|
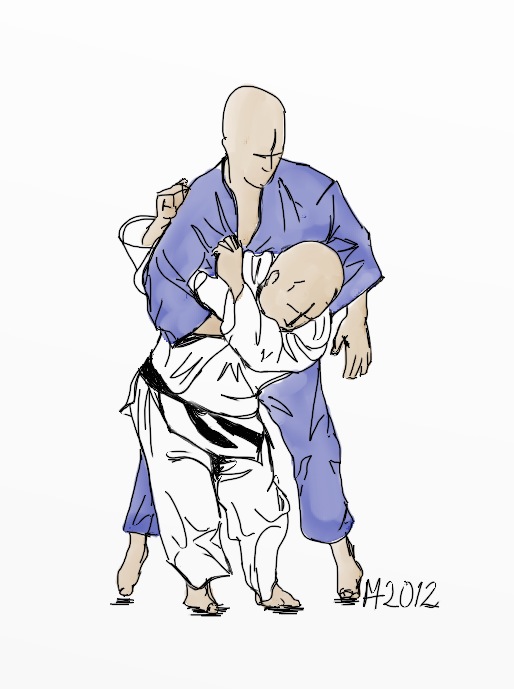
Seoi Nage
is a throw in judo. It is one of the traditional forty throws of judo as developed by Jigoro Kano. It belongs to the first group, Dai Ikkyo, of the traditional throwing list, Gokyo (no waza), of Kodokan Judo. It is also part of the current official throws of Kodokan Judo. It is classified as a hand technique, te-waza, and is the second throw performed in the Nage-no-kata. Seoi nage literally means "over the back throw", but has also been translated as a "shoulder throw", as the opponent or uke is thrown over the thrower or tori's shoulder. Variations Eri Seoi Nage/kata-eri-seoi-nage: tori grips the sleeve and lapel on the same side. The specific techniques of morote-seoi-nage (two hands seoi-nage), or eri-seoi, are usually generalised as simply seoi-nage. Ippon seoi-nage: Ippon seoi-nage is a forward throw that involves securing one arm and rotating, throwing over the back or shoulder. Typically one hand remains gripping the sleeve while the other slides under uke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nage-waza
In martial arts, a throw is a grappling technique that involves off-balancing or lifting an opponent, and throwing them to the ground, in Japanese martial arts referred to as ''nage-waza'', 投げ技, "throwing technique". Throws are a subset of takedown (grappling). Certain throwing techniques called sacrifice throws (''sutemi-waza'', 捨身技, "sacrifice technique") involve putting oneself in a potentially disadvantageous position, such as on the ground, in order to execute a throw. Types of throws There are several major types of throw, among Asian martial arts, Judo has the most developed throwing techniques and throws are considered its specialty. Most throws are named by describing the circumvention point of the throw (e.g., hip throw, shoulder throw, wrist throw etc.), or the nature of effect of the throw on the opponent (e.g., heaven and earth throw, valley drop, body drop) with variations being given descriptive names. The names used here are attributed to Jujutsu thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uke (martial Arts)
() is in Japanese martial arts the person who "receives" a technique. The exact role of ''uke'' varies between the different arts and often within the art itself depending on the situation. For instance, in aikido, judo kata, and bujinkan ninjutsu, ''uke'' initiates an attack against their partner, who then defends, whereas in competition judo, there is no designated ''uke''. An ''uke'' typically partners with a partner or nominal opponent. The latter person may be referred to by any of several terms, again depending on the art or situation. They include , , and . ''Ukemi'' The action of ''uke'' is called "taking ." Literally translated as "receiving body", it is the art of knowing how to respond correctly to an attack and often incorporates skills to allow one to do so safely. These skills can include moves similar to tumbling and are often used as a valid exercise in itself. In aikido and judo training for instance, many classes begin with ''ukemi'' training as conditioni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kodokan
The , or ''Kōdōkan'' (講道館), is the headquarters of the worldwide judo community. The ''kōdōkan'' was founded in 1882 by Kanō Jigorō, the founder of judo, and is now an eight-story building in Tokyo. Etymology Literally, ''kō'' (講) means "to lecture", ''dō'' (道) means "gendai budo, way," and ''kan'' (館) is "a public building". Together it can be translated as "a place for the study of the way." Function The Kodokan Institute offers classes for those who want to master judo. The program is authorized as a non-regular school by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government. Its courses include the theories and practice of judo, and matters of general education. The course is divided into two parts: a general course for novices, and special courses for those who have completed the general course or its equivalent. The Kodokan also issues ranks, and many ''judoka'' (practitioners of judo) around the world become Kodokan members and have their ranks registered with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tai Otoshi
, is one of the original 40 throws of Judo is an unarmed gendai budō, modern Japanese martial art, combat sport, Olympic sport (since 1964), and the most prominent form of jacket wrestling competed internationally.『日本大百科全書』電子版【柔道】(CD-ROM version of Encyc ... as developed by Jigoro Kano. It belongs to the second group, Dai Nikyo, of the traditional throwing list, Gokyo (no waza), of Kodokan Judo. It is also part of the current 67 Throws of Kodokan Judo. It is classified as a hand technique, Te-waza. References * Ohlenkamp, Neil (2006) Judo Unleashed' basic reference on judo. . Laszlo Horvath: 120 Judo FundamentsYoutube playlisreferred on Hungarian Judo Association webpage International Judo Federation: Tai-otoshi External links American Judo: 3 types of Tai Otoshi Further reading * Judo technique Throw (grappling) {{Judo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuttle Publishing
Tuttle Publishing, originally the Charles E. Tuttle Company, is a book publishing company that includes Tuttle, Periplus Editions, and Journey Editions.Tutttle Publishing: About us Retrieved on April 17, 2010.Grant, T. (1997): ''International directory of company histories'' (Vol. 86, 2nd ed., pp. 404–405). Chicago, IL: Saint James Press. () A company profile describes it as an "International publisher of innovative books on design, cooking, martial arts, language, travel and spirituality with a focus on China, Japan and Southeast Asia."The London Book Fair: Tuttle Publishing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jujutsu
Jujutsu ( , or ), also known as jiu-jitsu and ju-jitsu (both ), is a Japanese martial art and a system of close combat that can be used in a defensive or offensive manner to kill or subdue one or more weaponless or armed and armored opponents. A subset of techniques from certain styles of jujutsu were used to develop many modern martial arts and combat sports, such as judo, aikido, sambo, Brazilian jiu-jitsu, ARB, and mixed martial arts. Characteristics " Jū" can be translated as "gentle, soft, supple, flexible, pliable, or yielding", and " jutsu" can be translated as "art or technique". "Jujutsu" thus has the meaning of "yielding-art", as its core philosophy is to manipulate the opponent's force against themself rather than confronting it with one's own force. Jujutsu developed to combat the samurai of feudal Japan as a method for defeating an armed and armored opponent in which one uses no form of weapon, or only a short weapon. Because striking against an armored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choi Min-ho (judoka)
Choi Min-ho (; ; born 18 August 1980) is a South Korean judoka. He was born in Gimcheon, Gyeongsangbuk-do, South Korea. Career He competed in the 2004 Summer Olympics where he won the bronze medal and defeated then world champion Craig Fallon. He also competed in the 2008 Summer Olympics, where he won the gold medal in the 60 kg extra-lightweight category. In Beijing, he ended all 5 of his matches by Ippon and defeated former European champion Ludwig Paischer Ludwig Paischer (born 28 November 1981 in Oberndorf bei Salzburg) is an Austrian judoka is an unarmed gendai budō, modern Japanese martial art, combat sport, Olympic sport (since 1964), and the most prominent form of jacket wrestling compe ... in the final for the gold medal. Choi was voted as the 2008 ''Best Judoka of the Year'' by ''L´Esprit du Judo'' magazine of France.http://kr.news.yahoo.com/service/news/shellview.htm?linkid=406&articleid=2009020910351777870&newssetid=28 References External l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toshihiko Koga
was a Japanese judoka, 9th degree black belt and Olympic champion who competed in the –71 kg and –78 kg divisions. Koga is regarded as having perhaps the greatest ippon seoi nage ever. He died of cancer on 24 March 2021 at the age of 53. Biography Koga was born in Kitashigeyasu, Saga, Japan. He began judo in elementary school. He traveled to Tokyo during junior-high school to enter Kodogakusha, a judo school later attended by Olympic gold medalists Hidehiko Yoshida and Makoto Takimoto. He continued his education at the Nippon Sport Science University, and captured several awards including five consecutive championships at the Kodokan Cup and six consecutive championships at the All-Japan Judo Championships (all in the 71 kg division). He placed 3rd in the 1987 World Judo Championships held in Essen, and was chosen to participate in the 1988 Summer Olympics, where he lost in the 3rd round of the competition. Koga returned to the Olympics in 1992 after winnin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isao Okano
is a retired judoka who competed in the middleweight division (80 kg) in the 1964 Summer Olympics. Biography Okano entered the 1964 Summer Olympics while studying at Chuo University's law school, and won the gold medal in the middleweight division. He won another gold medal at the World Judo Championships in 1965, becoming the champion of his division at only 21 years of age. He also won the open-weight class division of the All-Japan Judo Championships in 1967 and 1969, and placed second in 1968. At 80 kg, he and Shinobu Sekine remain the lightest ever competitors to win these championships. Okano suddenly retired from competitive judo at only 25 years of age, and founded the Sekijuku (currently the Ryutsu Keizai University's judo team) in 1970, where he instructed future Olympic gold medalist Kazuhiro Ninomiya. He also served as a coach for the Japanese team during the 1976 Summer Olympics. He later worked as a judo instructor at Keio University from 1989 to 1998, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ippon Seoi-nage
The is a throw in judo.Mifune, Kyuzo: ''The Canon of Judo'', Kodansha International Ltd. (Tokyo) 2004, , p. It is a variant of Seoi nage, and is one of the nineteen accepted techniques in Shinmeisho No Waza of Kodokan Judo. It is classified as a hand throwing technique, or ''te-waza''. Ippon seoi nage literally means "one arm over the back throw", but has also been translated as a "one arm shoulder throw", as the opponent or uke is thrown over the thrower or tori's shoulder. Description Ippon seoi nage begins with one judo player ( tori) breaking another's ( uke's) balance in the forward direction. With one hand holding uke's arm, tori steps forward and turns inward. Tori then passes their arm up under uke's and clamps it. Tori lifts uke off of the ground and throws in the forward direction. Similar techniques and variants Ippon seoi nage is similar to morote seoi nage and other. They differ in that these throws use a two-handed grip. With morote seoi nage, tori grips the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hand Throwing Techniques
A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the koala (which has two opposable thumbs on each "hand" and fingerprints extremely similar to human fingerprints) are often described as having "hands" instead of paws on their front limbs. The raccoon is usually described as having "hands" though opposable thumbs are lacking. Some evolutionary anatomists use the term ''hand'' to refer to the appendage of digits on the forelimb more generally—for example, in the context of whether the three digits of the bird hand involved the same homologous loss of two digits as in the dinosaur hand. The human hand usually has five digits: four fingers plus one thumb; however, these are often referred to collectively as five fingers, whereby the thumb is included as one of the fingers. It has 27 bones, not including the sesamoid bone, the number of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |