|
Sequelae
A sequela (, ; usually used in the plural, sequelae ) is a pathological condition resulting from a disease, injury, therapy, or other trauma. Derived from the Latin word meaning "sequel", it is used in the medical field to mean a complication or condition following a prior illness or disease. A typical sequela is a chronic complication of an acute condition—in other words, a long-term effect of a temporary disease or injury—which follows immediately from the condition. Sequelae differ from late effects, which can appear long after—even several decades after—the original condition has resolved. In general, non-medical usage, the terms ''sequela'' and ''sequelae'' mean consequence and consequences. Examples and uses Chronic kidney disease, for example, is sometimes a sequela of diabetes; "chronic constipation" or more accurately "obstipation" (that is, inability to pass stool or gas) is a sequela to an intestinal obstruction; and neck pain is a common sequela of whipl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complication (medicine)
A complication in medicine, or medical complication, is an unfavorable result of a disease, health condition, or therapy, treatment. Complications may adversely affect the prognosis, or outcome, of a disease. Complications generally involve a worsening in the severity of the disease or the development of new signs, symptoms, or pathology, pathological changes that may become widespread throughout the body and affect other organ systems. Thus, complications may lead to the development of new diseases resulting from previously existing diseases. Complications may also arise as a result of various treatments. The development of complications depends on a number of factors, including the degree of vulnerability, susceptibility, senescence, age, health status, and immune system condition. Knowledge of the most common and severe complications of a disease, procedure, or treatment allows for prevention and preparation for treatment if they should occur. Complications are not to be confus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathological
Pathology is the study of disease. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area that includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue and human cell samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases (as in the statement "the many different forms of cancer have diverse pathologies", in which case a more proper choice of word would be " pathophysiologies"). The suffix ''pathy'' is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment (as in cardiomyopathy) and psychological conditions (such as ps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion characterised by an unpleasant state of inner wikt:turmoil, turmoil and includes feelings of dread over Anticipation, anticipated events. Anxiety is different from fear in that fear is defined as the emotional response to a present threat, whereas anxiety is the anticipation of a future one. It is often accompanied by nervous behavior such as pacing back and forth, Somatic anxiety, somatic complaints, and Rumination (psychology), rumination. Anxiety is a feeling of uneasiness and worry, usually generalized and unfocused as an overreaction to a situation that is only subjectively seen as menacing. It is often accompanied by muscular tension, restlessness, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, inability to catch one's breath, tightness in the abdominal region, nausea, and problems in concentration. Anxiety is closely related to fear, which is a response to a real or perceived immediate threat (fight-or-flight response); anxiety involves the expectation of a future t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural network in the nervous system. They are located in the nervous system and help to receive and conduct impulses. Neurons communicate with other cells via synapses, which are specialized connections that commonly use minute amounts of chemical neurotransmitters to pass the electric signal from the presynaptic neuron to the target cell through the synaptic gap. Neurons are the main components of nervous tissue in all Animalia, animals except sponges and placozoans. Plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Molecular evidence suggests that the ability to generate electric signals first appeared in evolution some 700 to 800 million years ago, during the Tonian period. Predecessors of neurons were the peptidergic secretory cells. They eventually ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ataxia
Ataxia (from Greek α- negative prefix+ -τάξις rder= "lack of order") is a neurological sign consisting of lack of voluntary coordination of muscle movements that can include gait abnormality, speech changes, and abnormalities in eye movements, that indicates dysfunction of parts of the nervous system that coordinate movement, such as the cerebellum. These nervous system dysfunctions occur in several different patterns, with different results and different possible causes. Ataxia can be limited to one side of the body, which is referred to as hemiataxia. Friedreich's ataxia has gait abnormality as the most commonly presented symptom. Dystaxia is a mild degree of ataxia. Types Cerebellar The term cerebellar ataxia is used to indicate ataxia due to dysfunction of the cerebellum. The cerebellum is responsible for integrating a significant amount of neural information that is used to coordinate smoothly ongoing movements and to participate in motor planning. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphasia
Aphasia, also known as dysphasia, is an impairment in a person's ability to comprehend or formulate language because of dysfunction in specific brain regions. The major causes are stroke and head trauma; prevalence is hard to determine, but aphasia due to stroke is estimated to be 0.1–0.4% in developed countries. Aphasia can also be the result of brain tumors, epilepsy, autoimmune neurological diseases, brain infections, or neurodegenerative diseases (such as dementias). To be diagnosed with aphasia, a person's language must be significantly impaired in one or more of the four aspects of communication. In the case of progressive aphasia, a noticeable decline in language abilities over a short period of time is required. The four aspects of communication include spoken language production, spoken language comprehension, written language production, and written language comprehension. Impairments in any of these aspects can impact functional communication. The difficulties o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
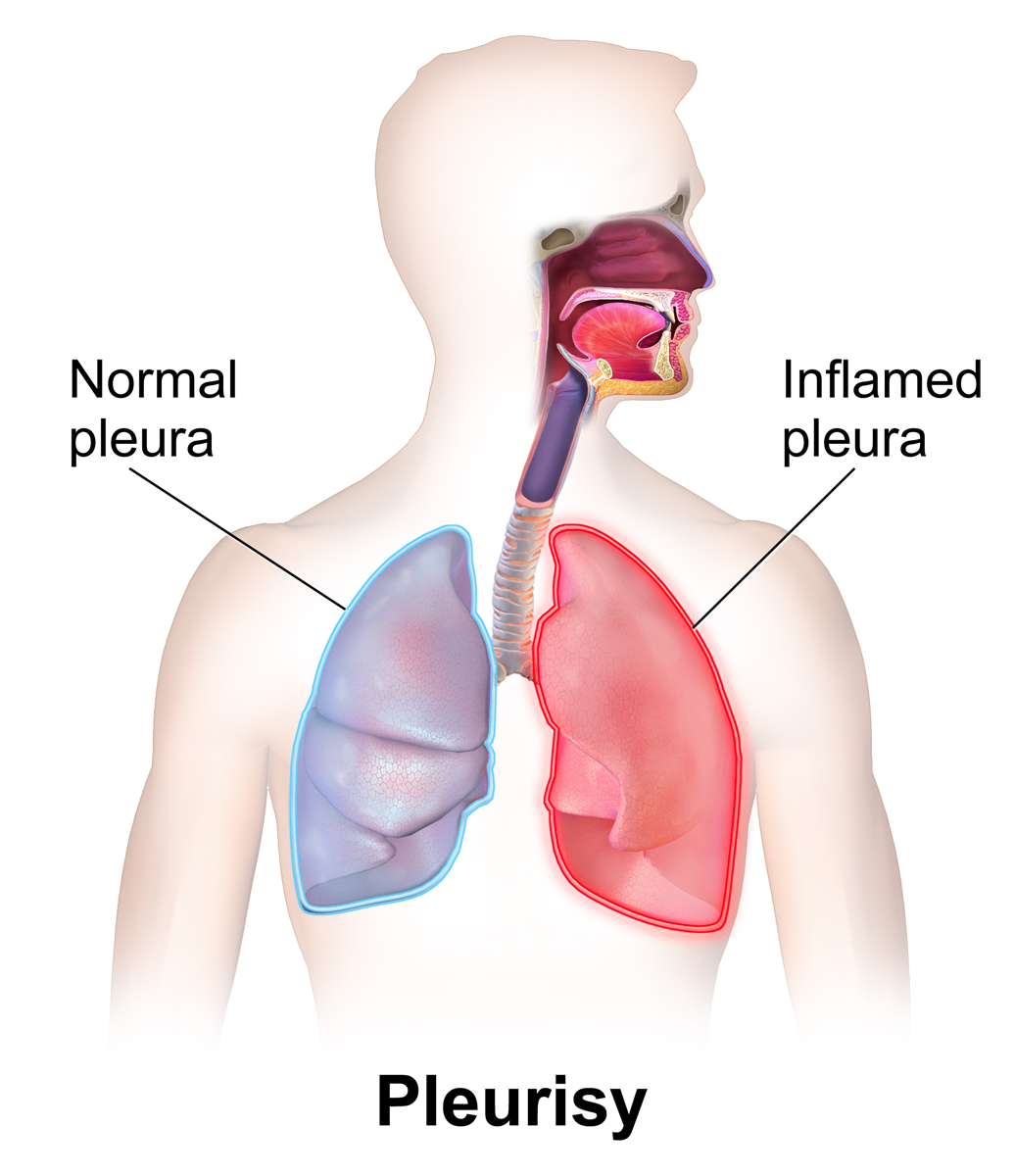
Pleurisy
Pleurisy, also known as pleuritis, is inflammation of the membranes that surround the lungs and line the chest cavity (Pulmonary pleurae, pleurae). This can result in a sharp chest pain while breathing. Occasionally the pain may be a constant dull ache. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, cough, fever, or weight loss, depending on the underlying cause. Pleurisy can be caused by a variety of conditions, including viral or bacterial infections, autoimmune disorders, and pulmonary embolism. The most common cause is a viral infection. Other causes include bacterial infection, pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, autoimmune disorders, lung cancer, following heart surgery, pancreatitis and asbestosis. Occasionally the cause remains unknown. The underlying mechanism involves the rubbing together of the pleurae instead of smooth gliding. Other conditions that can produce similar symptoms include pericarditis, myocardial infarction, heart attack, cholecystitis, pulmonary embolism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retrospective Diagnosis
A retrospective diagnosis (also retrodiagnosis or posthumous diagnosis) is the practice of identifying an illness after the death of the patient (sometimes a historical figure) using modern knowledge, methods and disease classifications. Alternatively, it can be the more general attempt to give a modern name to an ancient and ill-defined scourge or plague. Historical research Retrospective diagnosis is practised by medical historians, general historians and the media with varying degrees of scholarship. At its worst it may become "little more than a game, with ill-defined rules and little academic credibility". The process often requires "translating between linguistic and conceptual worlds separated by several centuries", and assumes our modern disease concepts and categories are privileged. Crude attempts at retrospective diagnosis fail to be sensitive to historical context, may treat historical and religious records as scientific evidence, or ascribe pathology to behaviours tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clouding Of Consciousness
Clouding of consciousness, also called brain fog or mental fog, occurs when a person is conscious Consciousness, at its simplest, is awareness of a state or object, either internal to oneself or in one's external environment. However, its nature has led to millennia of analyses, explanations, and debate among philosophers, scientists, a ... but slightly less wakefulness, wakeful or awareness, aware than normal. They are less aware of time and their surroundings, and find it difficult to Attentional control, pay attention. People describe this subjectivity, subjective sensation as their mind being "foggy". Background The term ''clouding of consciousness'' has always denoted the main pathogenetic feature of delirium since physician Georg Greiner pioneered the term (') in 1817. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, The ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM) has historically used the term in its definition of delirium. The DSM-III-R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long COVID
Long may refer to: Measurement * Long, characteristic of something of great duration * Long, characteristic of something of great length * Longitude (abbreviation: long.), a geographic coordinate * Longa (music), note value in early music mensural notation Places Asia * Long District, Laos * Long District, Phrae, Thailand * Longjiang (other) or River Long (lit. "dragon river"), one of several rivers in China * Yangtze River or Changjiang (lit. "Long River"), China Elsewhere * Long, Somme, France People * Long (Chinese surname) * Long (Western surname) Fictional characters * Long (''Bloody Roar''), in the video game series * Long, Aeon of Permanence in Honkai: Star Rail Sports * Long, a fielding term in cricket * Long, in tennis and similar games, beyond the service line during a serve and beyond the baseline during play Other uses * , a U.S. Navy ship name * Long (finance), a position in finance, especially stock markets * Lòng, name for a laneway in Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. In January 2020, the disease spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic. The symptoms of COVID‑19 can vary but often include fever, fatigue, cough, breathing difficulties, anosmia, loss of smell, and ageusia, loss of taste. Symptoms may begin one to fourteen days incubation period, after exposure to the virus. At least a third of people who are infected asymptomatic, do not develop noticeable symptoms. Of those who develop symptoms noticeable enough to be classified as patients, most (81%) develop mild to moderate symptoms (up to mild pneumonia), while 14% develop severe symptoms (dyspnea, hypoxia (medical), hypoxia, or more than 50% lung involvement on imaging), and 5% develop critical symptoms (respiratory failure, shock (circulatory), shock, or organ dysfunction, multiorgan dysfunction). Older people have a higher risk of developing severe symptoms. Some complicati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |