|
Shah Of Iran
The monarchs of Iran ruled for over two and a half millennia, beginning as early as the 7th century BC and enduring until the 20th century AD. The earliest Iranian king is generally considered to have been either Deioces of the Median dynasty () or Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty (550–330 BC). The last Iranian king was Mohammad Reza Pahlavi of the Pahlavi dynasty (1925–1979), which was overthrown by the Islamic Revolution. Since then, Iran has been governed as an Islamic republic#Iran, Islamic republic. In classical antiquity, Iran reached the peak of its power and prestige under the Achaemenid Empire, which stretched from Achaemenid Egypt, Egypt and parts of Southeast Europe in the west to the Achaemenid conquest of the Indus Valley, Indus Valley and parts of Central Asia in the east. By 323 BC, the Achaemenid Empire's territories had been conquered by the Macedonian Empire during the Wars of Alexander the Great, bringing Iran into the Hellenistic period, Hellenist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Language
Persian ( ), also known by its endonym and exonym, endonym Farsi (, Fārsī ), is a Western Iranian languages, Western Iranian language belonging to the Iranian languages, Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian languages, Indo-Iranian subdivision of the Indo-European languages. Persian is a pluricentric language predominantly spoken and used officially within Iran, Afghanistan, and Tajikistan in three mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible standard language, standard varieties, respectively Iranian Persian (officially known as ''Persian''), Dari, Dari Persian (officially known as ''Dari'' since 1964), and Tajik language, Tajiki Persian (officially known as ''Tajik'' since 1999).Siddikzoda, S. "Tajik Language: Farsi or not Farsi?" in ''Media Insight Central Asia #27'', August 2002. It is also spoken natively in the Tajik variety by a significant population within Uzbekistan, as well as within other regions with a Persianate society, Persianate history in the cultural sphere o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iranian Peoples
Iranian peoples, or Iranic peoples, are the collective ethnolinguistic groups who are identified chiefly by their native usage of any of the Iranian languages, which are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages within the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. The Proto-Iranian language, Proto-Iranians are believed to have emerged as a separate branch of the Indo-Iranians in Central Asia around the mid-2nd millennium BC. At their peak of expansion in the mid-1st millennium BC, the territory of the Iranian peoples stretched across the entire Eurasian Steppe; from the Danube, Danubian Plains in the west to the Ordos Plateau in the east and the Iranian Plateau in the south.: "From the first millennium b.c., we have abundant historical, archaeological and linguistic sources for the location of the territory inhabited by the Iranian peoples. In this period the territory of the northern Iranians, they being equestrian nomads, extended over the whole zone of the ste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Conquest Of The Indus Valley
Around 535 BCE, the Persian king Cyrus the Great initiated a protracted campaign to absorb parts of India into his nascent Achaemenid Empire. In this initial incursion, the Persian army annexed a large region to the west of the Indus River, consolidating the early eastern borders of their new realm. With a brief pause after Cyrus' death around 530 BCE, the campaign continued under Darius the Great, who began to re-conquer former provinces and further expand the Achaemenid Empire's political boundaries. Around 518 BCE, the Persian army pushed further into India to initiate a second period of conquest by annexing regions up to the Jhelum River in what is today known as Punjab. At peak, the Persians managed to take control of most of modern-day Pakistan and incorporate it into their territory. The first secure epigraphic evidence through the Behistun Inscription gives a date before or around 518 BCE. Persian penetration into the Indian subcontinent occurred in multiple stages, begi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southeast Europe
Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe is a geographical sub-region of Europe, consisting primarily of the region of the Balkans, as well as adjacent regions and Archipelago, archipelagos. There are overlapping and conflicting definitions of the region, due to political, economic, historical, cultural, and geographical considerations. Sovereign state, Sovereign states and territories that may be included in the region are Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia (alternatively placed in Central Europe), Greece (alternatively placed in the broader region of Southern Europe), Kosovo, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Romania (alternatively placed in Eastern Europe), Serbia, and the East Thrace, European part of Turkey (alternatively placed in the broader region of Southern Europe, also in West Asia, Western Asia with the rest of the country). Sometimes, Cyprus (most often placed in West Asia), Hungary (most often placed in Central Europe), Moldova (most often placed in Easte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Egypt
The history of Persian Egypt refers to the two periods when ancient Egypt was controlled by the Achaemenid Empire: * Twenty-seventh Dynasty of Egypt (525–404 BC), established by the first Achaemenid conquest of Egypt. * Thirty-first Dynasty of Egypt (343–332 BC), established by the second Achaemenid conquest of Egypt. These two periods of satrapies were punctuated by a brief interval of Egyptian independence from 404 BC to 343 BC. Background In the 6th century BC, Persian rulers, particularly Cyrus the Great, sought to expand their imperialist agenda to include Egypt. Expansionism was a key strategy for empires of the ancient world to establish military and economic dominance, and Egypt was a priority of Cyrus the Great's, in large part due to the desirability of the Nile river and valley as economic assets. The contemporaneous Egyptian pharaoh, Amasis, attempted to ward off the occupation by forming alliances with neighbouring rulers, in particular Polycrates of Samos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Antiquity
Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural History of Europe, European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the interwoven civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome, Rome known together as the Greco-Roman world, centered on the Mediterranean Basin. It is the period during which ancient Greece and Rome flourished and had major influence throughout much of Europe, North Africa, and West Asia. Classical antiquity was succeeded by the period now known as late antiquity. Conventionally, it is often considered to begin with the earliest recorded Homeric Greek, Epic Greek poetry of Homer (8th–7th centuries BC) and end with the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 AD. Such a wide span of history and territory covers many disparate cultures and periods. ''Classical antiquity'' may also refer to an idealized vision among later people of what was, in Ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Republic
The term Islamic republic has been used in different ways. Some Muslim religious leaders have used it as the name for a form of Islamic theocratic government enforcing sharia, or laws compatible with sharia. The term has also been used for a sovereign state taking a compromise position between a purely Islamic caliphate and a secular, nationalist republic. The term is currently used in the official title of three states — the Islamic Republics of Iran, Pakistan, and Mauritania. Pakistan first adopted the title under the constitution of 1956. Mauritania adopted it on 28 November 1958. Iran adopted it after the 1979 Iranian Revolution that overthrew the Pahlavi dynasty. Despite having similar names, the countries differ greatly in their governments and laws. Iran and Mauritania are religious theocratic states. Pakistan adopted the name in 1956 before Islam was yet to be declared the state religion, this happened at the adoption of the 1973 constitution. Iran officially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pahlavi Dynasty
The Pahlavi dynasty () is an List of monarchs of Iran, Iranian royal dynasty that was the Pahlavi Iran, last to rule Iran before the country's monarchy was abolished by the Iranian Revolution in 1979. It was founded in 1925 by Reza Shah, Reza Shah Pahlavi, a non-aristocratic Iranian soldier of Mazanderani people, Mazanderani origin, who took on the name of the Pahlavi scripts of the Middle Persian, Middle Persian language from the Sasanian Empire of Muslim conquest of Persia, pre-Islamic Iran. The dynasty largely espoused this form of Iranian nationalism rooted in the pre-Islamic era (notably based on the Achaemenid Empire) during its time in power, especially under its last king Mohammad Reza Pahlavi. The dynasty replaced the Qajar dynasty in 1925 after the 1921 Persian coup d'état, 1921 coup d'état, beginning on 14 January 1921 when 42-year-old soldier Reza Shah, Reza Khan was promoted by British General Edmund Ironside, 1st Baron Ironside, Edmund Ironside to lead the Britis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reza Shah
Reza Shah Pahlavi born Reza Khan (15 March 1878 – 26 July 1944) was shah of Iran from 1925 to 1941 and founder of the roughly 53 years old Pahlavi dynasty. Originally a military officer, he became a politician, serving as minister of war and Prime Minister of Iran, prime minister of Iran, and was elected shah following the deposition of the last monarch of the Qajar dynasty. Reza Shah's reign ended when he was forced to abdicate after the Anglo-Soviet invasion of Iran in 1941. He was succeeded by his eldest son, Mohammad Reza Shah. A moderniser, Reza Shah clashed with the Shia clergy and introduced social, economic, and political reforms during his reign, ultimately laying the foundations of the History of Iran#Late modern period, modern Iranian state. Therefore, he is regarded by many as the founder of modern Iran, until his ouster by the Islamic Revolution. At the age of 14, Reza Khan joined the Persian Cossack Brigade. He rose through the ranks, becoming a brigadier gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary'' is a large American dictionary, first published in 1966 as ''The Random House Dictionary of the English Language: The Unabridged Edition''. Edited by Editor-in-chief Jess Stein, it contained 315,000 entries in 2256 pages, as well as 2400 illustrations. The CD-ROM version in 1994 also included 120,000 spoken pronunciations. History The Random House publishing company entered the reference book market after World War II. They acquired rights to the ''Century Dictionary'' and the ''Dictionary of American English'', both out of print. Their first dictionary was Clarence Barnhart's ''American College Dictionary'', published in 1947, and based primarily on ''The New Century Dictionary'', an abridgment of the ''Century''. In the late 1950s, it was decided to publish an expansion of the ''American College Dictionary'', which had been modestly updated with each reprinting since its publication. Under editors Jess Stein and Laurence Urdan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
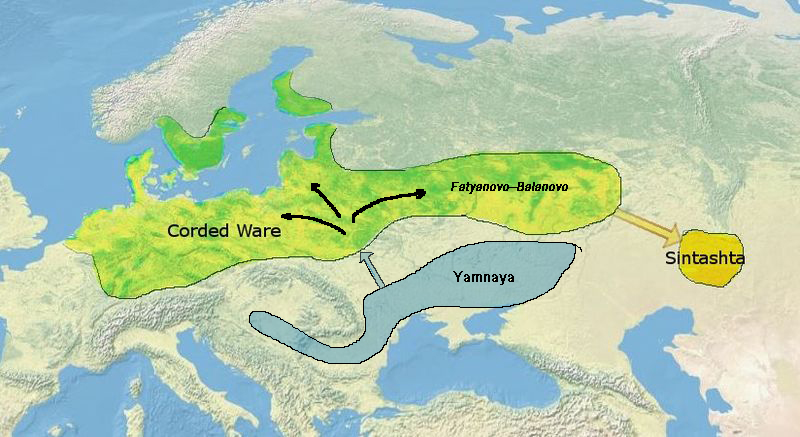
Proto-Indo-Iranians
The Indo-Iranian peoples, also known as Ā́rya or Aryans from their self-designation, were a group of Indo-European speaking peoples who brought the Indo-Iranian languages to parts of Europe, Central Asia, and South Asia in waves from the first part of the 2nd millennium BC onwards. They eventually branched out into the Iranian peoples and Indo-Aryan peoples. Nomenclature The term ''Aryan'' has long been used to denote the ''Indo-Iranians'', because ''Ā́rya'' was the self-designation of the ancient speakers of the Indo-Iranian languages, specifically the Iranian and the Indo-Aryan peoples, collectively known as the Indo-Iranians. Despite this, some scholars use the term Indo-Iranian to refer to this group, though the term "Aryan" remains widely used by most scholars, such as Josef Wiesehofer, Will Durant, and Jaakko Häkkinen. Population geneticist Luigi Luca Cavalli-Sforza, in his 1994 book ''The History and Geography of Human Genes'', also uses the term Aryan to describ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arya (Iran)
Arya (, ; , ; , ; , ; , ) was the ethnonym used by Iranians during the early History of Iran. In contrast to cognates of Arya used by the Vedic people and Iranic steppe nomads, the term is commonly translated using the modern ethnonym Iranian. During Old Iranian times, the term was connected with one's lineage, with speaking an Iranian language and with the worship of Ahura Mazda. Being an Arya, therefore, had ethnic, linguistic and religious aspects. During the Middle Iranian period, it acquired a distinct political aspect through the concept of Eran Shahr (''Aryas' dominion''). Arya was also contrasted with Anarya (, ; , ), denoting non-Iranian lands and peoples. After the Islamic conquest of Iran, the ethnonym fell out of use, but the term Eran experienced a revival during the Iranian Renaissance, now as a toponym for Greater Iran. The modern ethnonym Iranian is a back-formation from the toponym Eran, itself a back-formation from the older Arya. Origin and deline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |