukraine (), usually refers to territory on either side of the middle course of the Dnieper River. The Ukrainian name derives from ''nad‑'' (prefix: "above, over") + ''Dnipró'' ("Dnieper") + ''‑shchyna'' (suffix denoting a geographic region). Historically, this region is tightly entwined with the history of Ukraine and is considered as the heart of the country. Due to its size, the region is conditionally subdivided into Upper Dnieper Ukraine, Central Dnieper Ukraine, and Lower Dnieper Ukraine in reference to Dnieper's stream flow. Upper and Central separate at mouth of Desna River which is roughly the city of Kyiv, while Lower and Central around Khortytsia which is roughly the city of Zaporizhia. The term ''Dnieper Ukraine'' appeared soon after the partitions of Poland when Ukraine as former territory of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth became divided between the Russian Empire and Austrian Empire and was referred to the Russian controlled Ukraine. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnography
Ethnography is a branch of anthropology and the systematic study of individual cultures. It explores cultural phenomena from the point of view of the subject of the study. Ethnography is also a type of social research that involves examining the behavior of the participants in a given social situation and understanding the group members' own interpretation of such behavior. As a form of inquiry, ethnography relies heavily on participant observation, where the researcher participates in the setting or with the people being studied, at least in some marginal role, and seeking to document, in detail, patterns of social interaction and the perspectives of participants, and to understand these in their local contexts. It had its origin in social and cultural anthropology in the early twentieth century, but has, since then, spread to other social science disciplines, notably sociology. Ethnographers mainly use Qualitative research, qualitative methods, though they may also include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symon Petliura
Symon Vasyliovych Petliura (; – 25 May 1926) was a Ukrainian politician and journalist. He was the Supreme Commander of the Ukrainian People's Army (UNA) and led the Ukrainian People's Republic during the Ukrainian War of Independence, a part of the wider Russian Civil War. Petliura was born to a family of Cossack heritage in Poltava. From an early age he embraced socialism and Ukrainian nationalism, which he advocated through his highly prolific career as a journalist. After the 1917 February Revolution overthrew the Tsarist monarchy, the Ukrainian People's Republic was proclaimed and Petliura was elected head of its military. The Republic was briefly interrupted by the pro-German Ukrainian State, but in late 1918 Petliura, along with other members of the socialist Directorate of Ukraine, organised a revolt and overthrew the regime, restoring the Republic. He became the leader of the Directorate in early 1919, after the Bolsheviks invaded Ukraine and drove the UNA to Galic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesya Ukrainka
Lesya Ukrainka (, ; born Larysa Petrivna Kosach, ; – ) was one of Ukrainian literature's foremost writers, best known for her poems and plays. She was also an active political, civil, and feminist activist. Among her best-known works are the collections of poems ''On the Wings of Songs'' (1893), ''Thoughts and Dreams'' (1899), ''Echos'' (1902), the epic poem ''Ancient Fairy Tale'' (1893), ''One Word'' (1903), plays ''Princess'' (1913), ''Cassandra'' (1903–1907), ''In the Catacombs'' (1905), and '' Forest Song'' (1911). Biography Lesya Ukrainka was born in 1871 in the town of Novohrad-Volynskyi (now Zviahel) of Ukraine. She was the second child of Ukrainian writer and publisher Olha Drahomanova-Kosach, better known under her pen-name Olena Pchilka. Ukrainka's father was Petro Kosach (from the Kosača noble family), head of the district assembly of conciliators, who came from the northern part of Chernihiv province. After completing high school in Chernihiv Gymnasium, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Franko
Ivan Yakovych Franko (, ; 27 August 1856 – 28 May 1916) was a Ukrainian poet, writer, social and literary critic, journalist, translator, economist, political activist, doctor of philosophy, ethnographer, and the author of the first detective novels and modern poetry in the Ukrainian language. He was a political radical, and a founder of the socialist and nationalist movement in Western Ukraine. In addition to his own literary work, he also translated into Ukrainian the works of such renowned figures as William Shakespeare, Lord Byron, Pedro Calderón de la Barca, Dante Alighieri, Victor Hugo, Adam Mickiewicz, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe and Friedrich Schiller. His translations appeared on the stage of the Ruska Besida Theatre. Along with Taras Shevchenko, he has had a tremendous influence on modern literary and political thought in Ukraine. Biography Early years Franko was born in the Ukrainian village of Nahuievychi, then located in the Austrian '' kronland'' of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makarov Anatolii Mykolaiovych
Makarov or Makarow may refer to: __NOTOC__ Places * Makarov, Russia, a town in Sakhalin Oblast * Makarov Basin, in the Arctic Ocean * Makariv, a town in Ukraine, often known by the Russian form People * Makarov (Hasidic dynasty) * Makarov (surname) Other uses * 5545 Makarov, an asteroid * 9×18mm Makarov, a pistol cartridge * Makarov PM The Makarov pistol or PM ( rus, Пистолет Макарова, r=Pistolet Makarova, p=pʲɪstɐˈlʲet mɐˈkarəvə, t=Makarov's Pistol) is a Soviet semi-automatic pistol. Under the project leadership of Nikolay Fyodorovich Makarov, it bec ..., a semi-automatic pistol * Vladimir Makarov, a fictional character in the ''Call Of Duty: Modern Warfare'' series See also * Admiral Makarov (other) * * Makarovsky (other) {{Disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yushchenko Oleksa Yakovlevych
Viktor Andriiovych Yushchenko (, ; born 23 February 1954) is a Ukrainian politician who was the third president of Ukraine from 23 January 2005 to 25 February 2010. He aimed to orient Ukraine towards the West, European Union, and NATO. Yushchenko's first career was in the banking industry. In 1993, he became governor of the National Bank of Ukraine, presiding over their response to hyperinflation and the introduction of a national currency. From 1999 to 2001 he was prime minister under President Leonid Kuchma. After his dismissal as prime minister, Yushchenko went into opposition to President Kuchma and founded Our Ukraine Bloc, which at the 2002 parliamentary election became Ukraine's most popular political force. As an informal leader of the Ukrainian opposition coalition, he was one of the two main candidates in the 2004 Ukrainian presidential election, the other being Prime Minister Viktor Yanukovych. During the election campaign in late 2004, Yushchenko became the victim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perestroika
''Perestroika'' ( ; rus, перестройка, r=perestrojka, p=pʲɪrʲɪˈstrojkə, a=ru-perestroika.ogg, links=no) was a political reform movement within the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) during the late 1980s, widely associated with CPSU general secretary Mikhail Gorbachev and his '' glasnost'' (meaning "transparency") policy reform. The literal meaning of ''perestroika'' is "restructuring," referring to the restructuring of the political economy of the Soviet Union in an attempt to end the Era of Stagnation. ''Perestroika'' allowed more independent actions from various ministries and introduced many market-like reforms. The purported goal of ''perestroika'' was not to end the planned economy, but rather to make socialism work more efficiently to better meet the needs of Soviet citizens by adopting elements of liberal economics. The process of implementing ''perestroika'' added to existing shortage and created political, social, and economic tensions wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks, led by Vladimir Lenin, were a radical Faction (political), faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) which split with the Mensheviks at the 2nd Congress of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party, Second Party Congress in 1903. The Bolshevik party, formally established in 1912, seized power in Russia in the October Revolution of 1917, and was later renamed the Russian Communist Party, All-Union Communist Party, and ultimately the Communist Party of the Soviet Union. Its ideology, based on Leninism, Leninist and later Marxism–Leninism, Marxist–Leninist principles, became known as Bolshevism. The origin of the RSDLP split was Lenin's support for a smaller party of professional revolutionaries, as opposed to the Menshevik desire for a broad party membership. The influence of the factions fluctuated in the years up to 1912, when the RSDLP formally split in two. The political philosophy of the Bolsheviks was based on the Leninist pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |