|
Sexual Bimaturism
Sexual bimaturism describes a difference in developmental timing between males and females of the same species. Sexual bimaturism can result in sexual dimorphism, but sexual dimorphism could also develop through differential rates of development. In many insects, the larval period of females is longer than that of males, and as a result of this extended growth period, these female insects are larger than their male conspecifics. Male simian primates are generally larger than females of the same species due in part to extended growth periods. Gorillas demonstrate a particularly high degree of sexual bimaturism. Bimaturism can refer to developmental differences within a sex related to secondary sex characteristics. For example, male orangutans reach sexual maturity around age 15 but undergo an additional period of development later in life before they exhibit cheek flanges. Flanged males are generally preferred by females so that unflanged males need different mating strategies to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where sexes of the same species exhibit different Morphology (biology), morphological characteristics, including characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most dioecy, dioecious species, which consist of most animals and some plants. Differences may include secondary sex characteristics, size, weight, color, markings, or behavioral or cognitive traits. Male-male reproductive competition has evolved a diverse array of sexually dimorphic traits. Aggressive utility traits such as "battle" teeth and blunt heads reinforced as battering rams are used as weapons in aggressive interactions between rivals. Passive displays such as ornamental feathering or song-calling have also evolved mainly through sexual selection. These differences may be subtle or exaggerated and may be subjected to sexual selection and natural selection. The opposite of dimorphism is ''monomorphism'', when both biological sexes are phenotype, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simian
The simians, anthropoids, or higher primates are an infraorder (Simiiformes ) of primates containing all animals traditionally called monkeys and apes. More precisely, they consist of the parvorders New World monkey, Platyrrhini (New World monkeys) and Catarrhini, the latter of which consists of the family Cercopithecidae (Old World monkeys in the stricter sense) and the superfamily Hominoidea (apesincluding humans). The simians are sister group to the Tarsiiformes, tarsiers (Tarsiiformes), together forming the Haplorhini, haplorhines. The Evolutionary radiation, radiation occurred about 60 million years ago (during the Cenozoic era); 40 million years ago, simians colonized South America, giving rise to the New World monkeys. The remaining simians (catarrhines) split about 25 million years ago into Old World monkey, Cercopithecidae and apes (including humans). Taxonomy In earlier classification, New World monkeys, Old World monkeys, apes, and humans – collectively known as s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorillas
Gorillas are primarily herbivorous, terrestrial great apes that inhabit the tropical forests of equatorial Africa. The genus ''Gorilla'' is divided into two species: the eastern gorilla and the western gorilla, and either four or five subspecies. The DNA of gorillas is highly similar to that of humans, from 96 to 99% depending on what is included, and they are the next closest living relatives to humans after the chimpanzees. Gorillas are the largest living primates, reaching heights between , weights between , and arm spans up to , depending on species and sex. They tend to live in troops, with the leader being called a silverback. The eastern gorilla is distinguished from the western by darker fur colour and some other minor morphological differences. Gorillas tend to live 35–40 years in the wild. Gorillas' natural habitats cover tropical or subtropical forest in Sub-Saharan Africa. Although their range covers a small percentage of Sub-Saharan Africa, gorillas co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Sex Characteristics
A secondary sex characteristic is a physical characteristic of an organism that is related to or derived from its sex, but not directly part of its reproductive system. In humans, these characteristics typically start to appear during puberty—and include enlarged breasts and widened hips of females, facial hair and Adam's apples on males, and pubic hair on both. In non-human animals, they can start to appear at sexual maturity—and include, for example, the manes of male lions, the bright facial and rump coloration of male mandrills, and horns in many goats and antelopes. Secondary sex characteristics are particularly evident in the sexually dimorphic phenotypic traits that distinguish the sexes of a species. In evolution, secondary sex characteristics are the product of sexual selection for traits that show fitness, giving an organism an advantage over its rivals in courtship and in aggressive interactions. Many characteristics are believed to have been established b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orangutans
Orangutans are great apes native to the rainforests of Indonesia and Malaysia. They are now found only in parts of Borneo and Sumatra, but during the Pleistocene they ranged throughout Southeast Asia and South China. Classified in the genus ''Pongo'', orangutans were originally considered to be one species. In 1996, they were divided into two species: the Bornean orangutan (''P. pygmaeus'', with three subspecies) and the Sumatran orangutan (''P. abelii''); a third species, the Tapanuli orangutan (''P. tapanuliensis''), was identified definitively in 2017. The orangutans are the only surviving members of the subfamily Ponginae, which diverged genetically from the other hominids (gorillas, chimpanzees, and humans) between 19.3 and 15.7 million years ago. The most arboreal of the great apes, orangutans spend most of their time in trees. They have proportionally long arms and short legs, and have reddish-brown hair covering their bodies. Adult males weigh about , while females we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
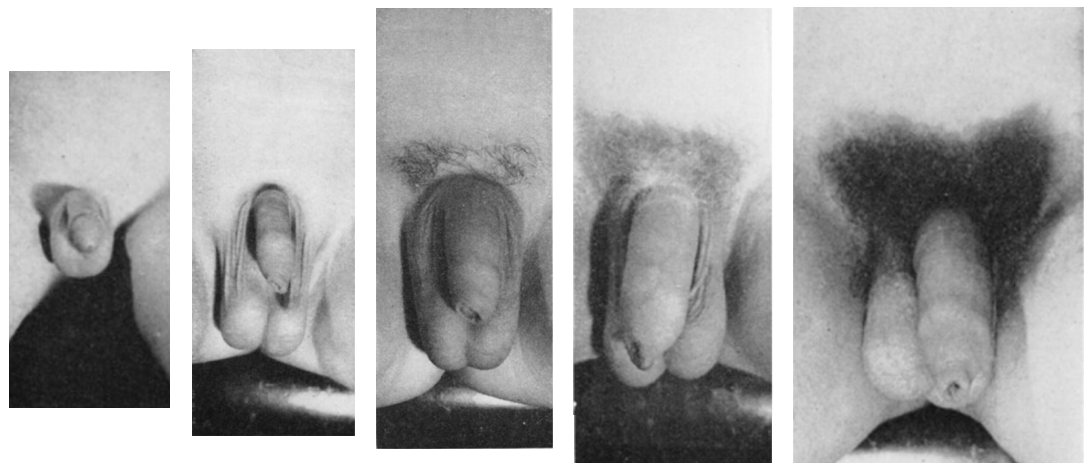
Puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles in a male. In response to the signals, the gonads produce hormones that stimulate libido and the growth, function, and transformation of the brain, bones, muscle, blood, skin, hair, breasts, and sex organs. Physical growth—height and weight—accelerates in the first half of puberty and is completed when an adult body has been developed. Before puberty, the external sex organs, known as primary sexual characteristics, are sex characteristics that distinguish males and females. Puberty leads to sexual dimorphism through the development of the secondary sex characteristics, which further distinguish the sexes. On average, females begin puberty at age 10½ and complete puberty at ages 15-17; males begin at ages 11½-12 and complete pube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |