|
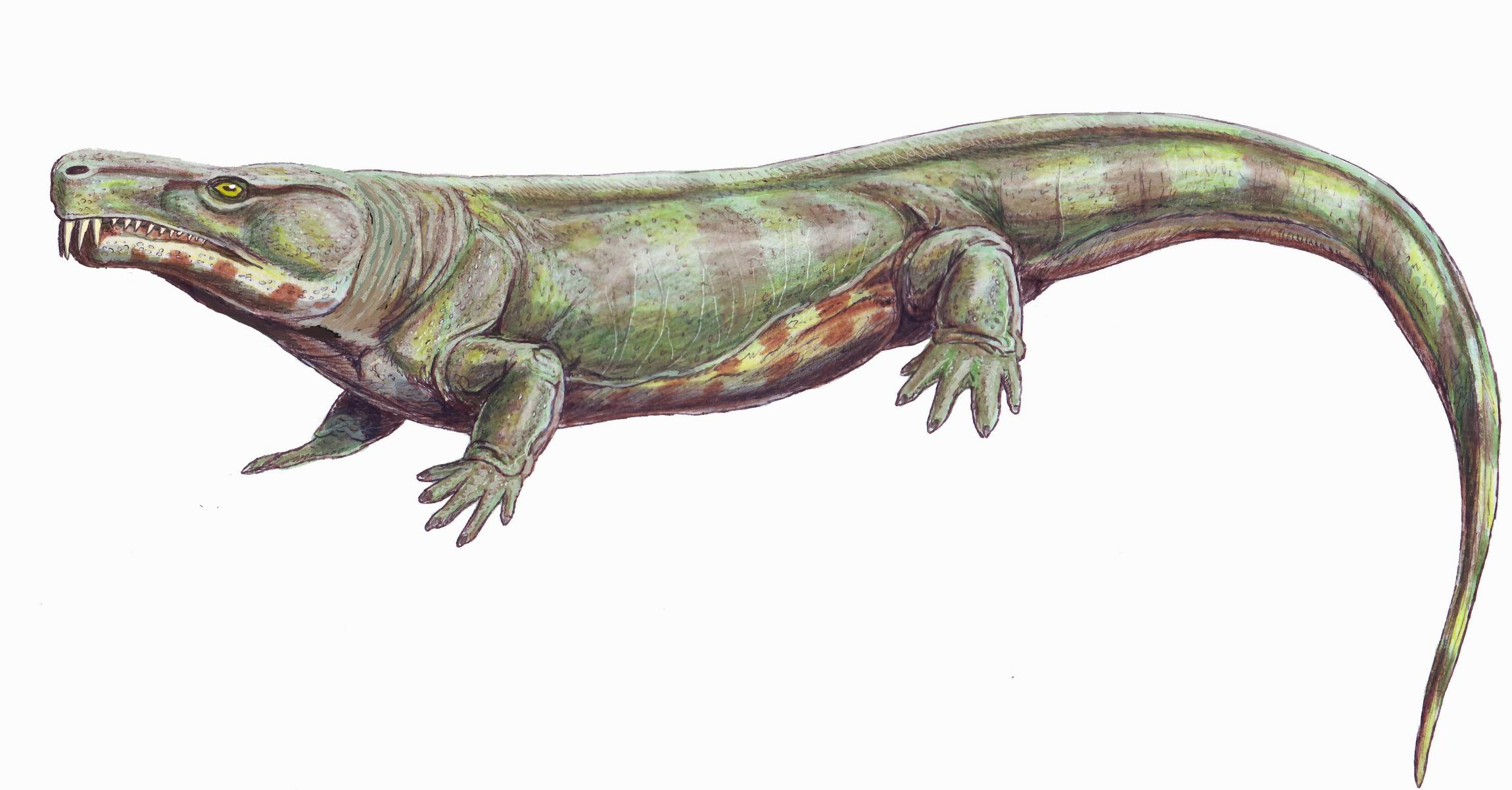
Seymouriamorpha
Seymouriamorpha were a small but widespread group of limbed vertebrates (tetrapods). They have long been considered stem group, stem-amniotes (reptiliomorphs), and most paleontologists still accept this point of view, but some analyses suggest that seymouriamorphs are stem-tetrapods (not more closely related to Amniota than to Lissamphibia). Many seymouriamorphs were terrestrial or semi-aquatic. However, aquatic larvae bearing external gills and grooves from the lateral line system have been found, making them unquestionably non-amniotes. As they matured, they became more terrestrial and reptile-like. They ranged from 30 cm (1 ft) long lizard-sized creatures to the 1.5 m (5 ft) long ''Enosuchus''. If seymouriamorphs are reptiliomorphs, they were the distant relatives of amniotes. Seymouriamorphs are divided into three main groups: Kotlassiidae, Discosauriscidae, and Seymouriidae, which includes the best-known genus, ''Seymouria''. The last seymouriamorphs became Permian-Triassic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiliomorph
Reptiliomorpha (meaning reptile-shaped; in PhyloCode known as ''Pan-Amniota'') is a clade containing the amniotes and those tetrapods that share a more recent common ancestor with amniotes than with living amphibians (lissamphibians). It was defined by Michel Laurin (2001) and Vallin and Laurin (2004) as the largest clade that includes ''Homo sapiens'', but not '' Ascaphus truei'' (tailed frog). Laurin and Reisz (2020) defined Pan-Amniota as the largest total clade containing ''Homo sapiens'', but not '' Pipa pipa'', '' Caecilia tentaculata'', and '' Siren lacertina''. The informal variant of the name, "reptiliomorphs", is also occasionally used to refer to stem-amniotes, i.e. a grade of reptile-like tetrapods that are more closely related to amniotes than they are to lissamphibians, but are not amniotes themselves; the name is used in this meaning e.g. by Ruta, Coates and Quicke (2003). An alternative name, " Anthracosauria", is also commonly used for the group, but is confusin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seymouria
''Seymouria'' is an extinct genus of seymouriamorph from the Early Permian of North America and Europe. Although they were amphibians (in a biological sense), ''Seymouria'' were well-adapted to life on land, with many reptilian features—so many, in fact, that ''Seymouria'' was first thought to be a primitive reptile. It is primarily known from two species, ''Seymouria baylorensis'' and ''Seymouria sanjuanensis''. The type species, ''S. baylorensis'', is more robust and specialized, though its fossils have only been found in Texas. On the other hand, ''S. sanjuanensis'' is more abundant and widespread. This smaller species is known from multiple well-preserved fossils, including a block of six skeletons found in the Cutler Formation of New Mexico, and a pair of fully grown skeletons from the Tambach Formation of Germany, which were fossilized lying next to each other. For the first half of the 20th century, ''Seymouria'' was considered one of the oldest and most "primitive" kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kotlassia
''Kotlassia'' (meaning "of Kotlas") extinct genus of kotlassiine seymouriamorph from the Late Permian of Russia. The type, and currently only, species is ''K. prima''. Discovery and naming During the 1890s, Russian paleontologist Vladimir Amalitsky discovered freshwater sediments dating from the Upper Permian in Northern Dvina, Arkhangelsk Oblast, northern European Russia. The locality, known as PIN 2005, consists of a creek with sandstone and lens-shaped exposures in a bank escarpment, containing many particularly well-preserved fossil skeletons, including the holotypes of ''Inostrancevia'' and ''Kotlassia''. Vladimir Amalitzky named and described ''Kotlassia prima'' in 1921 on the basis of the holotype specimen, an entire skeleton, and one additional skull; the additional skull has been described ad over-prepared by Bulanov (2003). It is often incorrectly assumed that ''Kotlassia prima'' was described by Amalitzky in 1898. A second species, ''K. secunda'', was also named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapods
A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek τετρα- ''(tetra-)'' 'four' and πούς ''(poús)'' 'foot') is any four- limbed vertebrate animal of the clade Tetrapoda (). Tetrapods include all extant and extinct amphibians and amniotes, with the latter in turn evolving into two major clades, the sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (extinct "pelycosaurs", therapsids and all extant mammals, including humans). Hox gene mutations have resulted in some tetrapods becoming limbless (snakes, legless lizards, and caecilians) or two-limbed (cetaceans, sirenians, some lizards, kiwis, and the extinct moa and elephant birds). Nevertheless, they still qualify as tetrapods through their ancestry, and some retain a pair of vestigial spurs that are remnants of the hindlimbs. Tetrapods evolved from a group of primitive semiaquatic animals known as the tetrapodomorphs which, in turn, evolved from ancient lobe-finned fish ( sarcopterygians) aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waggoneria
''Waggoneria'' is a genus of seymouriamorph from the Early Permian of Texas. It was named by American paleontologist Everett C. Olson in 1951 on the basis of a holotype fossil that included a weathered skull, lower jaws, vertebrae, and part of the pectoral girdle. The type and only species is ''W. knoxensis''. A new family, Waggoneriidae, was also erected for the specimen. The fossil was discovered in a conglomerated deposit of the Early Permian Vale Formation near the town of Vera in Knox County, Texas. The specimen was found in a nodule of rock that had broken, and much of the surface of the skull had weathered away. Because ''Waggoneria'' is known from a single fragmentary fossil, few features distinguish it from other reptiliomorphs. One distinction can be seen in the structure of the jaws. The surfaces of the upper and lower jaws are plate-like and contain several rows of teeth. The lower jaw is deep, possibly associated with the crushing function of the teeth. Olson onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utegenia
''Utegenia'' is a genus of early tetrapod. It is usually regarded as a basal seymouriamorph, but sometimes included in the Discosauriscidae or as a sister taxon of the latter. Only one species, ''Utegenia shpinari'', found from Kazakhstan, is known.Laurin, Michel. 1996. Utegenia shpinari. Version 1 January 1996. http://tolweb.org/Utegenia_shpinari/17542/1996.01.01 in The Tree of Life Web Project, http://tolweb.org/ ''Urumqia'', another basal seymouriamorph, from Ürümqi, Xinjiang of China is probably a junior synonym In taxonomy, the scientific classification of living organisms, a synonym is an alternative scientific name for the accepted scientific name of a taxon. The botanical and zoological codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. ... of ''Utegenia''. References Seymouriamorpha Cisuralian tetrapods Permian tetrapods of Asia Fossils of Kazakhstan {{paleo-tetrapod-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptoropha
''Leptoropha'' is an extinct genus of aquatic seymouriamorph known from the Middle Permian of Russia Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders .... References Seymouriamorpha Permian tetrapods of Asia {{paleo-tetrapod-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphisauropus
''Amphisauropus'' is an ichnogenus commonly found in assemblages of trace fossils dating from the Permian to the Triassic The Triassic ( ; sometimes symbolized 🝈) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.5 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.4 Mya. The Triassic is t .... The tracks have been considered to be made by amphibians or by seymouriamorphs. The genus has been found in Europe, Morocco, and North America. Description The foot impressions show five digits and clear palm prints, though the fifth digit is not always impressed. The digits are short and broad with rounded tips. The pes (rear foot) is longer than wide while the manus (front foot) is wider than long. A continuous tail impression is also present. The animal may have had a trunk length of about and likely moved quite slowly. References Vertebrate trace fossils {{Trace-fossil-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enosuchus
''Enosuchus'' is an extinct genus of seymouriamorphs from Russia during the Middle Permian The Guadalupian is the second and middle series/epoch of the Permian. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. It is named after the Guadalupe Mountains of New Mexico and Texas, and dates between 272.95 ± 0. .... Seymouriamorpha Paleozoic tetrapods of Asia {{paleo-tetrapod-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amniote
Amniotes are tetrapod vertebrate animals belonging to the clade Amniota, a large group that comprises the vast majority of living terrestrial animal, terrestrial and semiaquatic vertebrates. Amniotes evolution, evolved from amphibious Stem tetrapoda, stem tetrapod ancestors during the Carboniferous geologic period, period. Amniota is defined as the smallest crown clade containing humans, the Greek tortoise, and the Nile crocodile. Amniotes are distinguished from the other living tetrapod clade — the anamniote, non-amniote lissamphibians (frogs/toads, salamanders/newts and caecilians) — by: the development of three fetal membranes, extraembryonic membranes (amnion for embryonic protection, chorion for gas exchange, and allantois for metabolic waste disposal or storage); thicker and keratinized skin; rib, costal respiration (breathing by expanding/constricting the rib cage); the presence of adrenal cortex, adrenocortical and chromaffin cell, chromaffin tissues as adrenal g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lissamphibia
The Lissamphibia (from Greek λισσός (lissós, "smooth") + ἀμφίβια (amphíbia), meaning "smooth amphibians") is a group of tetrapods that includes all modern amphibians. Lissamphibians consist of three living groups: the Salientia (frogs and their extinct relatives), the Caudata (salamanders and their extinct relatives), and the Gymnophiona (the limbless caecilians and their extinct relatives). Salientians and caudatans are likely more closely related to each other than to caecilians. The name Batrachia is commonly used for the clade combining salientians and caudatans. A fourth group, the Allocaudata (also known as Albanerpetontidae) is also known, spanning 160 million years from the Middle Jurassic to the Early Pleistocene, but became extinct two million years ago. For several decades, this name has been used for a group that includes all living amphibians, but excludes all the main groups of Paleozoic tetrapods, such as Temnospondyli, Lepospondyli, Embolome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |